
Expanded Summary of the PISCES Trial
The PISCES randomized clinical trial, published in The New England Journal of Medicine in November 2025, enrolled 1,228 adults on maintenance hemodialysis across 26 sites in Canada and Australia. Participants were randomized to receive either 4 g of fish oil daily (providing ~1.6 g EPA and 0.8 g DHA) or a placebo (corn oil). Over a median follow-up of 3.5 years, the fish oil group experienced a 43% lower rate of major cardiovascular events compared with placebo.
Cardiovascular Outcomes
The reduction in risk was consistent across multiple endpoints:
-
Myocardial infarction (heart attack)
-
Stroke
-
Cardiovascular death
-
Peripheral vascular amputations
Notably, the trial reported no meaningful increase in adverse events, suggesting that fish oil supplementation was well tolerated in this population.
Why Dialysis Patients?
Researchers emphasized that the benefits were specific to patients with kidney failure on dialysis, who face an exceptionally high cardiovascular risk and often have low baseline omega-3 fatty acid levels. In contrast, large-scale studies in the general population have shown mixed or minimal benefits of fish oil supplementation for cardiovascular prevention. This underscores the importance of tailoring interventions to specific patient groups rather than assuming universal applicability.
Clinical Implications
-
Potential breakthrough: For dialysis patients, who have limited effective options for reducing cardiovascular risk, fish oil supplementation could represent a simple, low-cost intervention.
-
Caution required: Experts stress that replication in other cohorts and longer-term studies are needed before widespread clinical adoption. The trial’s findings, while robust, must be confirmed to ensure reliability.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Fish Oil (PISCES Trial) | Conventional Approaches in Dialysis |
|---|---|---|
| Population | 1,228 adults on maintenance hemodialysis | Dialysis patients worldwide |
| Intervention | 4 g fish oil daily (EPA + DHA) | Standard cardiovascular risk management (blood pressure control, statins, antiplatelets) |
| Follow-up | ~3.5 years | Variable, often lifelong |
| Outcome | 43% reduction in serious CV events | Modest benefit; high residual risk remains |
| Safety | No meaningful increase in adverse events | Known side effects from drugs (bleeding risk, muscle pain, etc.) |
| Generalisability | Specific to dialysis patients | Broader but less effective in this group |
Conclusion
The PISCES trial provides compelling evidence that fish oil supplementation can significantly reduce cardiovascular complications in dialysis patients, a population with few effective preventive strategies. However, experts caution against extrapolating these findings to the general population. Replication and further investigation are essential before fish oil can be recommended as a standard therapy in nephrology practice.
News in the same category


The Most Dangerous Time to Sleep

Doctor Shares Three Warning Signs That May Appear Days Before a Stroke

A Couple Diagnosed with Liver Cancer at the Same Time: When Doctors Opened the Refrigerator, They Were Alarmed and Said, “Throw It Away Immediately!”

Resveratrol–Copper Combination Shows Promise in Altering Glioblastoma Biology
Early Signs of Kidney Disease & How to Protect Your Kidneys (Evidence Based)

Sore Legs for No Reason: What It Means According to Science

How to Get Rid of Worms in Humans (Including Parasite Cleanse Diet)
14 Tips to Improve Varicose Veins Naturally + The Best Essential Oils for Varicose Veins

Study found that women with stronger leg muscles have younger, healthier brains and better cognitive function as they age.

In a study of 50 women, those who wore rose essential oil on their clothes daily for 30 days showed a measurable increase in gray matter volume across the whole brain on MRI scans

