
When Goosebumps May Be a Warning Sign

Goosebumps are one of those odd little bodily reactions we usually don’t think much about. You step into a chilly room, hear a moving piece of music, or feel fear creep in during a horror movie—and suddenly, tiny bumps rise on your arms. That tingling, raised-skin effect is goosebumps, and for the most part, they’re harmless.
But what if they show up without any clear reason?
Most of the time, goosebumps are simply part of your body’s natural defense and emotional response system. However, if they occur frequently, unexpectedly, or are accompanied by other symptoms, they could point to something more serious.
Let’s break down when goosebumps are normal, when they might be a red flag, and what you should do if they become persistent or concerning.
✅ What Are Goosebumps—and Why Do We Get Them?
Goosebumps happen when tiny muscles at the base of your hair follicles contract. This reaction is called piloerection. It makes your hairs stand upright, which—evolutionarily speaking—was useful for our ancestors to stay warm or appear larger in the face of danger.
Today, these tiny bumps are typically triggered by:
-
Cold temperatures
-
Strong emotions (awe, fear, excitement, nostalgia)
-
Music or visual art that stirs deep emotional responses
-
Sudden shocks, surprises, or memories
This is all part of the “fight or flight” response. When your brain senses a threat or emotional surge, it releases adrenaline—a hormone that activates several body changes, including goosebumps.
In these contexts, goosebumps are completely normal and temporary.
🚩 When Goosebumps Might Be a Warning Sign
If you notice that goosebumps occur frequently, without an obvious trigger, or are paired with other symptoms, it could suggest a deeper issue.
Here are several medical and psychological conditions where unexplained goosebumps may be a symptom:
1. 🧠 Nervous System Disorders
The autonomic nervous system controls involuntary body processes like heartbeat, digestion, and body temperature. When something goes wrong in this system, unusual symptoms can develop.
Goosebumps without emotional or cold stimuli may be related to conditions like:
-
Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
-
Autonomic neuropathy (often linked to diabetes)
-
Spinal cord injuries
-
Certain brain tumors
Symptoms may include:
-
Tingling, numbness, or prickling sensations
-
Unexplained chills
-
Shivering without being cold
-
Muscle weakness or coordination issues
👉 If these signs persist or progress, see a neurologist for evaluation and testing.
2. ⚡ Piloerection Seizures
In rare cases, goosebumps are linked to a form of focal seizure known as a piloerection seizure. These are non-convulsive seizures that involve abnormal electrical activity in specific parts of the brain—often the temporal lobe.
Common features include:
-
Sudden goosebumps (on one or both sides of the body)
-
Shivers or chills
-
Brief confusion or memory lapses
-
A “déjà vu” feeling or emotional surge
👉 These seizures can be subtle and easily overlooked. If you experience goosebumps paired with memory issues, blackouts, or odd sensations, consult a neurologist for an EEG or brain scan.
3. 🧪 Hormonal Imbalances or Tumors
Certain conditions cause hormonal surges that may provoke spontaneous goosebumps, including:
-
Pheochromocytoma (a rare adrenal gland tumor)
-
Hyperthyroidism
-
Adrenaline spikes from other causes
These conditions may also cause:
-
Sudden sweating or flushing
-
Racing heart (palpitations)
-
Headaches or high blood pressure
-
Anxiety or panic-like symptoms
👉 If goosebumps are paired with cardiovascular symptoms, get your hormone levels and adrenal function tested.
4. 😰 Anxiety, Stress, or Panic Disorders
Chronic emotional stress doesn’t just affect your mood—it can cause real, physical symptoms.
In people with anxiety disorders or chronic stress:
-
The body may stay in a heightened state of alert
-
Adrenaline is released even without danger
-
Goosebumps may occur randomly, along with:
-
Shaking or trembling
-
Rapid heartbeat
-
Shortness of breath
-
Chest tightness
-
👉 If you’re experiencing these symptoms regularly, a mental health provider can help with stress management, therapy, or medication.
5. 🧴 Skin Conditions That Mimic Goosebumps
Sometimes what looks like goosebumps isn’t actually piloerection at all.
Common skin issues include:
-
Keratosis pilaris: Small, rough bumps (often on arms, thighs, or cheeks)
-
Hives or allergic reactions: Raised, itchy areas that may come and go
-
Cold urticaria: A rare allergy to cold that causes welts, hives, or tingling skin
👉 If your “goosebumps” are persistent, itchy, or discolored, consult a dermatologist for an accurate diagnosis.
🩺 When to See a Doctor
You don’t need to panic over every chill or skin tingle—but persistent or unexplained goosebumps deserve attention, especially if they come with other warning signs.
❗Consult a healthcare provider if you notice:
-
Goosebumps without cold, fear, or emotional triggers
-
Neurological symptoms (numbness, tingling, blackouts)
-
Panic attacks or extreme stress
-
Irregular heartbeat or blood pressure
-
Fatigue, sweating, or dizziness
-
Skin changes that don’t resolve
Early medical intervention can help identify underlying issues like seizures, autoimmune disorders, or hormonal imbalances that may otherwise go undiagnosed.
🧘 Final Thoughts: Listen to Your Skin
Goosebumps are usually just a fleeting, benign reaction—a whisper from your body telling you it’s cold, excited, or emotionally moved. But if they show up frequently without reason, it may be your body's way of waving a red flag.
🧠 Pay attention to what else is going on when goosebumps occur. Are you feeling stressed? Are there other odd symptoms? Don’t brush off the signs if your instincts say something’s not right.
When in doubt, consult your doctor. Better safe than sorry—especially when your nervous system or hormones are involved.
News in the same category

