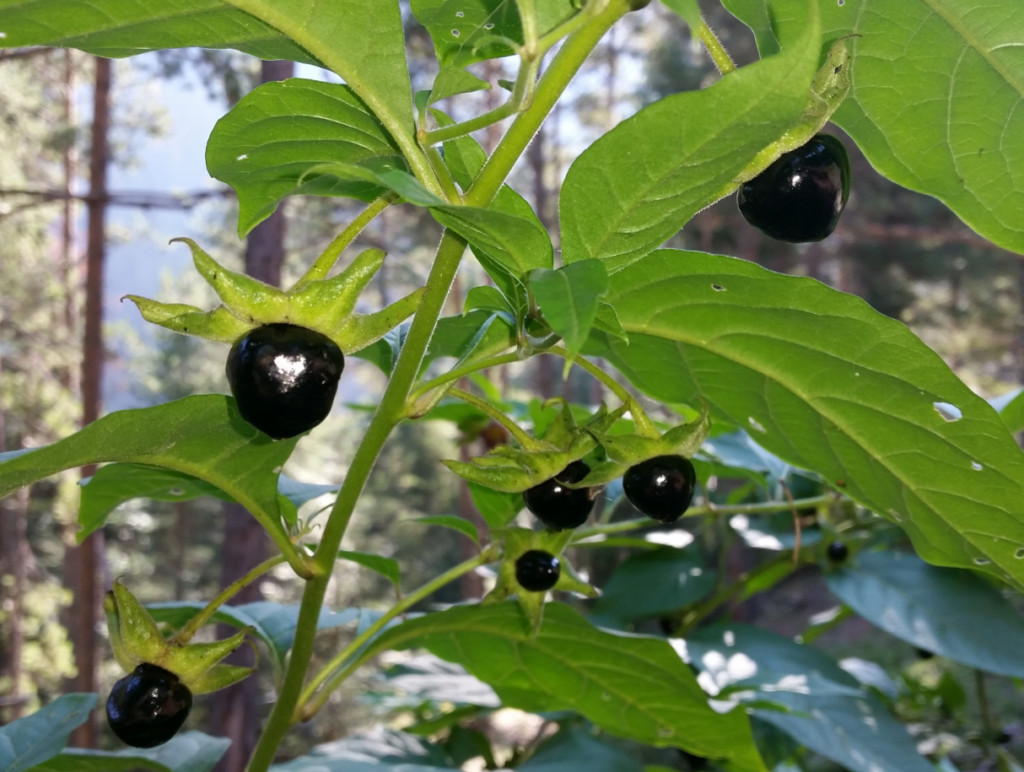
Deadly Nightshade Atropa Belladonna The Mysterious and Toxic Plant with a Dark History
Deadly Nightshade Atropa Belladonna is one of history’s most infamous toxic plants known for its beauty mystery and medicinal uses Despite its deadly nature it has been used in traditional medicine cosmetics and even poisons But what makes it so dangerous Can it be used safely or should it be avoided Let’s explore its history effects and risks

What is Deadly Nightshade
Deadly Nightshade Atropa Belladonna is a perennial plant from the nightshade family native to Europe North Africa and Western Asia With its dark purple berries and bell shaped flowers it looks beautiful but is extremely toxic every part of the plant contains deadly alkaloids
Toxic Components of Deadly Nightshade
Atropine Affects the nervous system causing hallucinations rapid heartbeat and paralysis
Scopolamine Known for its mind altering effects used historically in poisons and sedatives
Hyoscyamine Disrupts neurological functions leading to severe poisoning or death in high doses
These alkaloids block neurotransmitters in the body leading to a variety of toxic effects from blurred vision and dry mouth to respiratory failure in severe cases
The History and Folklore of Deadly Nightshade

Deadly Nightshade has been used medicinally magically and lethally throughout history Here are some fascinating historical uses
Ancient Rome and Greece


