
The Science of Touch: How Holding Hands Calms the Brain and Eases Pain
Holding hands does far more than provide emotional reassurance — it triggers a measurable and powerful physiological response inside the human brain. Research from the University of Virginia has shown that physical touch, especially hand-holding, can synchronize brain activity between two people, creating a shared sense of safety and significantly reducing the perception of pain. This phenomenon, often referred to as interpersonal neural synchronization, helps individuals cope more effectively with both physical discomfort and emotional strain.
Further studies support this mind-body connection. For example, research published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) found that when partners hold hands during moments of distress, their breathing, heart rate, and neural rhythms begin to align, creating a calming feedback loop. This synchronization can ease emotional tension by activating the parasympathetic nervous system — the body’s natural “rest and relax” response.
Hand-holding also boosts the release of oxytocin, commonly known as the “bonding hormone,” which plays a key role in trust, empathy, and emotional resilience. According to findings reported in Psychological Science and by researchers at the University of California, oxytocin helps reduce cortisol levels, thereby lowering stress and promoting a sense of safety and connection. These chemical changes explain why a simple touch can make overwhelming situations feel more manageable.
In moments of anxiety, pain, or uncertainty, even a gentle handhold can shift the brain into a calmer, more regulated state. It strengthens the social bond between individuals, enhances emotional well-being, and creates a shared sense of resilience. Ultimately, the science suggests that something as small as holding hands taps into deeply rooted biological pathways designed to protect, soothe, and connect us.
News in the same category

