
The Molecular Blueprint of Regrowth: How Axolotls Regenerate Entire Limbs
Axolotls possess one of the most extraordinary abilities in the animal kingdom: the power to regenerate entire limbs with full functionality, including bones, muscles, nerves, and skin. Recent research has begun to clarify the molecular logic that allows these amphibians to rebuild complex body structures with remarkable precision. A newly published study has identified two central players in this process—retinoic acid, a signaling molecule involved in development, and CYP26B1, an enzyme that regulates retinoic acid levels. Together, these molecules create a biochemical map that guides the axolotl through the regeneration sequence.
Scientists found that CYP26B1 shapes a gradient of retinoic acid, effectively telling the regenerating limb how much structure needs to be rebuilt. This gradient functions as a positional cue: depending on the concentration detected in the damaged region, the axolotl can determine whether to regenerate just a fingertip, an entire hand, or a full arm. Without this tightly controlled chemical balance, the regrowth process could become disorganized or incomplete. The discovery provides one of the clearest explanations so far for how axolotls achieve such highly accurate patterning during regeneration.
The research also draws attention to the involvement of the Shox gene, a developmental gene known for its role in skeletal formation in vertebrates. During the axolotl’s regenerative process, Shox becomes reactivated, helping orchestrate the rebuilding of limb structures with their correct proportions and orientations. Although Shox alone does not account for the entire regenerative capability, its activation provides an essential layer of regulation that ensures new tissues form in the proper configuration, mirroring the original limb.
One of the most compelling aspects of this discovery is that humans share many of these same genetic and molecular pathways. While humans cannot naturally regenerate limbs, the presence of conserved genes such as Shox and conserved pathways involving retinoic acid signaling suggests that the underlying biological “toolkit” still exists within our genome. This raises the possibility that, with deeper scientific understanding, a future may emerge in which severe injuries—currently resulting in scarring, amputation, or loss of function—could instead trigger controlled tissue regeneration.
This line of research marks an important milestone in regenerative biology. It demonstrates how studying a highly regenerative species like the axolotl can reveal principles relevant to human medicine and tissue engineering. The findings not only deepen our understanding of developmental biology but also establish a foundation for future therapies aimed at stimulating regeneration in humans. Whether the goal is repairing damaged organs, regrowing tissues, or treating degenerative conditions, insights from axolotl research continue to illuminate new pathways toward medical breakthroughs.
Ultimately, this work underscores the value of fundamental biological research—the kind that investigates how nature solves complex problems. By unraveling the molecular mechanisms behind axolotl limb regeneration, scientists are moving closer to unlocking the human body’s latent capacity to repair itself. What currently seems like science fiction may one day form the basis of transformative medical treatments, with axolotls serving as a biological blueprint for healing.
News in the same category


The Science of Touch: How Holding Hands Calms the Brain and Eases Pain
If You Have These Two ‘Dimples’ on Your Lower Back

Why are some window bars curved at the bottom
When the Brain Begins to Consume Itself: The Hidden Costs of Chronic Sleep Loss

