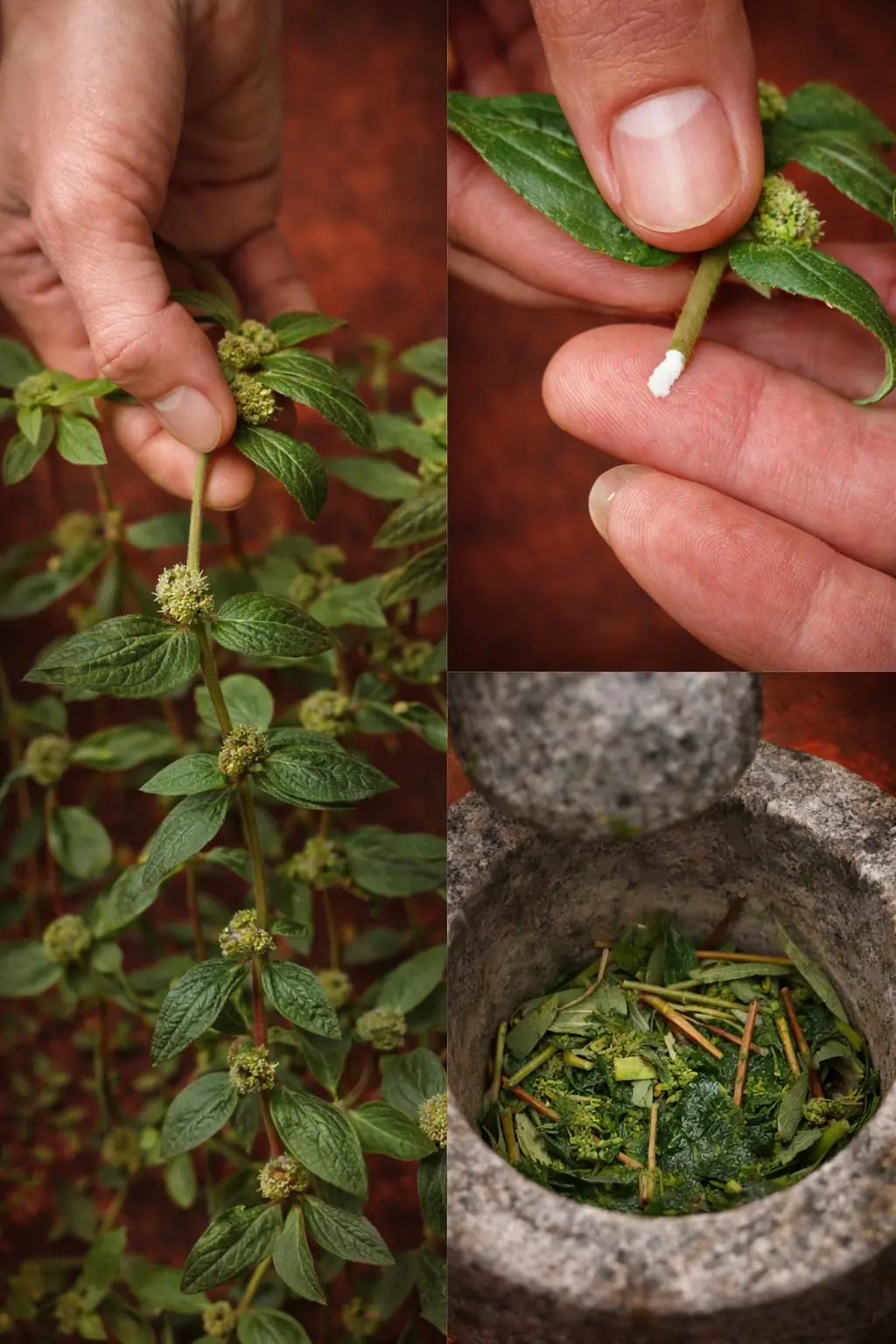
Euphorbia hirta (Asthma Plant): Traditional Respiratory Support for the Lungs
Euphorbia hirta, commonly known as the asthma plant, is a small herb that grows in warm climates around the world. Though easily overlooked because of its size, it has a long history of use in traditional medicine systems for breathing difficulties, chest congestion, persistent coughs, and spasmodic respiratory conditions.
Its common name reflects its most well-known traditional role: supporting lung function and respiratory comfort. Below is an overview of its potential benefits, common home preparations, identification tips, and important safety precautions.
Traditional Respiratory Benefits of Euphorbia hirta
1. Supports Easier Breathing
Euphorbia hirta has traditionally been described as having a mild bronchodilating effect, meaning it may help relax the bronchial tubes and support more comfortable airflow when the chest feels tight.
2. Helps Reduce Chest Congestion
The plant contains compounds that may help loosen mucus and encourage its removal from the lungs, making breathing feel lighter.
3. Traditionally Used for Wheezing and Spasmodic Cough
Herbal records note its use for calming sudden coughing fits and wheezing, likely due to antispasmodic properties that help relax respiratory muscles.
4. Supports Comfort During Respiratory Infections
With mild antibacterial and antiviral activity reported in traditional use, Euphorbia hirta has been used to support the body during common respiratory infections.
5. Soothes Irritated Throat and Airways
When prepared as a tea, it may help calm irritation and inflammation in the throat and upper airways, especially during dry or persistent coughs.
6. Used Traditionally for Bronchitis Symptoms
Its combination of mucus-loosening, soothing, and airway-relaxing actions has made it a common traditional remedy for both acute and chronic bronchitis.
7. Acts as a Natural Expectorant
Euphorbia hirta has been used to encourage the natural expulsion of phlegm, helping the lungs clear excess mucus more efficiently.
8. Helps Calm Dry, Tickling Coughs
Traditional use suggests it may help reduce cough reflex sensitivity, making it useful for non-productive coughs that irritate the chest.
9. Provides Mild Anti-Inflammatory Support
Inflammation can narrow airways. The plant’s gentle anti-inflammatory action may help support smoother breathing.
10. Helps Relax Breathing Muscles
Some traditional systems used Euphorbia hirta for breathing difficulty related to stress or chest tension, due to its relaxing effect on smooth muscles.
Additional Traditional Uses (Beyond Respiratory Support)
While best known for lung health, Euphorbia hirta has also been used traditionally for:
-
General immune support
