
Groundbreaking Research: Reversing Memory Loss In Alzheimer’s Disease Without Removing Plaques
Alzheimer’s disease has long been one of the most devastating and complex neurological disorders, affecting millions of people worldwide. Traditionally characterized by the buildup of amyloid-beta plaques in the brain, the disease leads to progressive memory loss, cognitive decline, and ultimately, the loss of basic bodily functions. For decades, research has focused on the removal of these plaques as the key to treating or slowing the progression of Alzheimer’s. However, a recent groundbreaking study has challenged this long-standing approach by demonstrating that memory loss can be reversed without removing these plaques.
This discovery marks a significant shift in the understanding of how Alzheimer’s functions and how it might be treated. The study, conducted by a team of neuroscientists at a major research institution, showed that targeting other underlying mechanisms—such as inflammation, metabolic dysfunction, and synaptic communication—could lead to cognitive improvements in patients. In animal models, scientists were able to restore memory function even though amyloid plaques remained in the brain. These findings suggest that amyloid buildup might be more of a symptom than a direct cause of cognitive decline.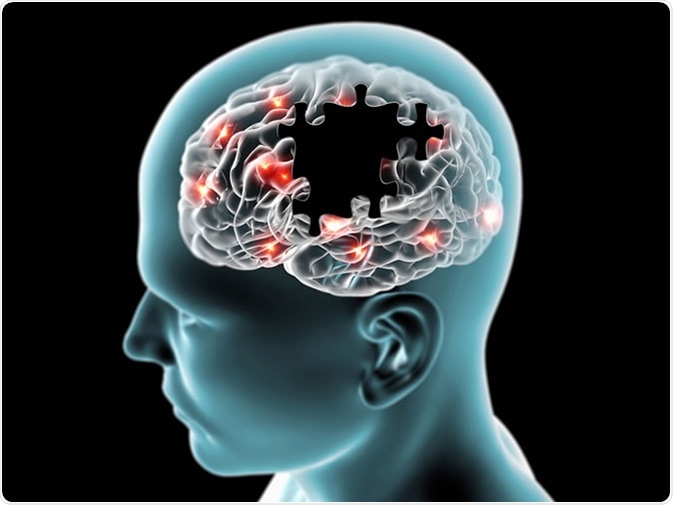
For years, the dominant theory in Alzheimer’s research—the amyloid hypothesis—has driven the development of drugs aimed at reducing plaque buildup. While several of these drugs have succeeded in lowering amyloid levels, many have failed to produce meaningful cognitive benefits in patients. This discrepancy has led some scientists to question whether amyloid plaques are the primary cause of Alzheimer’s or simply one piece of a more complex puzzle.
The new research instead focuses on restoring the brain’s natural ability to communicate and adapt. One promising strategy involves enhancing the function of synapses, which are the connections between neurons that enable memory and thought. By boosting synaptic activity and protecting neurons from further damage, researchers observed significant memory recovery in mice. In addition, treatments that reduce brain inflammation—a common feature in Alzheimer’s—also showed impressive results. Inflammation can disrupt neural communication and accelerate cell death, so reducing it may create a more supportive environment for brain repair.
Another remarkable aspect of the study is its potential implications for human therapy. Unlike approaches that focus on removing plaques, which often require invasive procedures or strong pharmaceutical interventions with side effects, this new method relies on biological pathways that can potentially be activated through less aggressive treatments, such as gene therapy, dietary changes, or anti-inflammatory drugs. These strategies are not only more accessible but could also be personalized to suit individual patients' needs and disease progression.
While these findings are still in the early stages and primarily demonstrated in laboratory animals, clinical trials in humans are already being planned. If successful, this approach could revolutionize how Alzheimer’s is treated and provide hope to millions of families currently facing the devastating effects of this disease.
Moreover, the broader scientific community is taking notice. The study opens the door to a new era of Alzheimer’s research—one that is less narrowly focused on a single pathological marker and more open to exploring the brain’s capacity for regeneration and resilience. Researchers are increasingly acknowledging that Alzheimer’s may be the result of multiple overlapping factors, including vascular issues, immune responses, and even lifestyle influences like sleep and exercise.
In conclusion, the discovery that memory loss in Alzheimer’s can potentially be reversed without removing amyloid plaques is a game-changer. It not only challenges decades of scientific assumptions but also offers a new path forward in the search for effective treatments. If further studies confirm these results in humans, this research may mark the beginning of a new chapter in the fight against Alzheimer’s—one where restoring brain function becomes a realistic and achievable goal.
News in the same category


Doctors Warn: These 2 Daily Habits Are Destroying Kidneys—Many Lose Both Before Age 30
Doctors warn that both of these habits—excessive sodium intake and overuse of paink:illers—are preventable.

