
The Role of Diet in Protecting Lung Health and Reducing Cancer Risk for Smokers
Groundbreaking research has recently shed light on the significant role that diet plays in protecting lung health, particularly for individuals who smoke or have smoked in the past. Multiple large-scale studies, including research published in reputable journals like the Asia Pacific Journal of Clinical Nutrition (APJCN), PubMed, BioMed Central, and Nature, consistently confirm that maintaining a diet rich in fruits and vegetables can reduce the risk of lung cancer for smokers. This finding offers new hope for those who have been affected by smoking, suggesting that dietary choices may play a crucial role in long-term health outcomes.
One particularly notable study, a case-control analysis, found a clear link between overall dietary patterns and reduced lung cancer risk in individuals who had ever smoked. The results were compelling: individuals who incorporated more fruits and vegetables into their diet exhibited lower rates of lung cancer compared to those who did not. Furthermore, the study revealed that a greater variety of produce, especially colorful fruits and vegetables, offered even stronger protection, particularly for current smokers. This underscores the importance of a diverse, plant-based diet for supporting respiratory health and resilience, even for those who may have a history of smoking.
While no single food can prevent cancer, experts emphasize that a broad and varied diet is the key to improving health outcomes. The protective effects of a diet rich in fruits and vegetables are most evident when individuals consistently include a wide range of plant-based foods in their daily meals. This approach helps counteract some of the harmful effects of smoking, including oxidative stress and inflammation, which contribute to the development of lung cancer and other respiratory diseases.
A plant-focused lifestyle not only supports lung health but also contributes to overall well-being, offering benefits for other vital organs and systems. By prioritizing fruits and vegetables, smokers and former smokers alike can significantly improve their health prospects. The studies collectively suggest that while it is never too late to make positive dietary changes, those who have smoked may particularly benefit from adopting a plant-based diet to support their respiratory function and reduce the risks associated with smoking.
In conclusion, the research highlights the importance of a diet rich in fruits and vegetables as a vital factor in reducing lung cancer risk, especially for smokers. Although quitting smoking remains the most effective measure for preventing lung cancer, these findings offer an additional tool for enhancing lung health and resilience. By focusing on dietary diversity and incorporating a wide array of plant-based foods, individuals can improve their respiratory health and overall quality of life.
News in the same category