-
Mild digestive regulation
-
Fever support
-
Topical use for minor skin irritations
-
Mild diuretic support
These secondary uses may indirectly support respiratory comfort by promoting overall balance in the body.
How Euphorbia hirta Is Commonly Used
1. Euphorbia hirta Tea (Most Common)
Ingredients
-
1–2 teaspoons dried Euphorbia hirta
-
250 ml hot (not boiling) water
Method
-
Pour hot water over the dried herb
-
Steep for 8–10 minutes
-
Strain and drink once or twice daily
Traditionally used for: coughs, phlegm, wheezing, and general lung support.
2. Steam Inhalation
Ingredients
-
A handful of fresh or dried plant
-
1 liter hot water
Method
-
Place the herb in a bowl
-
Pour hot water over it
-
Cover your head with a towel and inhale steam for 5–8 minutes
Traditionally used for: chest congestion, sinus blockage, thick mucus.
3. Powdered Form
Dried leaves can be ground into a fine powder.
How to use
-
Mix ¼ teaspoon into warm water or honey once daily
-
Use sparingly in herbal blends
Traditionally used for: gentle, ongoing respiratory support.
4. Decoction (Stronger Preparation)
Ingredients
-
1 tablespoon dried plant
-
500 ml water
Method
-
Boil gently for 10 minutes
-
Strain and cool
-
Drink ½ cup up to twice daily
Traditionally used for: persistent chest congestion or heavy mucus.
5. Topical Chest Poultice
Method
-
Crush fresh leaves
-
Wrap in cloth and warm gently
-
Apply to chest for 10–15 minutes
Traditionally used for: chest tightness and coughing discomfort.
How to Identify Euphorbia hirta (Quick Guide)
-
Low-growing plant forming small mats
-
Hairy stems and small oval leaves
-
Leaves often have a reddish or purplish tint
-
White, milky sap appears when stems are broken
-
Tiny clustered flowers at leaf joints
⚠️ Always confirm identification carefully, as many Euphorbia species look similar.
Precautions and Possible Side Effects
All Euphorbia plants produce a milky latex sap, which can be irritating if misused.
Use caution if you have:
-
Severe asthma or chronic lung disease
-
Heart or kidney conditions
-
Latex sensitivity
-
Pregnancy or breastfeeding
Possible side effects with overuse:
-
Stomach upset or diarrhea
-
Nausea
-
Skin or eye irritation from sap
-
Increased heart rate
Important:
Always start with very small amounts and never use large doses.
Disclaimer
This article is for informational and educational purposes only.
Euphorbia hirta has a long history of traditional use, but it is not a substitute for medical treatment, especially for serious conditions such as asthma attacks, pneumonia, or chronic lung disease.
Consult a qualified healthcare professional before using herbal remedies, particularly if you are pregnant, breastfeeding, taking medications, or managing ongoing health conditions.
News in the same category


