How To Remove Gas From Stomach Instantly
To remove gas from your stomach quickly, you can try over-the-counter (OTC) medications, make simple dietary changes, and adjust how you eat. Eating more slowly and avoiding certain trigger foods may also help prevent gas from building up in the first place.
How Does Gas Feel?
Gas symptoms vary from person to person and depend on diet, digestion, and overall health. Common signs include:
-
Belching or burping: Releasing gas from the stomach through the mouth
-
Bloating: A feeling of fullness or visible swelling in the abdomen
-
Flatulence: Passing gas through the rectum
-
Pain or discomfort: Trapped gas in the digestive tract can cause pressure or cramping
In some cases, gas pain may feel sharp or similar to stomach cramps, especially when gas becomes trapped in the intestines.
Instant Remedies to Remove Gas From Your Stomach
Natural remedies are generally safe for most people, though their effectiveness can vary. It may take some trial and error to find what works best for your body.
Light Exercise or Physical Activity After Eating
A short 10–15 minute walk after meals can stimulate digestion and help gas move through the digestive system more easily. Gentle yoga poses may also reduce gas and improve symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), which often involves excess gas.
Abdominal Massage
Massaging the abdomen in a circular motion can promote bowel movement and relieve pressure from trapped gas. This technique may also help ease constipation-related bloating.
Hot Compresses
Applying a warm compress or heating pad to your abdomen can relax intestinal muscles and encourage gas release. Heat therapy can also reduce pain associated with bloating.
Dietary Changes
Certain herbs and spices may help reduce gas production and soothe digestion. These include dill, ginger, parsley, coriander, and fennel. Herbal teas such as ginger or chamomile tea may also calm the digestive tract and reduce bloating.
What Over-the-Counter Treatment Looks Like
Several OTC medications are available to relieve gas-related discomfort.
Simethicone
Simethicone works by breaking up gas bubbles in the stomach and intestines, making them easier to pass through burping or flatulence.
Common brands include Alka-Seltzer, Gas-X, and Gas-Aide.
Lactase
Lactase is an enzyme that helps digest lactose, the sugar found in dairy products. People with lactose intolerance do not produce enough lactase and may experience gas, bloating, and diarrhea after eating dairy.
Lactase supplements are sold under names like Lactaid and Dairy Ease.
Alpha-Galactosidase
Alpha-galactosidase is an enzyme that helps break down complex sugars found in beans, legumes, and certain vegetables.
Products such as Beano and BeanAssist can reduce gas by helping the body digest these sugars more efficiently.
Tips for Preventing Excess Gas
Preventive strategies can significantly reduce gas symptoms and related discomfort.
Swallow Less Air
We naturally swallow air while eating and drinking. To reduce excess air intake:
-
Avoid smoking
-
Do not eat while walking, standing, or talking
-
Eat slowly and chew thoroughly
-
Limit chewing gum, hard candy, and carbonated drinks
-
Ensure dentures fit properly if you wear them
Dietary Changes
Gas is mainly produced when bacteria in the large intestine break down carbohydrates. Certain foods are more likely to cause gas, including:
-
Cruciferous vegetables: broccoli, cauliflower, kale, cabbage, and collard greens
-
Gluten-containing foods: bread, pasta, cereals, and crackers
-
Lactose-containing foods: milk, cheese, yogurt, and ice cream
-
Fruits: apples, pears, peaches, and fruit juices
-
High-fat foods: fried foods, beef, pork, and foods high in butter or oil
-
Legumes: beans, peas, and lentils
-
Whole grains and high-fiber foods
Keeping a food diary may help identify which foods trigger your symptoms so you can limit or avoid them.
When to Seek Medical Care
Although gas is a normal part of digestion, certain symptoms should not be ignored. Sudden or severe changes in gas patterns, persistent bloating, or gas accompanied by weight loss, vomiting, or severe pain may signal an underlying condition.
Conditions linked to excessive gas include lactose intolerance, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), celiac disease, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), and other digestive disorders. If gas symptoms interfere with daily life or worsen over time, it is best to consult a healthcare provider for proper evaluation.
News in the same category

Six Oils That May Support Your Arteries and Circulation

Soak yellowed pillowcases in this mixture, and even the dirtiest ones will become bright and clean like new.

Tips for removing the unpleasant smell from pork.

When boiling shrimp, don't use onions or ginger to remove the fishy smell; just add a few of these seeds and the shrimp will turn bright red and have a rich, natural sweetness.

The secret to making delicious sweet spring rolls that remain crispy even after being frozen for several days.

Throw Watermelon Away Immediately If It Looks Like This

A Traditional Natural Compress for Joint and Tendon Comfort

Boiling sweet potatoes with this ingredient guarantees they'll be 100% soft and melt in your mouth.

Boiling sweet potatoes with this ingredient guarantees they'll be 100% soft and melt in your mouth.

Avoid Infections with Your Partner by Adopting This Simple Habit

4 surprising uses of egg boiling water.

Burn rosemary in your home and in 10 minutes you'll thank me for the results.

No strenuous scrubbing required; grease in your air fryer disappears on its own with just one simple trick.

Rice often gets infested with weevils after purchase; just insert this packet and the rice will remain fragrant, white, and delicious all year round without any worries.

Buying meat and immediately freezing it is a mistake: A shop owner shares a trick to keep meat from spoiling for "a whole year"

The Surprising Health Benefits of Coffee

Simple Ways to Slow Wrinkles and Keep Your Skin Glowing

Abdominal Pain: How to Identify the Cause by Location and When to Seek Medical Help
News Post

This carrot soup is like medicine for my stomach! Simple and delicious recipe!

Beets The Superfood That Actually Lives Up to the Hype

Signs and Symptoms of Thyroid Cancer

The Truth Behind White Skin Spots

Cinnamon and Vinegar: Potential Benefits, Risks, and What Science Says
Foods Commonly Linked to Parasitic Infections and How to Avoid the Risks

Why Sweet Potatoes Are One of the Healthiest Foods You Can Eat

One Teaspoon a Day: The Health Claims Behind Honey, Lemon, Garlic, Onion, and Ginger
Can One Food Rebuild Knee Cartilage in 24 Hours? Separating Fact from Hype

What Happens to Your Body When You Eat Broccoli Regularly
Avoid These Foods to Help Prevent and Relieve Arthritis Discomfort

How to Manage Joint Pain During Menopause: Effective Tips and Treatments
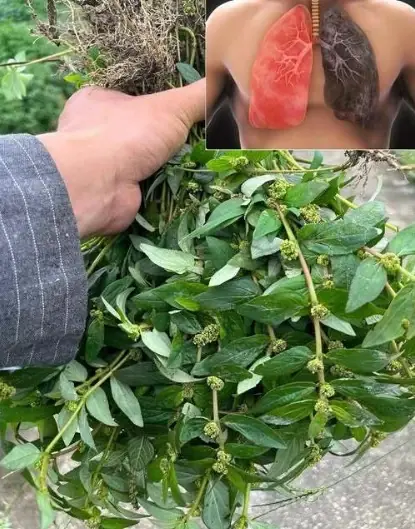

This “Weed” Could Be One of the Most Valuable Plants in Your Garden

Signs and Symptoms of Parkinson's Disease

Pain on the Right Side of the Body

Here's the ideal frequency for staying healthy.

Signs and Symptoms That May Indicate High Cholesterol Levels

10 Probiotic Foods to Improve Your Gut Health Naturally