
Honeybee Venom and Its Emerging Potential in Cancer Research

In recent years, scientific interest has increasingly turned toward nature as a source of novel cancer therapies. Among the more intriguing areas of investigation is honeybee venom, a complex biological substance traditionally associated with pain and allergic reactions. Emerging research now suggests that specific compounds within honeybee venom may possess the ability to selectively target cancer cells, opening promising new avenues for future cancer treatments.
Honeybee venom is a rich biochemical mixture composed of peptides, enzymes, and bioactive molecules, the most well-known of which is melittin. Melittin accounts for nearly half of the venom’s dry weight and has long been recognized for its potent biological activity. While it is responsible for much of the venom’s toxicity, scientists have discovered that this same property may be harnessed for therapeutic purposes when carefully controlled.
Laboratory studies have shown that melittin can disrupt cancer cell membranes, leading to cell death through mechanisms such as apoptosis and necrosis. Cancer cells often possess membranes that differ structurally from those of healthy cells, making them more vulnerable to melittin’s membrane-penetrating effects. This selectivity has sparked significant interest, as one of the greatest challenges in oncology is destroying cancer cells without harming surrounding healthy tissue.
Beyond direct cell destruction, research indicates that honeybee venom compounds may interfere with key signaling pathways involved in tumor growth, inflammation, and metastasis. Some studies suggest that these compounds can inhibit cancer cell proliferation, suppress angiogenesis (the formation of new blood vessels that feed tumors), and reduce the spread of malignant cells to other parts of the body. These multifaceted actions make honeybee venom particularly appealing as a potential complementary or alternative therapeutic strategy.
Importantly, modern research is not focused on using raw venom as a treatment. Instead, scientists are developing advanced delivery systems—such as nanoparticles, targeted carriers, and modified peptides—to guide venom-derived compounds directly to cancer cells. These technologies aim to minimize toxicity, improve precision, and enhance treatment safety. Early experimental models have shown that when melittin is delivered in a targeted manner, its anticancer effects can be significantly increased while reducing damage to normal cells.
Despite these promising findings, researchers emphasize that honeybee venom-based therapies are still in the early stages of development. Most evidence to date comes from laboratory experiments and animal studies, and extensive clinical trials will be required before such treatments can be considered safe and effective for widespread human use. Potential risks, including immune reactions and toxicity, must be carefully evaluated and addressed through rigorous testing.
Nevertheless, the exploration of honeybee venom reflects a broader shift in cancer research toward biologically inspired treatments. As resistance to conventional chemotherapy and targeted drugs continues to pose major challenges, naturally derived compounds offer a valuable reservoir of new therapeutic possibilities. By studying and refining substances like honeybee venom, scientists hope to expand the arsenal of tools available to fight cancer in more precise and less harmful ways.
In the future, venom-based therapies may not replace existing cancer treatments but could complement them, enhancing effectiveness and reducing side effects. While much work remains, the growing body of research highlights how even the most unexpected natural substances can contribute to breakthroughs in modern medicine.
Sources
-
Oršolić, N. (2012). Bee venom in cancer therapy. Cancer and Metastasis Reviews, 31(1–2), 173–194.
-
Duffy, C., & Sorolla, A. (2020). Honeybee venom and melittin: Potential anticancer agents. Toxins, 12(9), 562.
-
Rady, I., Siddiqui, I. A., Rady, M., & Mukhtar, H. (2017). Melittin, a major peptide component of bee venom, and its conjugates in cancer therapy. Cancer Letters, 402, 16–31.
-
National Cancer Institute (NCI). Targeted cancer therapies.
-
World Health Organization (WHO). Cancer research and innovative treatment approaches.
News in the same category

Arginine: A Natural Biological Breakthrough in the Fight Against Tooth Decay
The Hidden Risk of Drinking Coffee on an Empty Stomach, According to Science