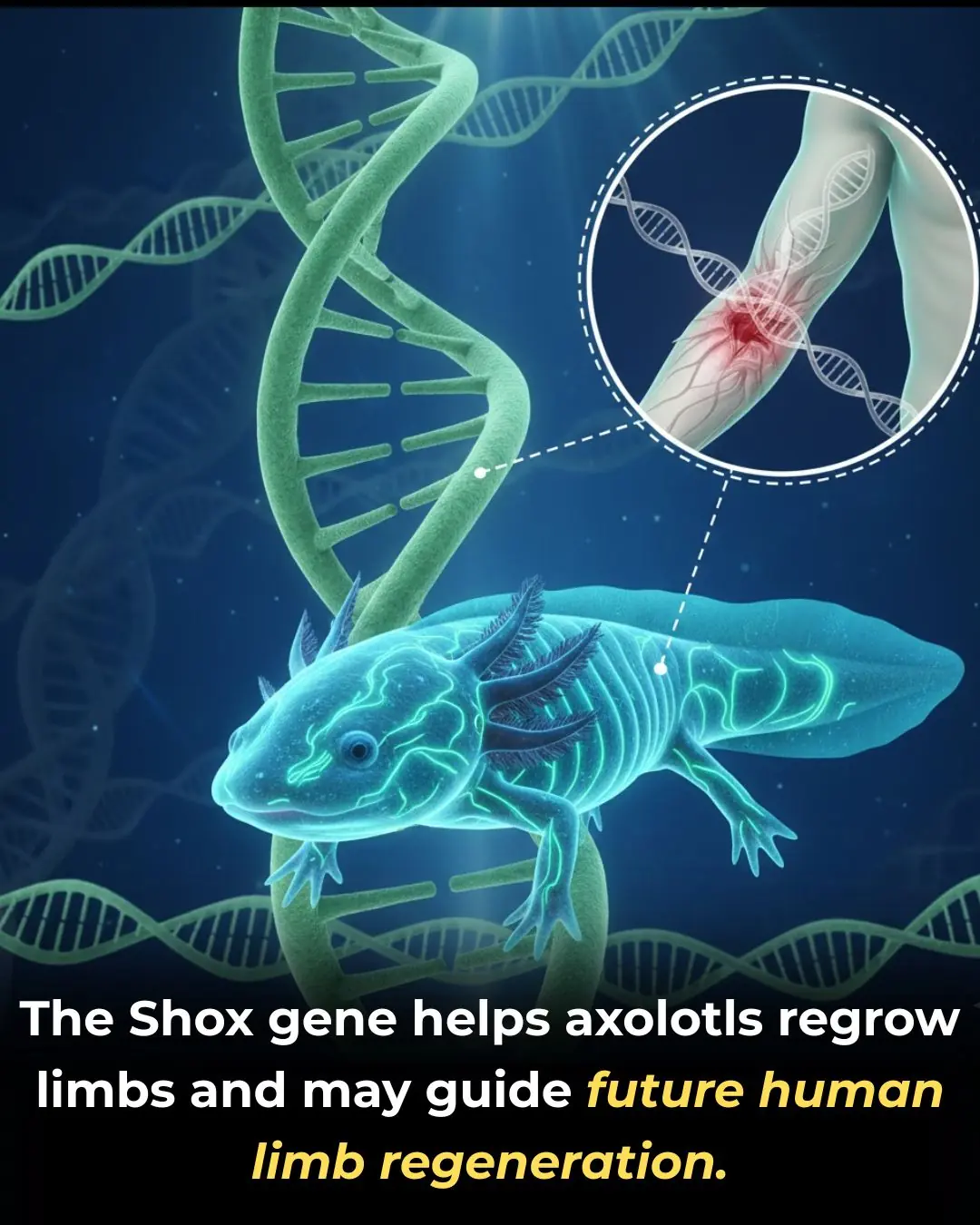
The Molecular Blueprint of Regrowth: How Axolotls Regenerate Entire Limbs
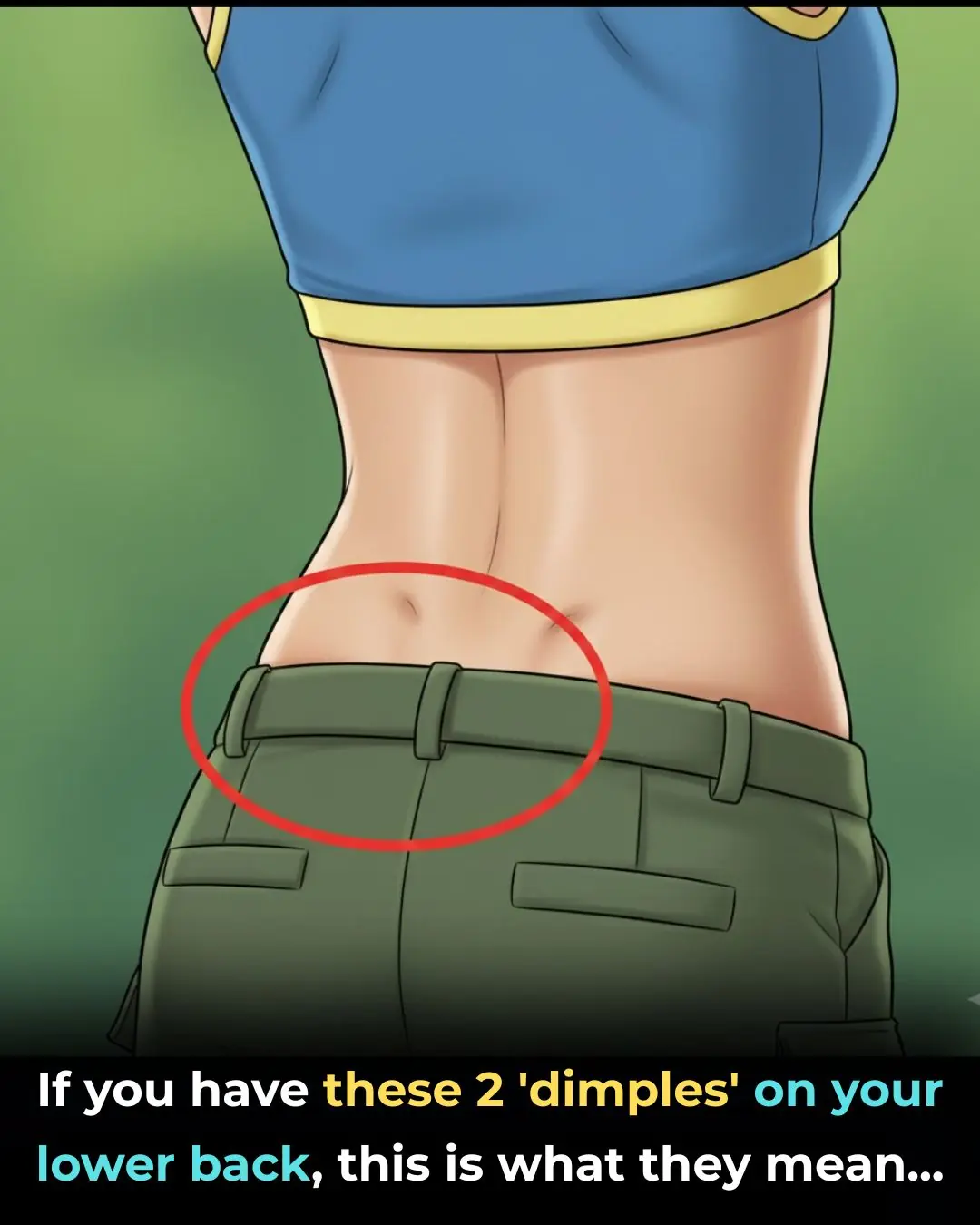
If You Have These Two ‘Dimples’ on Your Lower Back