You’re Made of Stardust – Literally! 🌌🚀

Sea Levels Are Rising Faster Than At Any Time In 4,000 Years 🌍

Your Dog Might Actually Love You More Than Food
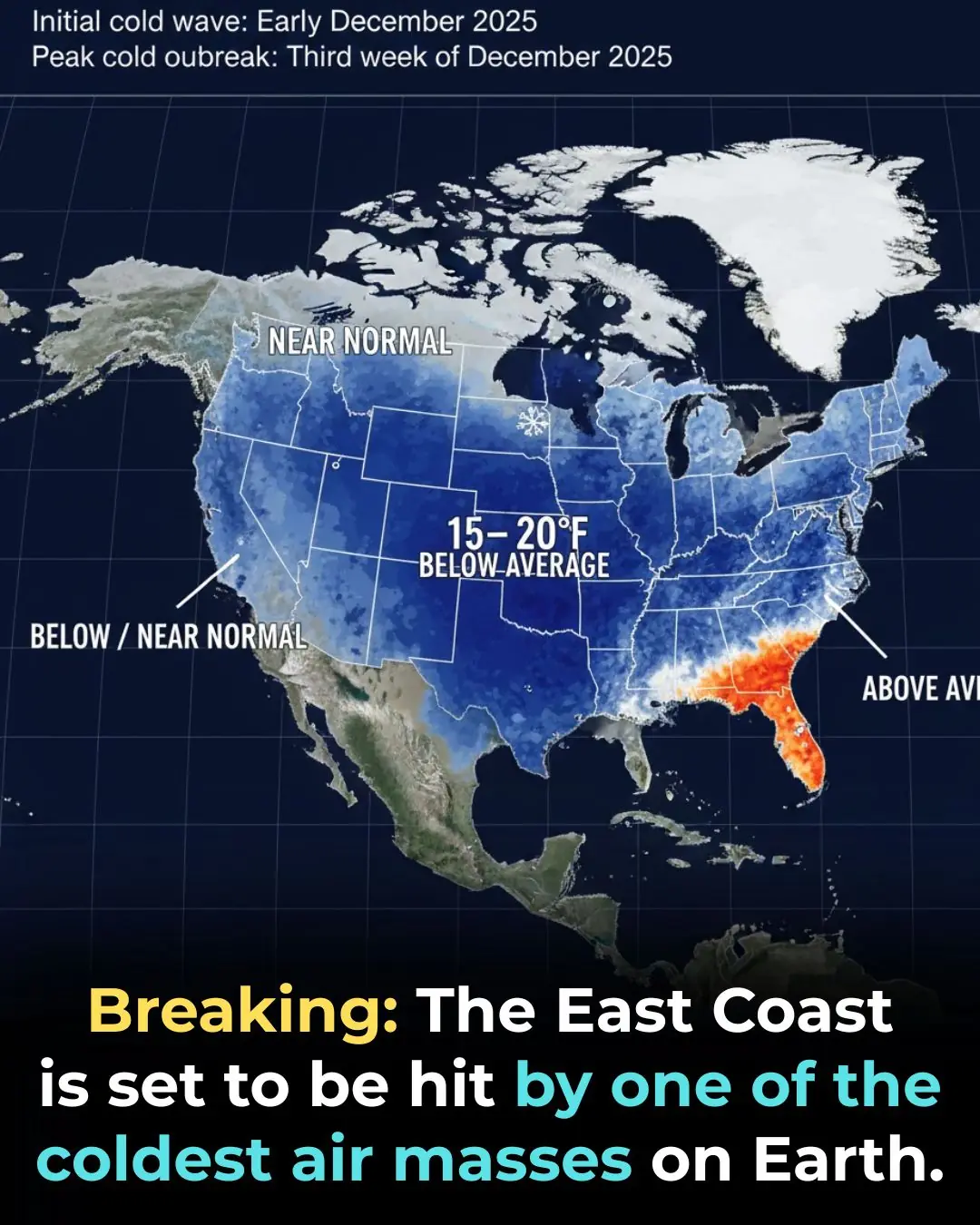
Deep Freeze Set to Slam the Eastern U.S. This December

Nike Co-Founder Phil Knight Makes Historic $2 Billion Donation to Cancer Research

Dutch Engineers Tackle the Pacific’s Plastic Crisis with 600-Meter Ocean Vacuum
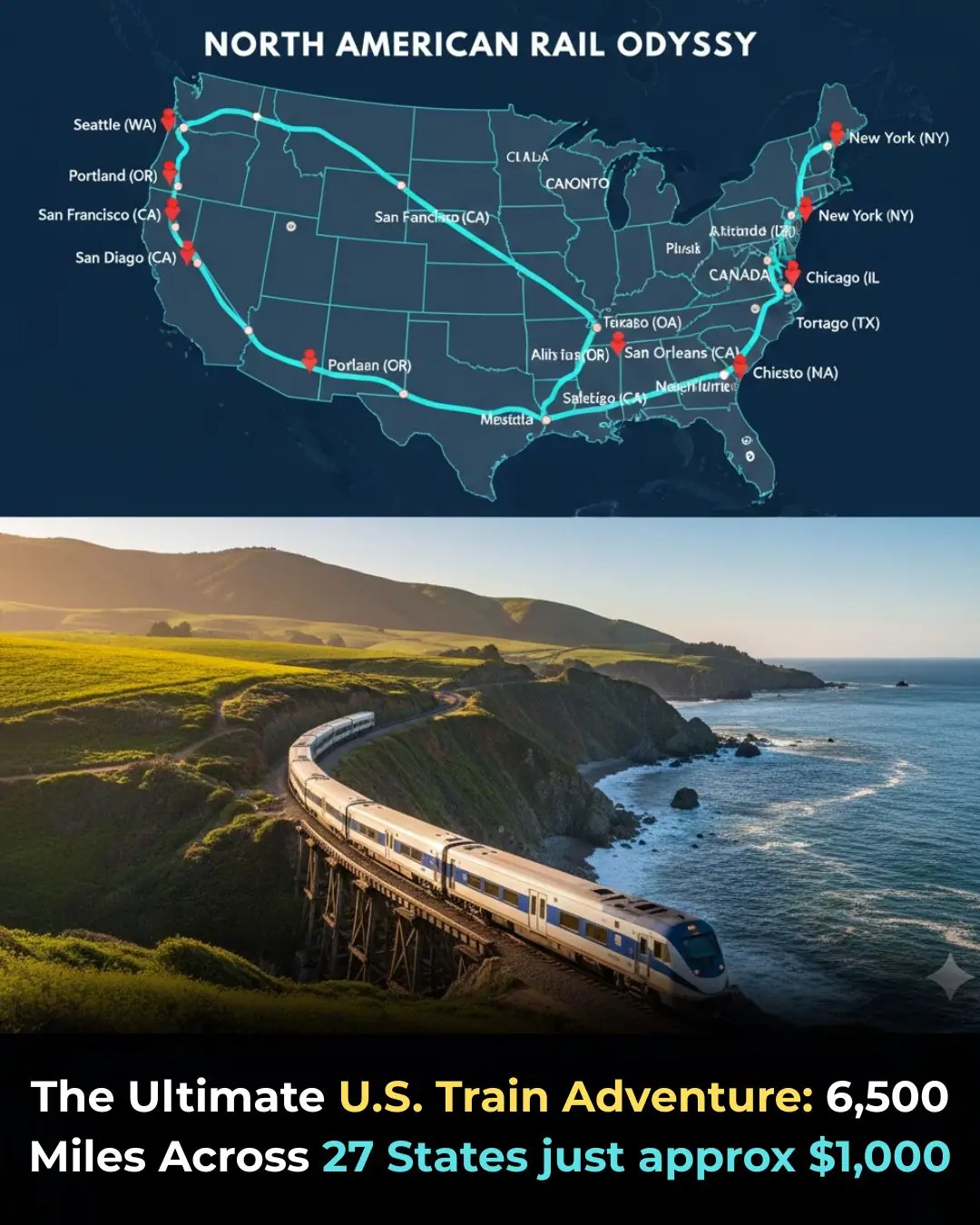
How to Take a Loop of the Entire U.S. by Train