The Truth About Eating the Black Vein in Shrimp Tails

Steps to Take When Your Adult Children No Longer Show Respect

5 Most Common Deathbed Regrets, According to Palliative Care Nurse

Robert F. Kennedy is Reportedly Pushing to Ban All Sodas & Candy From U.S. Food Stamp Benefits. Thoughts?

Donald Trump Asks Supporters To Donate $15 To ‘Get Him To Heaven’

Why Are Mirrors Commonly Installed in Elevators? The Unexpected Benefits of Elevator Mirrors

9 things you should never plug into a power strip

The Spiritual Meaning of Black Butterflies Entering Your Home Revealed
Black butterflies carry meanings that are as complex as they are beautiful.

Add This Simple Ingredient to Your Mop Water and Keep Floors Shiny for Weeks
You don’t need fancy, high-priced cleaners to enjoy spotless, long-lasting results.

The Secret Use of the Tiny Hole in a Safety Pin Finally Revealed
That tiny hole in a safety pin is more than just decoration—it’s a brilliant example of how even the simplest tools can hold hidden design secrets. W

Unbelievable amount Trump’s net worth has risen since taking office for second term
What the Shape of Your Legs Might Say About Your Personality

Weird Toothed Part on Kitchen Scissors

Ring Finger Longer Than An Index Finger

The Story Behind Two Runaway Graves in Savannah Airport

The Simple Object That Might Baffle the Younger Generation

Why Public Bathroom Doors Don’t Reach the Floor – The Real Reason Revealed
The gaps and inward-swinging doors are designed for practicality, serving purposes like enhancing safety and improving efficiency, rather than being the result of poor design.

World’s Oldest Woman Lived to 117 By Eating the Same Meal Every Day
Emma Martina Luigia Morano, the world’s oldest woman at the time of her passing, credited her extraordinary 117 years of life to a mix of genetics, resilience, and one very peculiar daily diet. Her remarkable story spans two World Wars, personal tragedy
News Post

Golden tips for choosing ham: Identify borax with a simple, absolutely safe method

What are the benefits of aloe vera? 11 benefits of aloe vera for health and skin

Smart Travelers Always Photograph Their Luggage Before Checking It In — Here’s Why

The Last Part of the Pig But One of the Most Beneficial
❗Avoid Cloves If You Have These Health Issues – What Doctors Rarely Warn You About
6 Coffee Eye Masks to Get Rid of Dark Circles | Under Eye Wrinkles | Eye bags & Puffy Eyes

