
Why Are 80% of People Magnesium Deficient? The Answer Will Surprise You
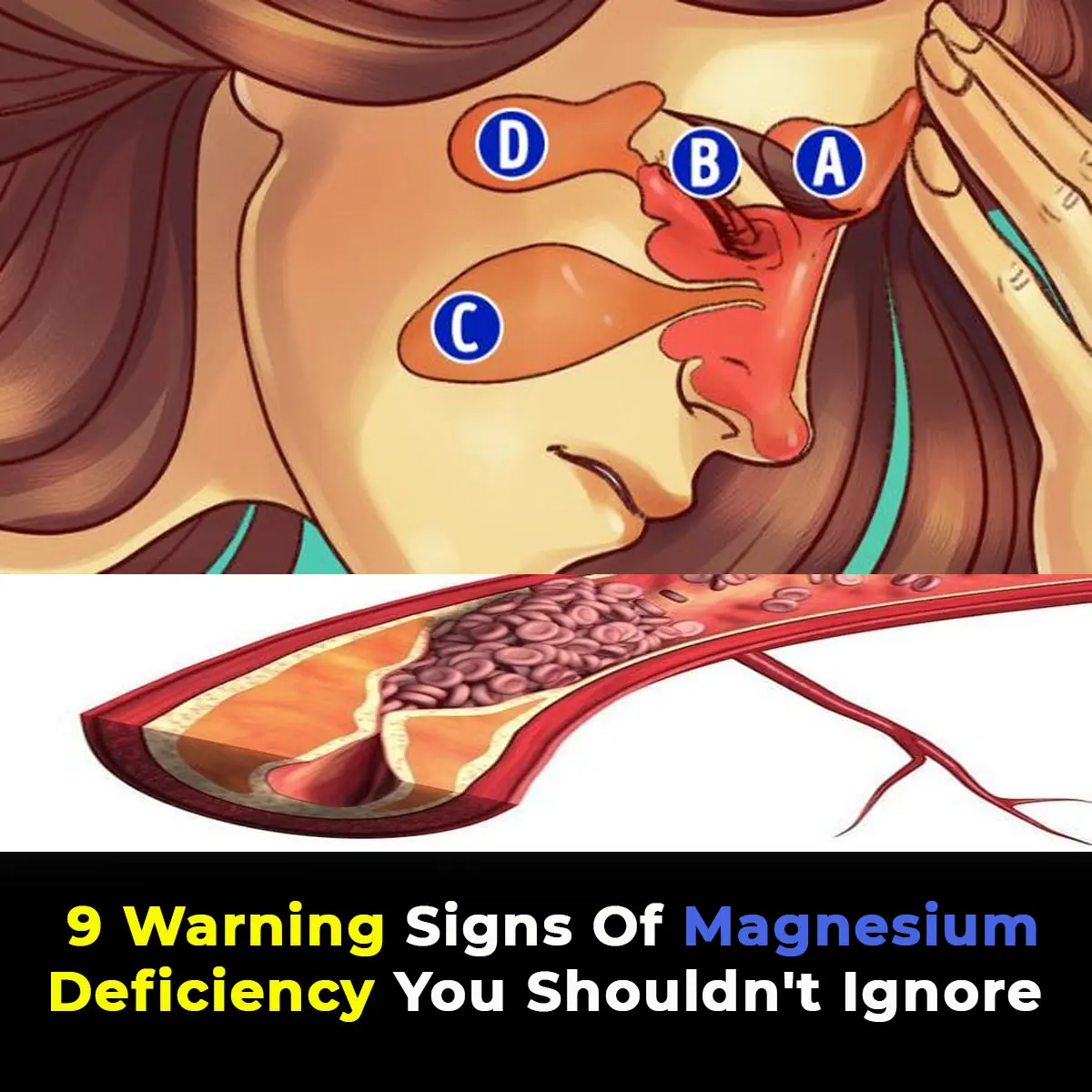
Magnesium is an essential mineral that plays a key role in our health. It supports numerous bodily functions, including sleep regulation and muscle recovery. Despite its importance, many individuals in the United States suffer from magnesium deficiency. Here's everything you need to know about magnesium, the signs of magnesium deficiency, and how to maintain healthy levels.
What is Magnesium and Why Is It So Important?
Magnesium is not only a mineral but also an important electrolyte. It occurs naturally in many foods and can also be added to some fortified products. This mineral is crucial for the proper function of our body's systems.
Magnesium acts as a cofactor for over 300 enzyme systems, influencing a wide range of chemical reactions in our body. These include muscle and nerve function, protein synthesis, blood glucose regulation, energy production, and blood pressure control. Magnesium is involved in DNA synthesis, the formation of antioxidants, and the transport of calcium and potassium across cell membranes, which helps our hearts maintain a regular rhythm.
Where Is Magnesium Stored in the Body?
The majority of the magnesium in our bodies is stored in the bones and soft tissues, with very little remaining in the bloodstream. Normal blood magnesium levels (serum magnesium) typically fall between 0.75 and 0.95 millimoles per liter. If your levels fall below 0.75, you may be experiencing hypomagnesemia or magnesium deficiency. While blood tests can measure magnesium levels, they don't necessarily reflect the amount of magnesium stored in the cells, so determining magnesium status can be difficult. Other tests, like saliva and urine tests, are also available but are not considered entirely reliable.
For adults, the recommended daily intake of magnesium ranges from 400mg to 420mg for men, depending on their age, and 310mg to 320mg for women. Pregnant women require slightly higher amounts, ranging from 360mg to 400mg. Lactating women also have increased needs, from 310mg to 360mg.
Signs of Magnesium Deficiency
Several factors can lead to magnesium deficiency, including poor diet, chronic illnesses, alcohol abuse, medications, and gastrointestinal issues like diarrhea. Common signs and symptoms of magnesium deficiency include:
-
Mild tremors
-
General weakness
-
Heart problems
-
High blood pressure
-
Irregular heartbeat
-
Asthma
-
Osteoporosis
-
Mental health issues
-
Muscle cramps and spasms
Magnesium deficiency is observed in approximately 2% of the general population, but the rates are higher in hospitalized patients (10%-20%) and in individuals with diabetes (25%). In intensive care settings, deficiency can affect 50%-60% of patients, and alcohol abuse can lead to deficiency in 30%-80% of cases. Research also suggests that 10% to 30% of the population in developed countries are magnesium deficient. These numbers tend to rise in postmenopausal women.
Foods Rich in Magnesium
Fortunately, magnesium is present in many common foods. Here is a list of magnesium-rich foods:
-
Pumpkin seeds (raw or roasted)
-
Chia seeds
-
Dry roasted almonds
-
Spinach
-
Dry roasted cashews
-
Shredded wheat cereal
-
Soy milk
-
Black beans
-
Edamame
-
Peanuts and peanut butter
-
Potatoes
-
Brown rice
-
Yogurt
-
Oatmeal
-
Fortified cereals
-
Kidney beans
-
Bananas
-
Atlantic salmon
-
Milk
-
Halibut
-
Raisins
-
Whole wheat bread
-
Avocados
-
Chicken breast
-
Lean ground beef
-
Broccoli
-
Apples
-
Carrots
In addition to these foods, magnesium supplements are widely available in forms such as magnesium citrate, oxide, chloride, and glycinate. These supplements come in various formats, including powders, liquids, and tablets. Before starting any new supplement, it is important to consult with your healthcare provider, especially if you are taking medications or other supplements.
Conclusion
Magnesium is vital for overall health, influencing a range of body functions from muscle relaxation to energy production. Regular intake of magnesium-rich foods can help prevent deficiency and support your body's well-being. If you're concerned about your magnesium levels, consider consulting a healthcare provider for advice and potentially incorporating magnesium supplements into your routine
News in the same category