The Quiet Rise of Everyday Health-Tracking Technology
The Hidden Toll of People-Pleasing: How Emotional Suppression Can Trigger Autoimmune Disorders

The Pudu: The World’s Tiniest Deer and Its Role in South America's Forest Ecosystems

Deep Water Cycle: Scientists Discover Hidden Ocean Beneath Earth's Surface

Mexico City’s Sweeping Bullfighting Ban Marks Major Shift in Cultural and Animal-Welfare Policy

Los Angeles County Erases $180 Million in Medical Debt for 39,000 Residents

The 2025 Atlantic Hurricane Season Intensifies: A Heightened Risk for Major Storms

Europe Faces Unprecedented Heatwave: Rising Temperatures Strain People, Infrastructure, and Agriculture

Revolutionary Light-Based Cancer Treatment Offers New Hope with High Success Rate

How Hunger Affects Mood: The Science Behind Irritability and Low Energy

Scientists Discover The Maximum Age a Human Can Live To
News Post

Nick Vujicic: Living Proof That the Human Spirit Knows No Limits

You’re Made of Stardust – Literally! 🌌🚀

Sea Levels Are Rising Faster Than At Any Time In 4,000 Years 🌍

Your Dog Might Actually Love You More Than Food

Deep Freeze Set to Slam the Eastern U.S. This December

Nike Co-Founder Phil Knight Makes Historic $2 Billion Donation to Cancer Research

Dutch Engineers Tackle the Pacific’s Plastic Crisis with 600-Meter Ocean Vacuum

Chronic Insomnia: When Sleeplessness Becomes a Serious Health Issue
Chronic Bronchitis: Causes, Symptoms, and Home Care Tips
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): What Makes the Condition Worse?

How to Take a Loop of the Entire U.S. by Train

The Quiet Rise of Everyday Health-Tracking Technology
Hepatitis B: High-Risk Groups and Prevention Measures
Anemia in Young Adults: Common Causes and How to Treat It

The Hidden Toll of People-Pleasing: How Emotional Suppression Can Trigger Autoimmune Disorders

The Pudu: The World’s Tiniest Deer and Its Role in South America's Forest Ecosystems

Deep Water Cycle: Scientists Discover Hidden Ocean Beneath Earth's Surface

Mexico City’s Sweeping Bullfighting Ban Marks Major Shift in Cultural and Animal-Welfare Policy

Anxiety Disorder: Psychological Signs People Often Misunderstand
