AVOID Bananas If You Suffer From These 5 Health Problems!

Bananas: A Nutritious Fruit Not Suitable for Everyone
Bananas are among the most widely consumed and beloved fruits around the world. They are not only delicious and convenient but also loaded with essential nutrients such as vitamins B6 and C, potassium, magnesium, and dietary fiber. These nutrients contribute to various health benefits, including improved digestion, heart health, and energy levels. However, despite their impressive nutritional profile, bananas are not the right choice for everyone. Certain medical conditions may require people to limit or even avoid banana consumption. Below are five health issues where bananas could potentially do more harm than good.
1. High Blood Sugar (Diabetes)
Bananas contain natural sugars such as fructose, glucose, and sucrose, which provide quick energy. Although they generally have a low to moderate glycemic index, ripe bananas—especially those with brown spots—can lead to a significant increase in blood sugar levels. This makes them a risky choice for individuals with diabetes or insulin resistance. Consistently consuming high-glycemic fruits can interfere with blood sugar management and increase the risk of complications over time.
If you are diabetic or pre-diabetic, it’s best to consume bananas in moderation and pair them with foods high in protein or healthy fats to slow sugar absorption. Unripe or green bananas, which are higher in resistant starch and lower in sugar, may be a better option. These can help with blood sugar regulation and improve gut health.
2. Kidney Disease
One of the standout nutrients in bananas is potassium, which supports nerve signaling, muscle contraction, and heart function. While potassium is essential for healthy individuals, those with chronic kidney disease (CKD) often need to limit their intake. When the kidneys are not functioning properly, they struggle to excrete excess potassium, leading to a condition known as hyperkalemia—an electrolyte imbalance that can cause muscle weakness, irregular heartbeat, and even cardiac arrest.
Patients with advanced kidney disease are often placed on a low-potassium diet. In such cases, high-potassium foods like bananas, oranges, avocados, and potatoes must be avoided or strictly regulated. Always consult a nephrologist or a dietitian before making dietary decisions if you have compromised kidney function.
3. Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) is a common gastrointestinal disorder characterized by symptoms such as bloating, abdominal pain, gas, and irregular bowel movements. Bananas, especially when fully ripe, are high in fermentable oligosaccharides, disaccharides, monosaccharides, and polyols (FODMAPs)—short-chain carbohydrates that can be poorly absorbed in the gut.
These FODMAPs can ferment in the colon, leading to increased gas and discomfort in people with IBS. If bananas consistently cause digestive upset, try switching to firmer, less ripe ones, which tend to be lower in FODMAPs. Additionally, tracking your symptoms with a food diary can help determine whether bananas are a trigger for you.
4. Latex Allergy
There is a well-documented link between latex allergy and sensitivity to certain fruits, including bananas, avocados, kiwis, and chestnuts. This condition, known as latex-fruit syndrome, occurs because the proteins in these fruits are structurally similar to latex proteins. When someone with a latex allergy eats bananas, their immune system may mistakenly react as if it's encountering latex.
Symptoms can vary in severity and may include itching or swelling of the lips and mouth, hives, skin rashes, respiratory symptoms, and in rare cases, anaphylaxis—a life-threatening reaction that requires immediate medical attention. If you have a known latex allergy, speak with your allergist or healthcare provider before including bananas in your diet.
5. Acid Reflux (GERD)
Although bananas are usually considered safe for individuals with acid reflux or gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), they may trigger symptoms in some people. While their low acidity generally makes them a reflux-friendly food, bananas can sometimes relax the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), allowing stomach acid to flow back up into the esophagus.
If you notice symptoms like heartburn, regurgitation, or chest discomfort after eating bananas, consider keeping a food journal to pinpoint whether bananas are a contributing factor. Everyone's body responds differently, so it’s important to identify your individual triggers and adjust your diet accordingly.
Conclusion
Bananas are a nutritious and accessible fruit that can be part of a healthy diet for most people. However, they may not be suitable for individuals dealing with specific health conditions such as diabetes, kidney disease, IBS, latex allergies, or acid reflux. Understanding how your body reacts to certain foods is key to maintaining good health. If you have a chronic medical condition or food sensitivities, consult a healthcare professional or registered dietitian before making dietary changes. Being informed and proactive will help you make the best nutritional choices for your unique needs.
News in the same category


Doctors reveal how many times you should be able to swallow in 30 seconds to be 'healthy' and the results are shocking

Crockpot Sausage and Potatoes

A New Type of Drink Found to Help 'Push Back' Cancer: It’s Not Tea or Coffee

Not So Impossible Cheeseburger Pie

35-Year-Old Man’s Sore Throat Turned into Cancer After 5 Chemotherapy Sessions—Doctor Urges: Throw These 2 Things Out of Your Fridge

Eight Early Symptoms Found in 23% of Cancer Patients: Warning Signs That Should Not Be Ignored

Doctors forced to apologize after 32-year-old woman given hysterectomy to treat 'tumor on her ovary' but biopsy showed no signs of cancer