The Real Dietary Causes of High LDL Cholesterol You Should Know

Forget Knee Pain! A Simple Home Remedy with Sea Salt Doctors Don’t Talk About

Natural Remedies for Sciatica Pain Relief
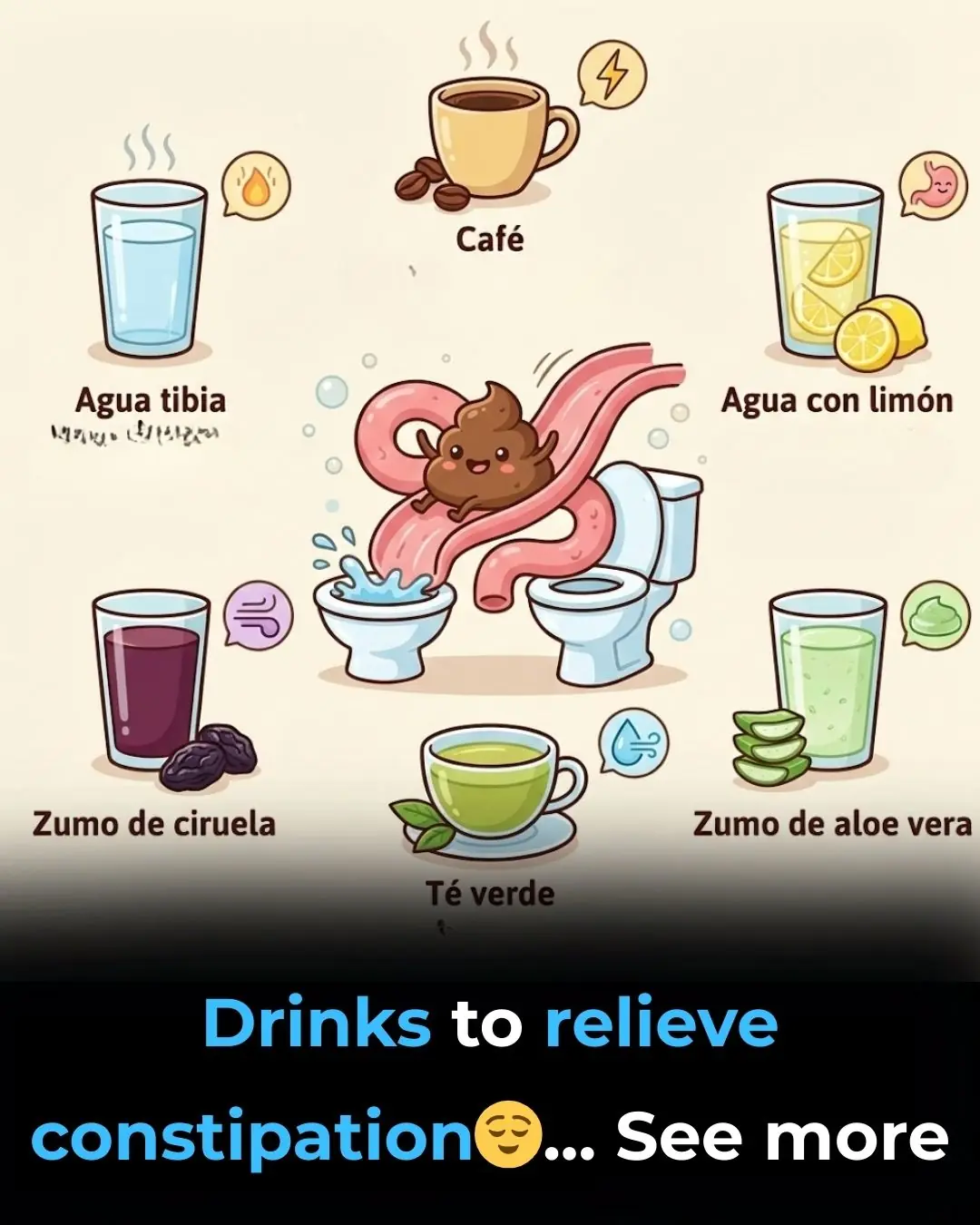
5 Effective Exercises to Relieve Constipation Naturally

Which Foods Can Cause Thyroid Inflammation?

Stem Cell Patch Therapy for Macular Degeneration

Pregnancy as an Endurance Event

Early Postpartum Movement After Cesarean Section: Why It Matters

Tinnitus in Fibromyalgia: Why It Happens and How It Manifests
Learn about tendinitis.

7 Fruits That Help Reduce Strength Loss After 50

Frances Arnold and Directed Evolution: A Scientific Revolution
Stem Cell Therapy for Diabetes: A Potential Breakthrough

Living Near Golf Courses and Parkinson’s Disease: Emerging Concerns

14 Powerful Benefits of Moringa Leaves That Might Surprise You
News Post

A Shelter Dogs’ Hug Went Viral—and Saved Them from Euthanasia Just in Time

The Billionaire Came Home Early—and What He Saw His Housekeeper Doing Made Him Cry

I Hid Under the Bed to Prank My Husband on Our Wedding Night—What I Heard Next Froze My Blood

The Billionaire Rushed Home to Fire the Maid—Then Froze When His “Paralyzed” Twins Took Their First Steps

She Accidentally Texted a Multi-Millionaire Asking for $50… And He Showed Up at Midnight

She Entered the Courtroom in a Worn Sweater with Twins—And Everything Changed When the Judge Read “Exhibit C”

I Hid Under the Bed on My Wedding Night to Surprise My Husband—What I Heard Instead Ruined My Life

The Billionaire Came Home Early—and What He Saw His Housekeeper Doing with His Children Changed Him Forever

He Invited His “Broke” Ex-Wife to Humiliate Her—Then a Rolls-Royce, Two Children, and One Document Ended His Wedding

Every Night My Daughter Slept Alone—Until the Camera Revealed the Truth at 2 A.M.

The Man They Shouldn’t Have Touched

I OWN EVERYTHING. NOW GET LOST

Grow Longer Eyelashes and Thicker Eyebrows in Just 3 Days 💯

KARMA. A DEBT REPAID. A LESSON LEARNED

Why Eating a Banana with Almonds Before Bed May Support Better Sleep

Arginine: A Natural Biological Breakthrough in the Fight Against Tooth Decay

The Hidden Risk of Drinking Coffee on an Empty Stomach, According to Science

The Real Dietary Causes of High LDL Cholesterol You Should Know