7 Reasons You’re Not Hitting Your A1C Goal

Researchers observed a 61% reduction in the risk of invasive cancer among patients who completed a home exercise program and took vitamin D3 and omega-3 fatty acids daily.
What Causes a Blood Clot to Form in the Arm?
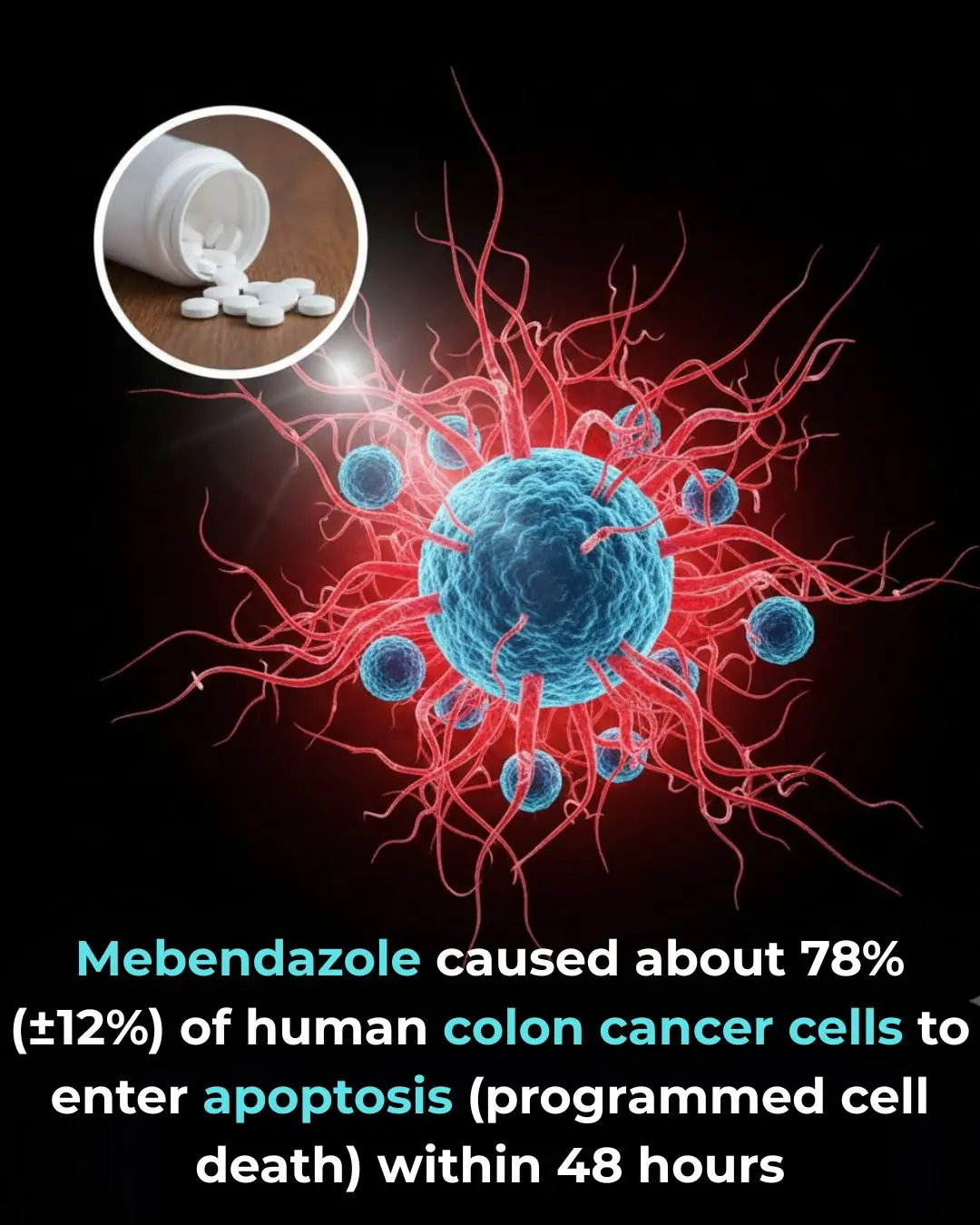
Mebendazole caused about 78% (±12%) of human colon cancer cells to enter apoptosis (programmed cell death) within 48 hours
Anthocyanin-containing purple-fleshed potatoes suppress colon tumorigenesis via elimination of colon cancer stem cells

🌿 Horsetail Herb: Nature’s Hidden Gem for Hair, Bones, Skin & More

Castor Oil + Garlic: A Timeless Remedy with Surprising Comforts

Norovirus Is Already Hitting Hard This Holiday Season
News Post

2 tips for boiling pig ears to keep them white, crispy, and odorless.

Tips for cleaning greasy plastic and glass containers without scrubbing.

Is your pan losing its non-stick coating? Add a few drops of this, and your old pan will be like new again.

Support Joint Health Naturally

The Most Dangerous Time to Sleep

Doctor Shares Three Warning Signs That May Appear Days Before a Stroke

A Couple Diagnosed with Liver Cancer at the Same Time: When Doctors Opened the Refrigerator, They Were Alarmed and Said, “Throw It Away Immediately!”

Resveratrol–Copper Combination Shows Promise in Altering Glioblastoma Biology

Your hair is aging you. 10 winter styling tweaks that instantly lift your look

These sudden purple patches on my arms won’t stop appearing, and my doctor is booked until January. What’s happening?
My ankles puff up every evening, and I can’t get in to see anyone until after the holidays. Should I worry?

I had no idea about this

Early Signs of Kidney Disease & How to Protect Your Kidneys (Evidence Based)

Sore Legs for No Reason: What It Means According to Science

How to Get Rid of Worms in Humans (Including Parasite Cleanse Diet)

14 Tips to Improve Varicose Veins Naturally + The Best Essential Oils for Varicose Veins

Woman Donates Entire $1B Fortune to Eliminate Tuition in NYC’s Poorest Area

Study found that women with stronger leg muscles have younger, healthier brains and better cognitive function as they age.