Why are some window bars curved at the bottom
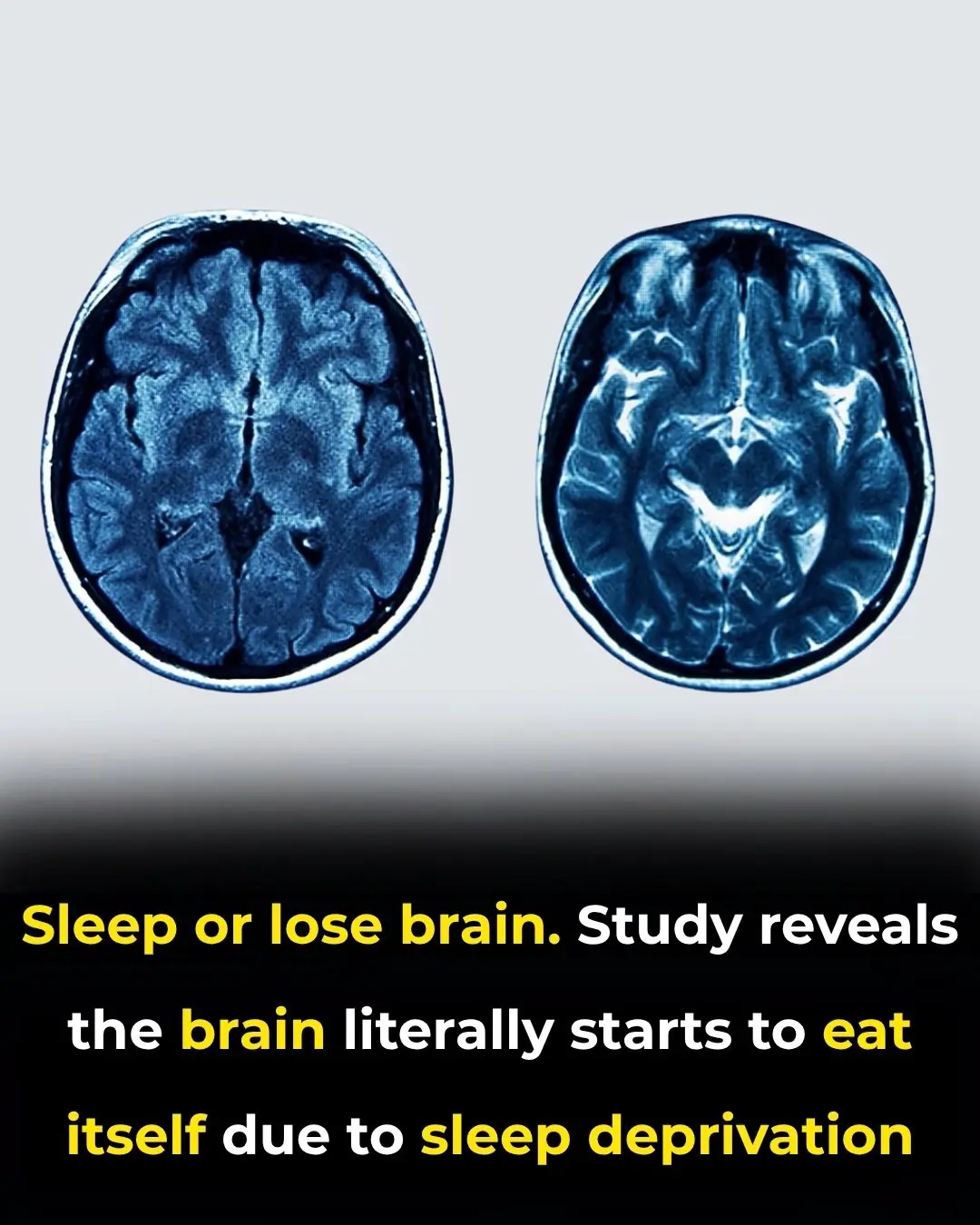
When the Brain Begins to Consume Itself: The Hidden Costs of Chronic Sleep Loss