What Happens To Your Blood Pressure When You Eat Bananas
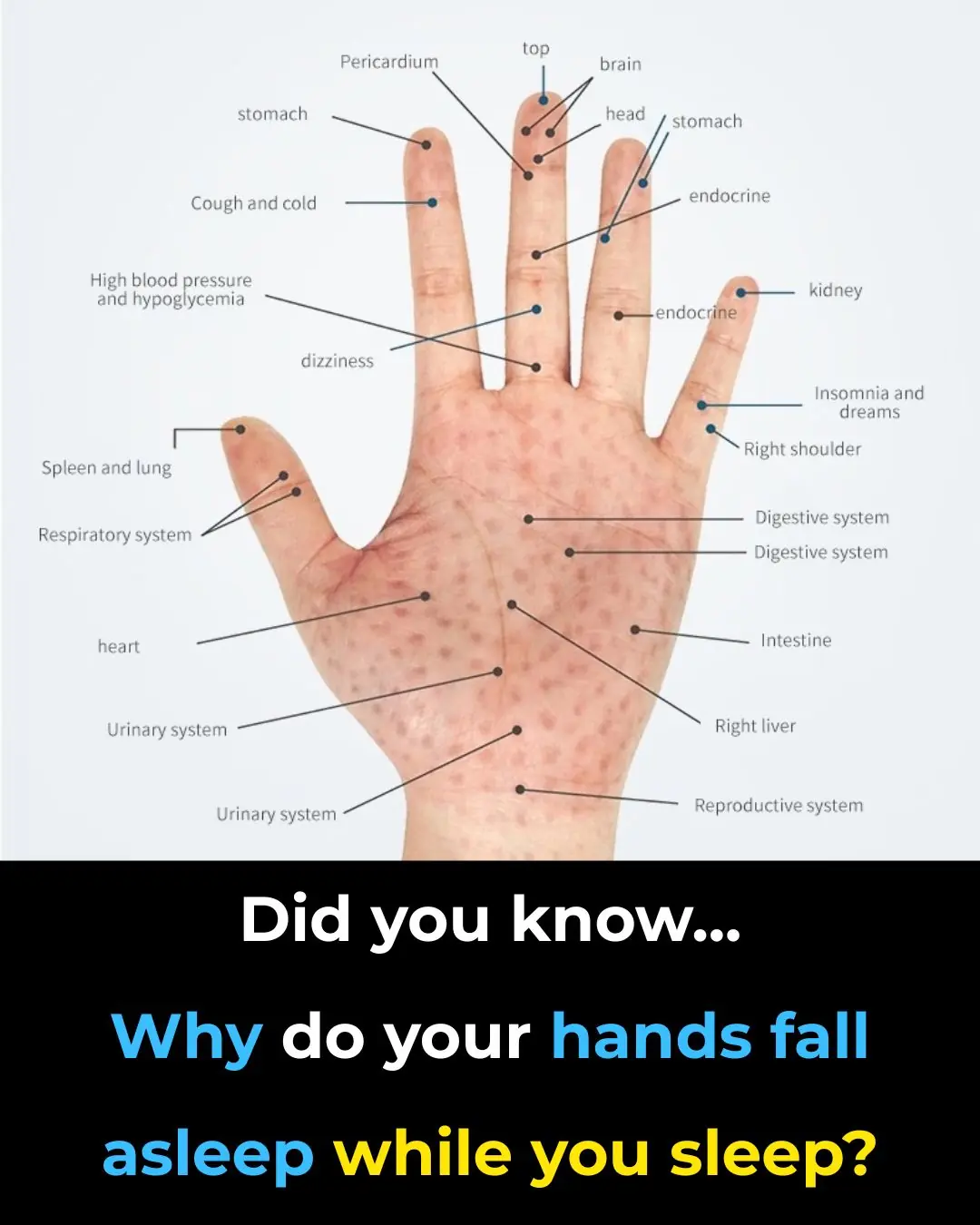
Why Your Hands Go Numb While You Sleep