6 Natural Ways To Stop Gum Disease Before It’s Too Late

Plant-Derived Nutrient Cocktail Achieves 100% Kill Rate of Breast Cancer Cells In Vitro

5 warning signs your heart is abnormally weak for your age

Active Vitamin D Levels, Not Storage Form, Linked to Greater Gut Microbiome Diversity in Older Men

Synergistic Anti-Cancer Effect: Curcumin and Silymarin 'One-Two Punch' Against Colon Cancer Cells

28-Year-Old Woman Develops Lung Cancer in Both Lungs Due to This Common Nighttime Habit

Purple Dead Nettle (Lamium purpureum): A Wild Ally for Circulation and Heart Health

Regular Yogurt Consumption Linked to Reduced Chronic Inflammation: Evidence from a University of Wisconsin Study

The Hidden Power of American Holly (Ilex opaca): More Than a Holiday Symbol

Oral Glutamine Supplementation Achieves Significant Symptom Relief in Post-Infectious IBS-D

Physician-Scientist Consumes 1,000 Sardines in 30 Days to Test Metabolic Impact

Early-Stage Fatty Liver: 5 Facial Signs You Should Never Ignore
Specific Extremely Low-Frequency Electromagnetic Field Inhibits Melanoma Cancer Cell Growth In Vitro
6 Warning Signs of Kidney Failure Many People Often Ignore