Liquid Gold Tea: A Natural Remedy for Inflammation

Caramel Apple Fudge

Mozzarella Fried Cheese Bites: Cheesy, Crunchy, and Irresistible

You are doing it all wrong. Here's how to drink 8 glasses of water each day
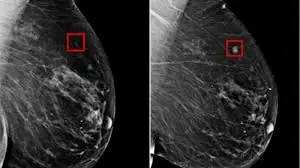
A new type of Artificial Intelligence can detect breast cancer 5 years before diagnosis

New Discovery: Protein AP2A1 May Hold the Key to Reversing Aging at the Cellular Level
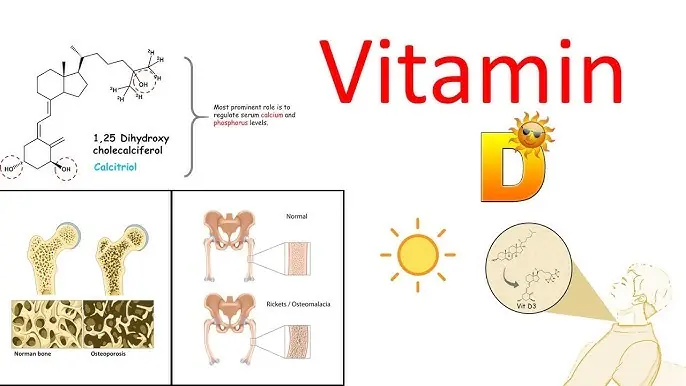
Why Vitamin D Is Essential for More Than Just Bone Health

Seniors: This Castor Oil + Baking Soda Trick Is Blowing Doctors’ Minds!

Lemon and Nopal Remedy: A Natural Boost for Your Body
65-Year-Old Man Dies at 11 PM: Doctor Warns Never to Drink These 4 Types of Beverages Before Bed – No Matter How Thirsty You Are
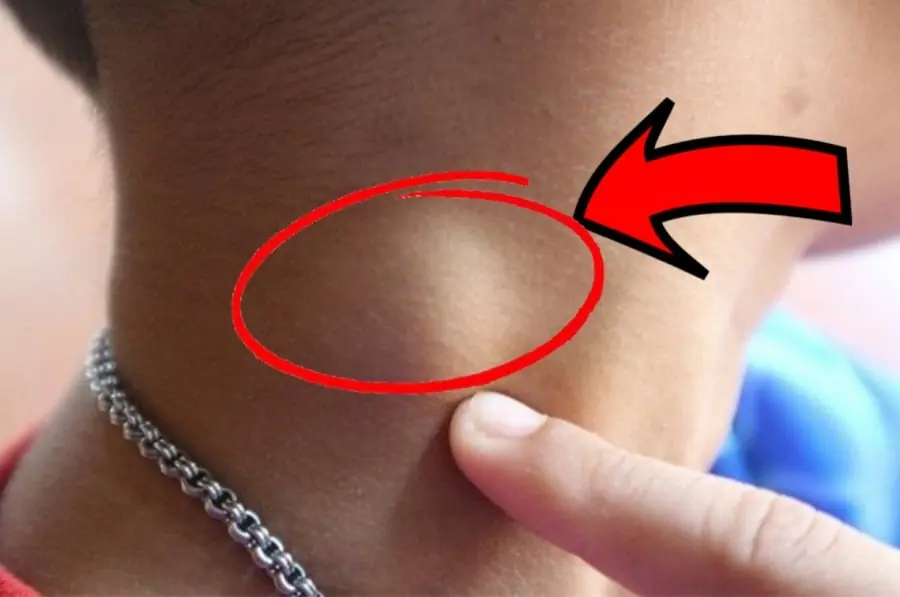
People at Risk of Cancer Often Show 3 Unusual Signs in the Neck – Even One Is a Health Warning
News Post

Homemade Vanilla Dessert Cream

Oatmeal and Guava: A Natural Remedy for Leg Cramps, Diabetes, and High Blood Pressure

My Greedy In-Laws Tried to Get Rid of Our Sick Mom, but She Brilliantly Taught Them a Lesson

I Got Back from a Work Trip and Found My House Completely Empty

3 Eye-Opening Stories About Husbands Who Didn't Appreciate Their Devoted Wives – And the Important Lessons They Learn in the End

Doctors reveal how many times you should be able to swallow in 30 seconds to be 'healthy' and the results are shocking

14 Fish You Should Consider Never Eating
40+ Weird Signs That Lead To a Cancer Diagnosis

Pudding Cool Whip Frosting

NASA’s Mars Rover Uncovers Mysterious Spheres On The Planet’s Surface, Leaving Experts Baffled

Depressing find at the bottom of the Mariana Trench is a warning to the world

Crockpot Sausage and Potatoes

People Freaked Out After Spotting Creepy Hidden Face in Group Photo

A New Type of Drink Found to Help 'Push Back' Cancer: It’s Not Tea or Coffee

This One Everyday Habit Is Draining Your Electricity Bill — And No One Talks About It

Not So Impossible Cheeseburger Pie

35-Year-Old Man’s Sore Throat Turned into Cancer After 5 Chemotherapy Sessions—Doctor Urges: Throw These 2 Things Out of Your Fridge

Eight Early Symptoms Found in 23% of Cancer Patients: Warning Signs That Should Not Be Ignored