Reason For Spots On Hands
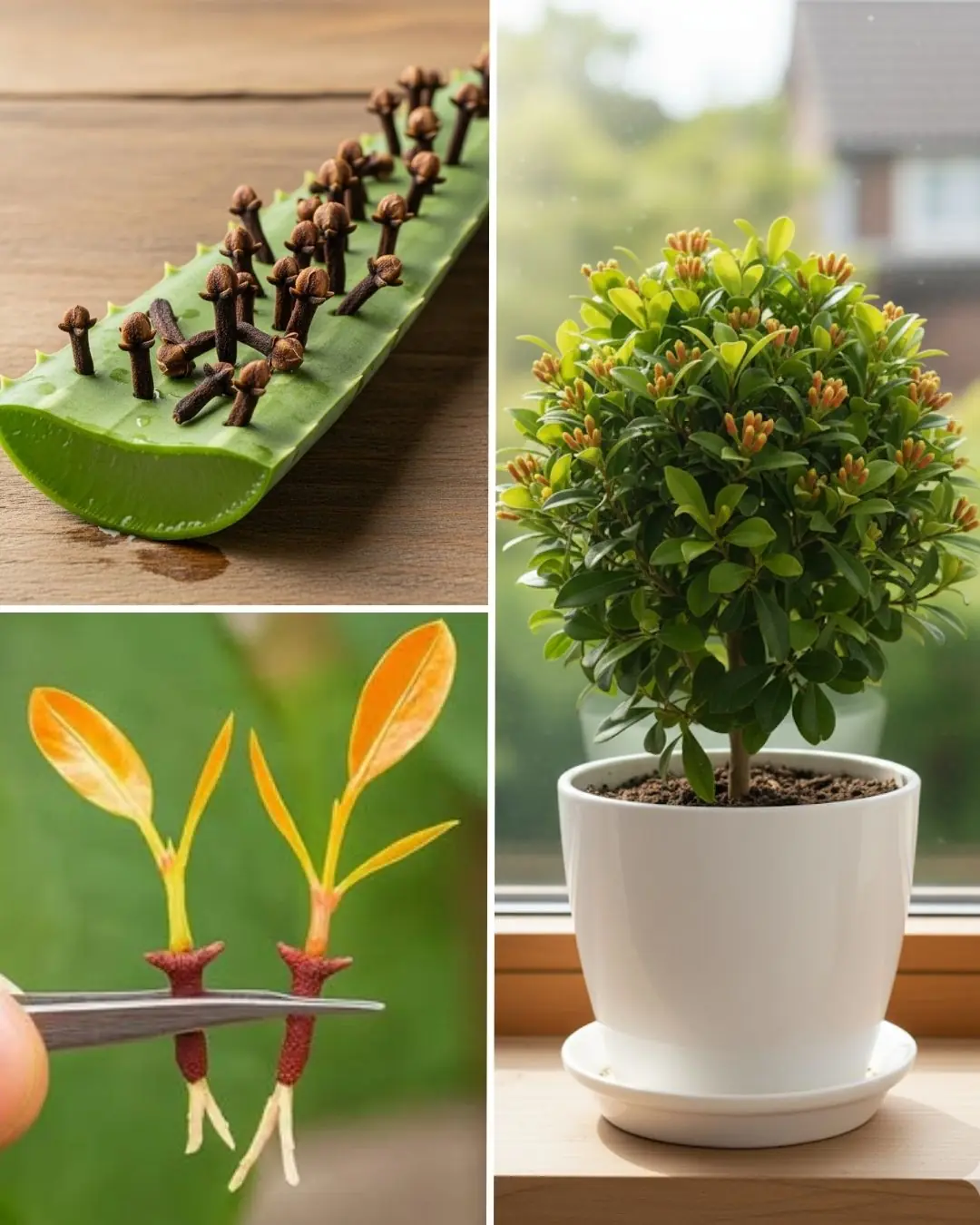

Easy Clove Growing: Seed to Spice

Clove Oil: Wrinkle Free Flawless Skin At Any Age
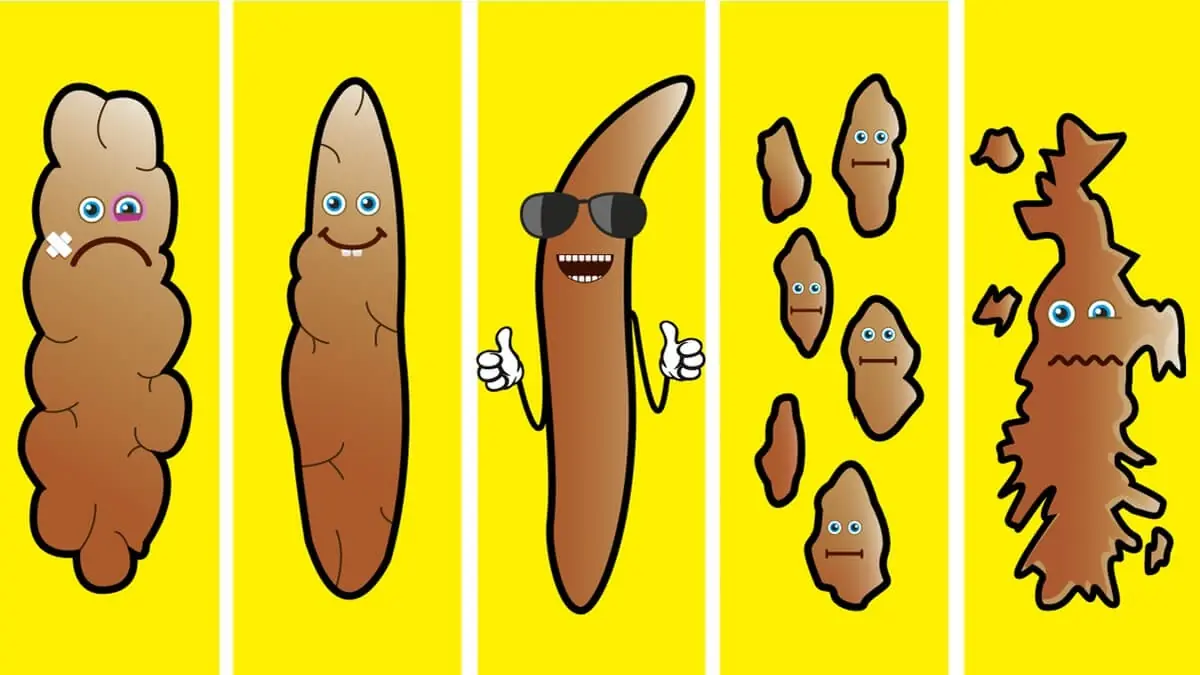
Here Is What Your Poop Says About Your Health

Secrets of Companion.Tomatoes Hate Cucumbers.Planting Combinations.

Reverse Hair Greying – Turn White Hair to Black

Secret Benefits of Onion Juice for Hair You Didn't Know

European Apple users left 'speechless' at price increases for iPhone 17

Tesla engineer quits company after 8 years with scathing message for Elon Musk on way out

Effective Methods to Keep Ginger Fresh for Extended Periods