Teen Warns Others After Doctors Ignored Symptom That Led To Her Collapsing In Class

According to a Psychologist, Narcissists Always Display This One Trait. Here’s What to Do If You See It

Man Who Drank 7 Liters Of Soda Daily For A Decade Suffers Severe Health Consequences
Could Your Food Be Hiding P@rasites? Neuroscientist Claims 3 Foods Can Cross into Your Br@in
Don’t Ignore These 10 Signs – Your Body May Be Telling You Something’s Wrong

Drink Clove Water for One Month and These 5 Benefits Will Follow
Why Are 80% of People Magnesium Deficient? The Answer Will Surprise You

First Male Birth Control Pill Revealed—Here’s What It Does to the Body
The first male birth control pill that is hormone-free has been shown to be safe in a trial
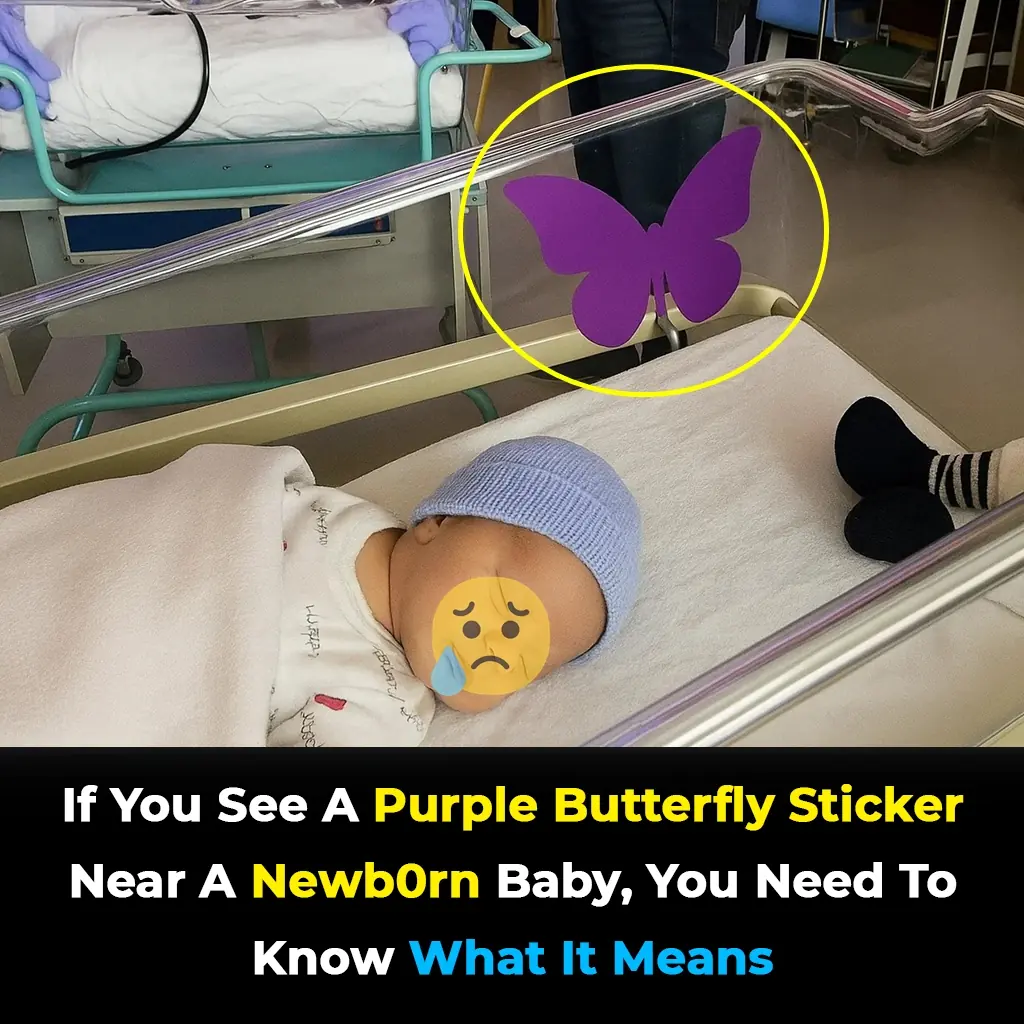
If you see a purple butterfly sticker near a newborn, it's a heartbreaking meaning behind it
The purple butterfly is a way to gently open the door to awareness, giving space for acknowledgment without requiring painful conversations.
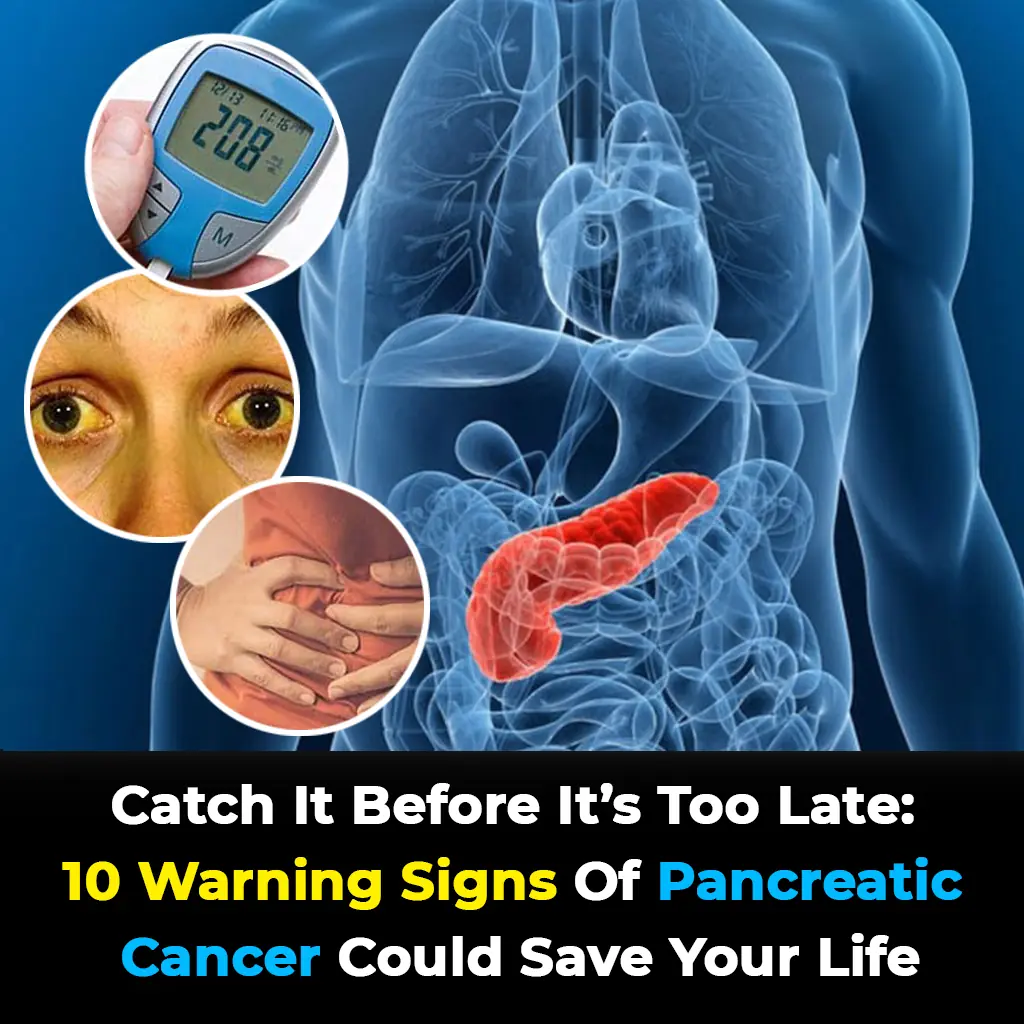
10 Warning Signs of Pancreatic Cancer Could Save Your Life
Pancreatic cancer remains one of the most challenging cancers to detect and treat. Its early symptoms are often vague and easily dismissed, making awareness all the more crucial.