Medieval Witchcraft and Sorcery


Renaissance Beauty


Symptoms and Effects of Deadly Nightshade Poisoning
Even small doses of Deadly Nightshade can cause severe poisoning Here’s what happens when someone ingests or comes into contact with the plant
Mild Symptoms




Severe Symptoms




Who is Most at Risk




Is There a Safe Way to Use Deadly Nightshade
Despite its deadly reputation Atropa Belladonna has been used in controlled medical settings Modern pharmaceuticals extract atropine and scopolamine from the plant for legitimate medical purposes
Medical Uses of Belladonna Extracts





How to Identify and Avoid Deadly Nightshade
Since Deadly Nightshade resembles edible berries it’s essential to know how to identify and avoid it in the wild
How to Identify Atropa Belladonna




Safe Foraging Practices



Should You Grow or Avoid Deadly Nightshade



While Deadly Nightshade is fascinating from a historical and medicinal perspective its toxic nature makes it a plant to admire from a distance rather than cultivate or consume
Key Takeaways




News in the same category


The Most Powerful Medicinal Plant Many People Still Ignore

This Powerful Green Plant May Help Cleanse Your Blood, Skin, Kidneys, Liver, and Pancreas — But Only If Used This Way

A Single Ingredient to Help Combat Bone Pain, Diabetes, Anxiety, Depression, and Constipation

Woman Suffers Sudden Kidney Failure After Dinner
Discover Nature's Oral Secret: 3 Simple Guava Leaf Remedies for Tooth Decay and Gum Health

Moringa Seeds: The Natural Secret Your Body Has Been Waiting For
🔔 Ringing in Your Ear? What Tinnitus Really Means—And When It’s Time to See a Doctor
What Happens If You Soak Your Feet in Apple Cider Vinegar for 15 Minutes???

Why You Might Want to Drink Chia Seed Water Daily

6 Vegetables That Naturally Contain Toxins
Health Benefits of Coffee

The Pre-Colonoscopy Question That Could Change Everything: “What Kind of Prep Will I Be On?”
What Causes Folliculitis and How To Prevent It

Top 9 Vegetables for Diabetics: How They Can Help in Managing Your Blood Sugar Levels Daily

A New Hope Emerges: The Natural Drink That May Help Fight Cancer

Doctors reveal that eating onion causes...

🌿 Clove Steam Inhalation for Sinus Relief: A Soothing Home Remedy—Done Safely & Effectively

Scientists Explain What Happens To Your Body When You Cut Back (But Don’t Quit) Alcohol

Eating Leftovers From the Fridge, 50-Year-Old Man Dies: 5 Foods You Should NEVER Keep Overnight . If Left Over, Throw It Away
News Post

No One Knew Who He Was

The Day the Mall Lost Its Mind

He broke the law… to save his family.

The Boy Who Stopped the Jet

The Boy She Refused to Trust Held Her Son’s Life

11 Reasons Why You Should Eat One Garlic Clove Daily

The Most Powerful Medicinal Plant Many People Still Ignore

This Powerful Green Plant May Help Cleanse Your Blood, Skin, Kidneys, Liver, and Pancreas — But Only If Used This Way

A Single Ingredient to Help Combat Bone Pain, Diabetes, Anxiety, Depression, and Constipation

Woman Suffers Sudden Kidney Failure After Dinner

Vicks VapoRub on the Feet: What It’s For and How to Use It

Rue: A Treasure of Nature

Discover Nature's Oral Secret: 3 Simple Guava Leaf Remedies for Tooth Decay and Gum Health

Moringa Seeds: The Natural Secret Your Body Has Been Waiting For

Did you know that if a white and yellow cat approaches you, it's because…

🔔 Ringing in Your Ear? What Tinnitus Really Means—And When It’s Time to See a Doctor

What Happens If You Soak Your Feet in Apple Cider Vinegar for 15 Minutes???

Flight Attendant Spits on Black Triplets — Then Realized Too Late Their Mother Runs the Airline

Why You Might Want to Drink Chia Seed Water Daily