From Self-Marriage to Self-Divorce: Suellen Carey’s Viral Journey of Self-Love

The Hidden Years of Postpartum Recovery: How Motherhood Reshapes the Brain

Unattractive Traits That Can Secretly Ruin a Relationship

Beware Portuguese Man-of-War Found on Beach

Why Your Dog Stares at You …What That Look Really Means

Do You Think Like an FBI Agent

Apple and Issey Miyake Redefine Tech Fashion With the $230 iPhone Pocket

A Simple Black Blade That Saves Birds: The Surprising Wind Turbine Breakthrough
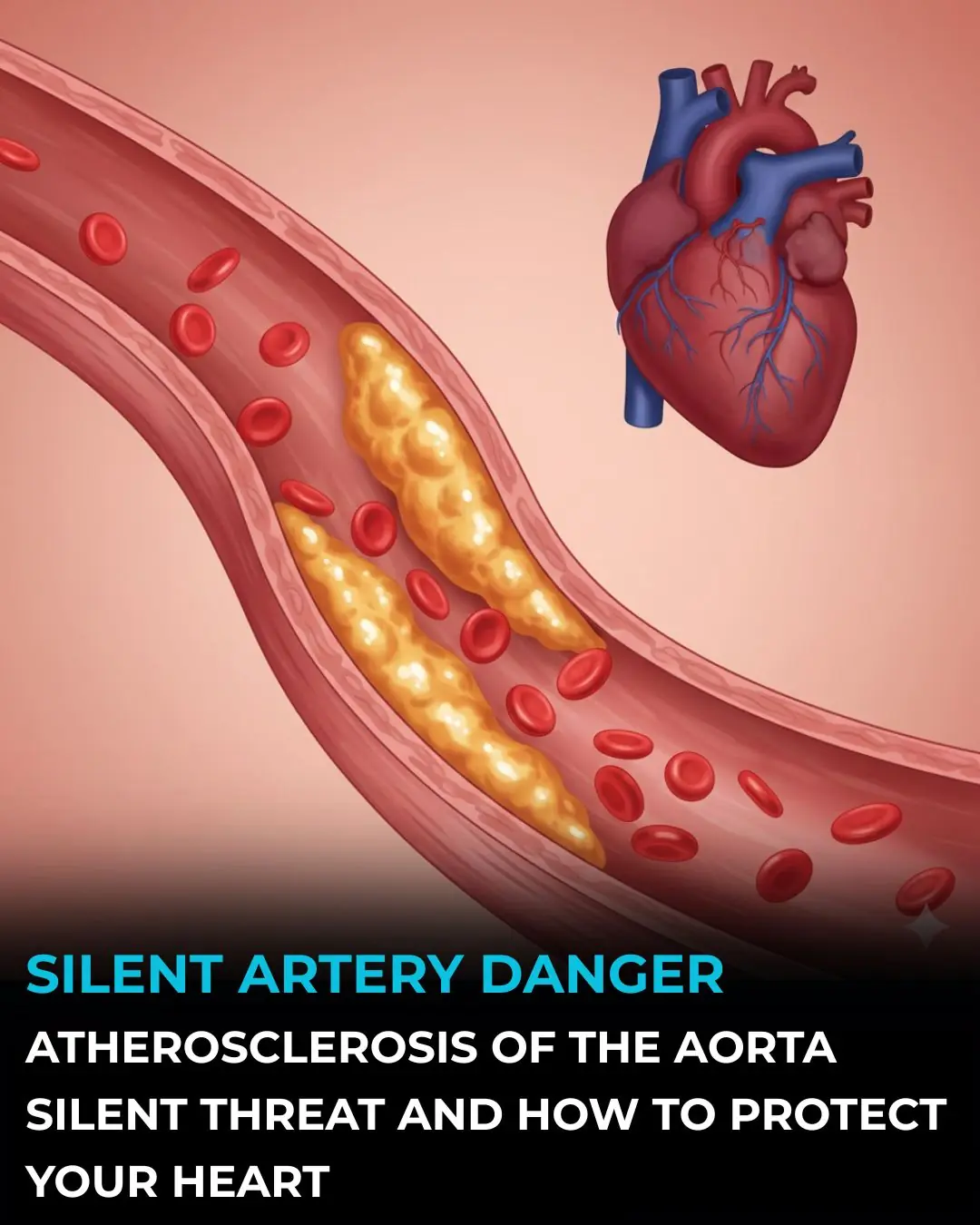
A Silent Threat: How Aortic Atherosclerosis Develops and How You Can Protect Yourself