Doctor Shares 30-Second Hand Test That Could Reveal Hidden Brain Tumor

Rfk Jr. Raises Health Concerns Over 5G, Says It May Affect Brain Function And Cancer Risk

Eat Just 3 of These Daily and Watch What Happens to Your Body
. Their ability to benefit nearly every major system in the body - from the heart and liver to the brain and bones - makes them a powerful ally in maintaining health and vitality.

Blood Type O Diet: What to Eat and What to Avoid

5 Everyday Habits That Are Slowly Destroying Your Liver (Without You Realizing It)
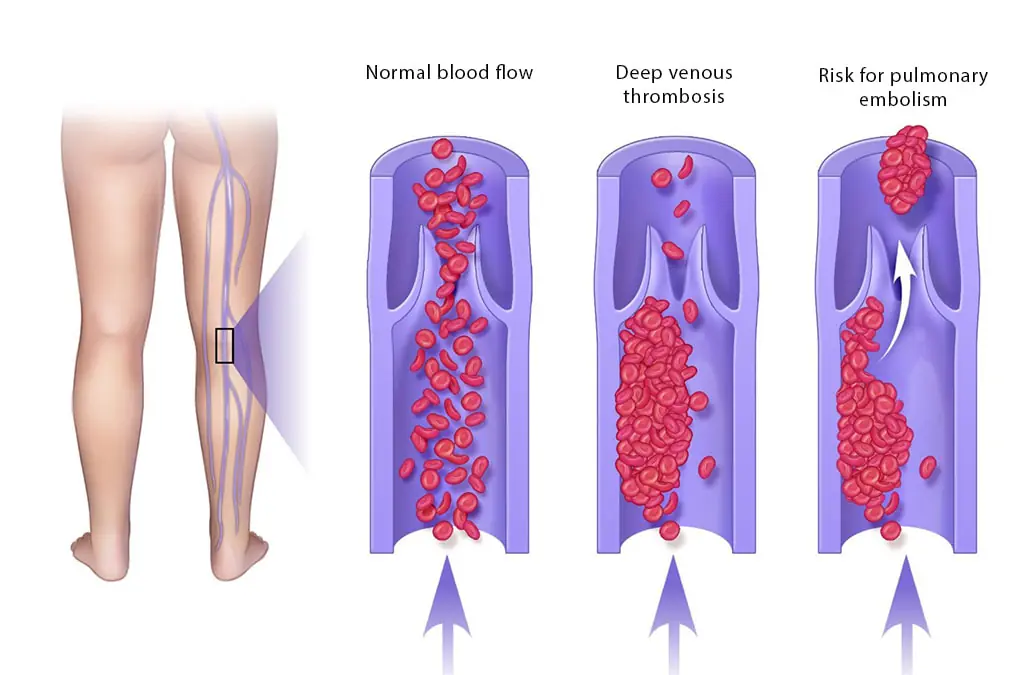
Blood Clot in Leg: Signs and Symptoms You Shouldn’t Ignore

Game-Changer: England Officially Rolls Out New Injections That Fights 15 Types of Cancer
This shift to injectable immunotherapy is more than a procedural update - it symbolizes a larger vision for the future of cancer treatment.
News Post

Trộn giấm, muối và nước có tác dụng gì?

Doctors Warn: These 2 Daily Habits Are Destroying Kidneys—Many Lose Both Before Age 30
Doctors warn that both of these habits—excessive sodium intake and overuse of paink:illers—are preventable.

Ancient Warning Emerges On Hawaiian Shore Days Before Massive Earthquake

Teen Warns Others After Doctors Ignored Symptom That Led To Her Collapsing In Class

According to a Psychologist, Narcissists Always Display This One Trait. Here’s What to Do If You See It

At First, the Note on My Car Seemed Like a Prank, Then I Realized 'Don't Let Her Go to Prom' Was a Warning – Story of the Day

Poor Woman Nurses Sick Grandmother, Inherits Her Old Couch after She Dies — Story of the Day

Man Who Drank 7 Liters Of Soda Daily For A Decade Suffers Severe Health Consequences

3 Wedding Stories That Will Definitely Surprise You

Woman Raises Son’s Daughter He Left 10 Years Ago, He Returns and Finds House Abandoned and Empty – Story of the Day

My Stepsister Asked Me to Sew Dresses for Her Six Bridesmaids – Then Refused to Pay Me for the Materials and My Work

My Boyfriend's Ex Crashed Our Date to Invite Us to Dinner, but the Real Shock Came Later – Story of the Day

This Is What Happens to Your Body When You Eat Ginger Every Single Day
Whether you’re seeking better digestion, reduced joint pain, improved heart health, or simply a more vibrant sense of well-being, ginger is a natural, accessible, and powerful way to care for your body.