From Self-Marriage to Self-Divorce: Suellen Carey’s Viral Journey of Self-Love

The Hidden Years of Postpartum Recovery: How Motherhood Reshapes the Brain

Unattractive Traits That Can Secretly Ruin a Relationship

Beware Portuguese Man-of-War Found on Beach

Why Your Dog Stares at You …What That Look Really Means

Do You Think Like an FBI Agent

Apple and Issey Miyake Redefine Tech Fashion With the $230 iPhone Pocket

A Simple Black Blade That Saves Birds: The Surprising Wind Turbine Breakthrough
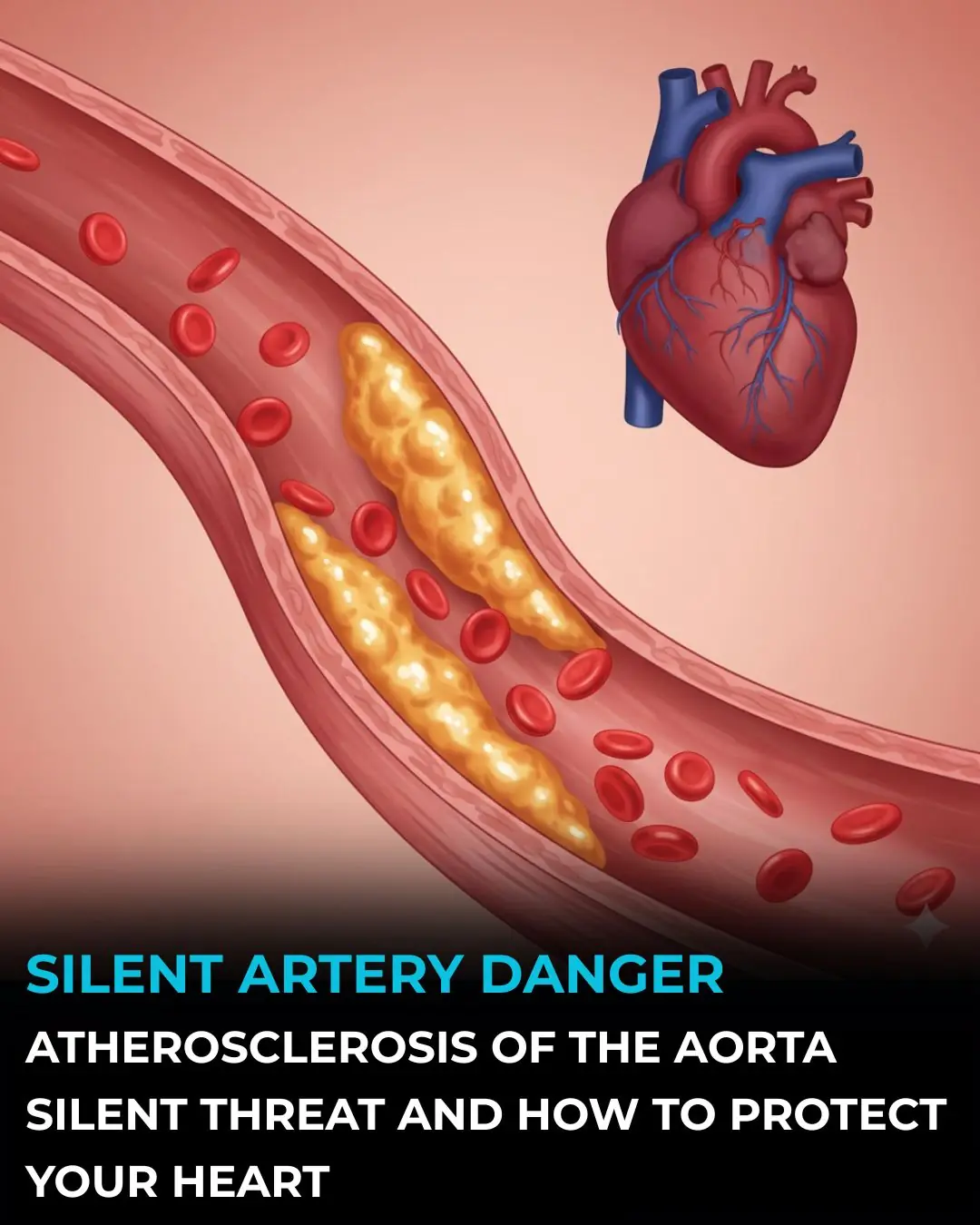
A Silent Threat: How Aortic Atherosclerosis Develops and How You Can Protect Yourself

Firefighters Want Everyone To Know What They Should Never Plug Into A Power Strip

Uncovering the Viral Trigger Behind Lupus: Scientists Reveal a Surprising Link

A Quiet Hero: The 24-Year-Old Saving Over 1,400 Animals from Euthanasia

New Study Shows Removing Processed Foods Can Reduce ADHD Symptoms by 53%

Kenyan Impostor Outsmarts Courts: Fake Lawyer Wins 26 Cases Before Shocking Unmasking
News Post

The Remarkable Benefits and Uses of Mullein Leaves

Meghan Markle speaks out after Balenciaga designer revealed she invited herself to Paris fashion week

Serial Brooklyn dine-and-dash influencer caught avoiding the bill in dramatic video as local eateries wise up to scheme

A-list actress looks completely unrecognizable in new ‘Hunger Games’ trailer

Joey and Jesse Buss fired by Lakers after $10 billion sale as family feud with Jeanie explodes

I’M A CELEB HAD A SPECIAL ‘SMOKO RULE’ THAT ONLY APPLIED TO ONE LEGENDARY STAR

Tips to clean shiny enamel at home without spending a penny

WHERE TO WATCH JOEY’S FRIENDS SPINOFF AS LOST EPISODES RELEASED AFTER 19 YEARS

PARIS JACKSON MAKES SHOCKING CLAIM ABOUT $10,000,000 WORTH OF DAD MICHAEL'S WILL

How to help you travel thousands of miles without getting motion sickness

GRAPHIC VIDEO SHOWS CARDI B HAVING UMBILICAL CORD BEING MADE INTO JEWELLERY

Making pickled garlic requires one more step

Revealing Hidden HIV: A Major Step Toward Achieving a Functional Cure

The Science of Touch: How Holding Hands Calms the Brain and Eases Pain

A Daughter Loses Over 50 Pounds To Donate A Life-Saving Kidney To Her Dad

Walmart Cashier’s Random Act Of Kindness Towards Woman With Cerebral Palsy Will Absolutely Touch Your Heart

When boiling shrimp, remember to add these 2 spices. The shrimp will be sweet, not fishy, and will have a bright red color.

Co-workers Surprise Adopted Colleague With African Inspired Celebration After Tracing Roots Back to Africa