Military Sleep Method Is 96% Successful and Will Send You to Sleep in Two Minutes
WHAT DO THESE RED DOTS ON YOUR SKIN MEAN?

7 Early Signs Your Heart May Be in Danger – Don’t Ignore #3!
If you have these two holes in your back, it means you don’t…Read more

Exact amount of time one single cigarette takes off your life revealed in new study

Breakthrough male birth control pill just passed human safety testing

What Mixing Vinegar, Salt, and Water Does?

Doctors Warn: These 2 Daily Habits Are Destroying Kidneys—Many Lose Both Before Age 30
Doctors warn that both of these habits—excessive sodium intake and overuse of paink:illers—are preventable.

Teen Warns Others After Doctors Ignored Symptom That Led To Her Collapsing In Class

According to a Psychologist, Narcissists Always Display This One Trait. Here’s What to Do If You See It

Man Who Drank 7 Liters Of Soda Daily For A Decade Suffers Severe Health Consequences
Could Your Food Be Hiding P@rasites? Neuroscientist Claims 3 Foods Can Cross into Your Br@in
Don’t Ignore These 10 Signs – Your Body May Be Telling You Something’s Wrong

Drink Clove Water for One Month and These 5 Benefits Will Follow

First Male Birth Control Pill Revealed—Here’s What It Does to the Body
The first male birth control pill that is hormone-free has been shown to be safe in a trial
If you see a purple butterfly sticker near a newborn, it's a heartbreaking meaning behind it
The purple butterfly is a way to gently open the door to awareness, giving space for acknowledgment without requiring painful conversations.
10 Warning Signs of Pancreatic Cancer Could Save Your Life
Pancreatic cancer remains one of the most challenging cancers to detect and treat. Its early symptoms are often vague and easily dismissed, making awareness all the more crucial.

Doctor Shares 30-Second Hand Test That Could Reveal Hidden Brain Tumor
News Post

Chaos as cruise ship passengers 'left behind' following major tsunami in Hawaii

Urgent warning issued to all iPhone users following release of iOS 18.6

13 of The Best Natural Muscle Relaxers to Help With Cramps

Military Sleep Method Is 96% Successful and Will Send You to Sleep in Two Minutes

WHAT DO THESE RED DOTS ON YOUR SKIN MEAN?

Skywatchers Delight: Dual Meteor Showers And Upcoming Celestial Events

Global Tsunami Alarms Following 8.8‑Magnitude Earthquake—Sixth Strongest On Record

7 Early Signs Your Heart May Be in Danger – Don’t Ignore #3!

If you have these two holes in your back, it means you don’t…Read more

Volcano Eruption Adds To Chaos After 8.8-Magnitude Quake Rocks Russia’s Far East

Scientists Spark Debate Over Interstellar Visitor’s Strange Behavior

Exact amount of time one single cigarette takes off your life revealed in new study

Breakthrough male birth control pill just passed human safety testing

Terrifying Optical Illusion Of A Woman Only Visible At A Certain Angle Leaves People Freaking Out

3-year-old boy finds a 16th century gold pendant worth $4M while playing with his dad’s metal detector

You’ll Never Guess What Happened at These 3 Weddings

What Mixing Vinegar, Salt, and Water Does?

Doctors Warn: These 2 Daily Habits Are Destroying Kidneys—Many Lose Both Before Age 30
Doctors warn that both of these habits—excessive sodium intake and overuse of paink:illers—are preventable.

Ancient Warning Emerges On Hawaiian Shore Days Before Massive Earthquake