Firefighters Want Everyone To Know What They Should Never Plug Into A Power Strip

Uncovering the Viral Trigger Behind Lupus: Scientists Reveal a Surprising Link

A Quiet Hero: The 24-Year-Old Saving Over 1,400 Animals from Euthanasia

New Study Shows Removing Processed Foods Can Reduce ADHD Symptoms by 53%

Kenyan Impostor Outsmarts Courts: Fake Lawyer Wins 26 Cases Before Shocking Unmasking
News Post

Revealing Hidden HIV: A Major Step Toward Achieving a Functional Cure

The Molecular Blueprint of Regrowth: How Axolotls Regenerate Entire Limbs

A Daughter Loses Over 50 Pounds To Donate A Life-Saving Kidney To Her Dad

Walmart Cashier’s Random Act Of Kindness Towards Woman With Cerebral Palsy Will Absolutely Touch Your Heart

When boiling shrimp, remember to add these 2 spices. The shrimp will be sweet, not fishy, and will have a bright red color.

Co-workers Surprise Adopted Colleague With African Inspired Celebration After Tracing Roots Back to Africa

The rats will disappear after just 1 month with only 3 potatoes, so easy and very effective

Why are cucumbers bitter? Is it okay to eat bitter cucumbers?

‘Jada Bout to Set That Red Table’: Jada Pinkett Smith Fans Warn Rapper Yo-Yo Over Her Shocking Confession About Tupac

How to make sesame and peanut sauce with just the right taste, keep it for a long time without getting too oily, eat it with cold rice is also delicious

‘Go Back Home Friend’: Vince Herbert’s Slim, Unrecognizable New Look Has Fans Telling Tamar Braxton It Might Be Time to Spin the Block

Grab A Tissue Before Watching This Father And Son Reunite After 37 Years

My Nana Taught Me a 1-Minute Hack to Remove Sticky Jar Labels — With Zero Effort

If You Have These Two ‘Dimples’ on Your Lower Back

Actor Brian Tyree Henry Has Heartwarming Reunion With Morehouse Professor Who Inspired Acting Career

Whoa, I Had No Idea This Is Why Milk Jugs Have That Dent

Blurred Vision in One Eye and a Headache

I Didn’t Know This Bee Sting Trick—My Dad Swears By It