Why You Shouldn’t Kill Wood Sorrel in Your Garden: 8 Compelling Reasons
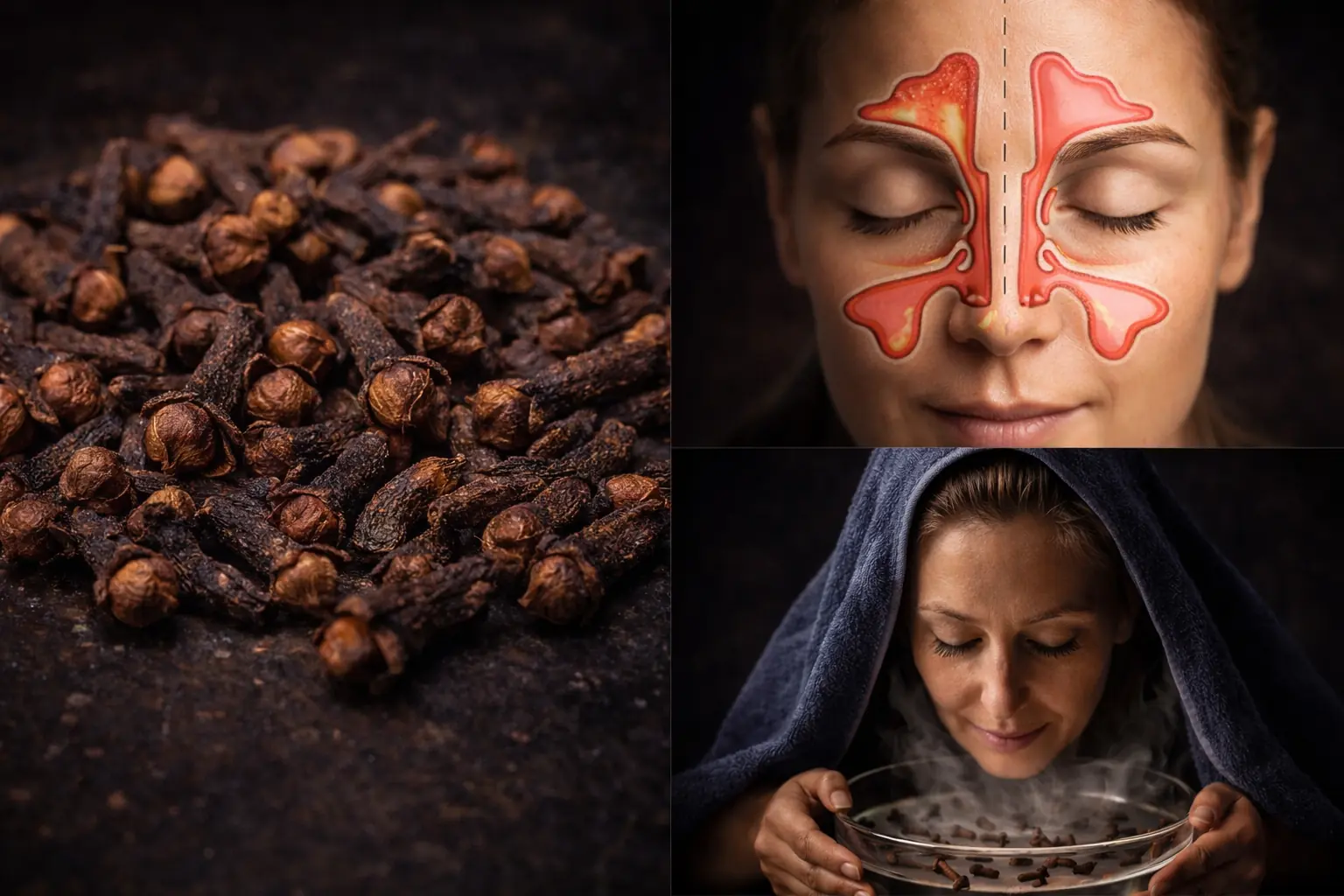

The Power of Clove Steam Inhalation (Respiratory Relief You Can Feel Immediately)

Stroke and Cerebral Infarction Prevention: Remember 3 Key Indicators, 1 Critical Disease, and 6 Warning Habits You Must Not Ignore

Tamarind: The Tangy Superfruit Your Body Will Thank You For
News Post

How to Reset Your Thyroid to Burn Fat and Activate Your Metabolism

6 Natural Ways To Stop Gum Disease Before It’s Too Late

Plant-Derived Nutrient Cocktail Achieves 100% Kill Rate of Breast Cancer Cells In Vitro

5 warning signs your heart is abnormally weak for your age

Active Vitamin D Levels, Not Storage Form, Linked to Greater Gut Microbiome Diversity in Older Men

Synergistic Anti-Cancer Effect: Curcumin and Silymarin 'One-Two Punch' Against Colon Cancer Cells

28-Year-Old Woman Develops Lung Cancer in Both Lungs Due to This Common Nighttime Habit

Purple Dead Nettle (Lamium purpureum): A Wild Ally for Circulation and Heart Health

Regular Yogurt Consumption Linked to Reduced Chronic Inflammation: Evidence from a University of Wisconsin Study

‘Black Diamond’ Apples Exist — A Rare Variety Only Found in China And Tibet

The Hidden Power of American Holly (Ilex opaca): More Than a Holiday Symbol

Oral Glutamine Supplementation Achieves Significant Symptom Relief in Post-Infectious IBS-D

Viking Sheep With Four Horns Have Returned From Near Extinction in Britain

Physician-Scientist Consumes 1,000 Sardines in 30 Days to Test Metabolic Impact

Early-Stage Fatty Liver: 5 Facial Signs You Should Never Ignore

Norway Declares Nationwide Ban on Deforestation In World-First

Specific Extremely Low-Frequency Electromagnetic Field Inhibits Melanoma Cancer Cell Growth In Vitro

The Person That Everyone Leans On—But No One Ever Checks On—Usually Displays These 9 Quiet Signs of Exhaustion