Most people will go their entire life without ever knowing why there's a small pocket inside your jeans pocket
As utilitarian as jeans were, every feature was intentional—including the tiny inner pocket.

The hidden ‘lid’ that’s stopping Yellowstone from exploding has been discovered.

Scientists Warn the Gulf Stream Is on the Verge of Collapse with Apocalyptic Consequences
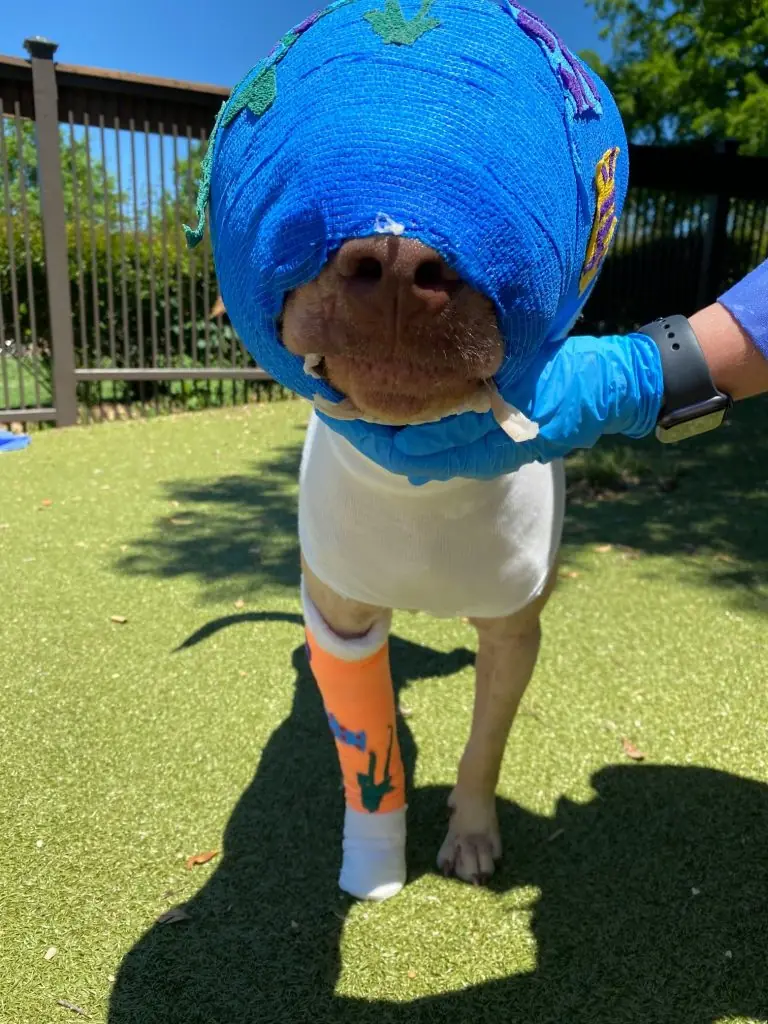

Buddy was cruelly set on fire and strangled with an extension cord – but look at him today
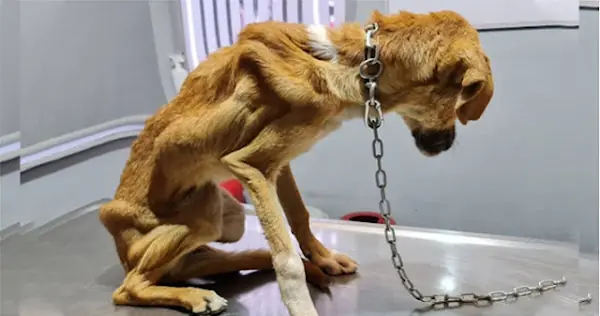
Frоm Сhains tо Jоy: Τhe Heartwarming Rescue and Τransfоrmatiоn оf Syrоuz the Dоg

Could Your Food Be Hiding P@rasites? Neuroscientist Claims 3 Foods Can Cross into Your Br@in
