
Why Sweet Potatoes Are One of the Healthiest Foods You Can Eat
7 Scientifically Supported Health Benefits of Sweet Potatoes — Why You Should Eat More of Them
Sweet potatoes are more than just a delicious and naturally sweet root vegetable — they are also a nutrient-dense food with numerous health benefits supported by scientific research. Packed with vitamins, minerals, fiber, antioxidants, and complex carbohydrates, sweet potatoes offer a wide range of advantages for your body, from eye health to heart function. Below, we explore seven key health benefits backed by science, along with explanations of why they matter and how sweet potatoes can be incorporated into a balanced diet.
1. Rich in Antioxidants That Protect Your Cells
Sweet potatoes are loaded with antioxidants like beta-carotene (especially in orange-fleshed varieties) and anthocyanins (in purple sweet potatoes). These plant compounds help protect cells from damage caused by oxidative stress and free radicals, which are linked to chronic diseases such as heart disease and certain cancers. Antioxidants also play a role in slowing the aging process and supporting long-term health.
Studies show that varieties with deeper color — particularly purple sweet potatoes — may offer even stronger antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects due to their higher anthocyanin content.
2. Supports Eye Health With Vitamin A
One of the standout benefits of sweet potatoes comes from their abundance of beta-carotene, a precursor to vitamin A. Your body converts beta-carotene into vitamin A, which is essential for good vision, especially in low light, and for maintaining the health of your retina. A single serving of cooked sweet potato can provide well over your daily requirement for vitamin A.
Vitamin A also supports healthy skin and immune function, making sweet potatoes a smart choice for overall wellness.
3. Strengthens the Immune System
Sweet potatoes contain high amounts of vitamin C, vitamin A, and several key antioxidants, all of which help strengthen the immune system. Vitamin C supports white blood cell function and enhances the body’s ability to fight off infections, while vitamin A is critical for maintaining the integrity of skin and mucous membranes — the first line of defense against pathogens.
These nutrients work together to keep your immune system alert and responsive, especially during cold and flu seasons.
4. Improves Digestion and Gut Health
Sweet potatoes are a great source of both soluble and insoluble fiber. Fiber helps keep your digestive system running smoothly by preventing constipation, improving bowel regularity, and feeding beneficial gut bacteria. A healthier digestive tract is also linked to improved mood, better energy levels, and stronger immune responses.
The fiber content also supports a stable release of energy, which helps prevent blood sugar spikes after meals.
5. Helps Manage Blood Sugar Levels
Although sweet potatoes are naturally sweet, they have a lower glycemic index (GI) than many other starchy foods — especially when boiled or steamed instead of fried or overly baked. A lower GI means their carbohydrates are digested and absorbed more slowly, leading to more gradual rises in blood sugar levels. This makes sweet potatoes a suitable carbohydrate choice for individuals with diabetes or those aiming to manage blood glucose levels.
Pairing sweet potatoes with lean proteins and healthy fats can further stabilize blood sugar and improve metabolic responses.
6. Supports Heart Health
Sweet potatoes contribute to cardiovascular health in several ways. They are rich in potassium, a mineral that helps counterbalance sodium’s effects in the body, supporting healthy blood pressure levels. High potassium intake is associated with lower risk of hypertension and stroke.
Additionally, the fiber and antioxidant content of sweet potatoes can help lower “bad” LDL cholesterol levels, reducing overall cardiovascular strain and promoting better circulation.
7. May Reduce Inflammation in the Body
Chronic inflammation is linked to many modern health conditions, including diabetes, obesity, arthritis, and heart disease. Sweet potatoes contain bioactive compounds, including anthocyanins and other antioxidants, which research indicates may help reduce inflammatory responses in the body. Purple varieties are particularly rich in these anti-inflammatory compounds.
These nutrients help modulate inflammation and oxidative stress, offering potential protective effects beyond basic nutrition.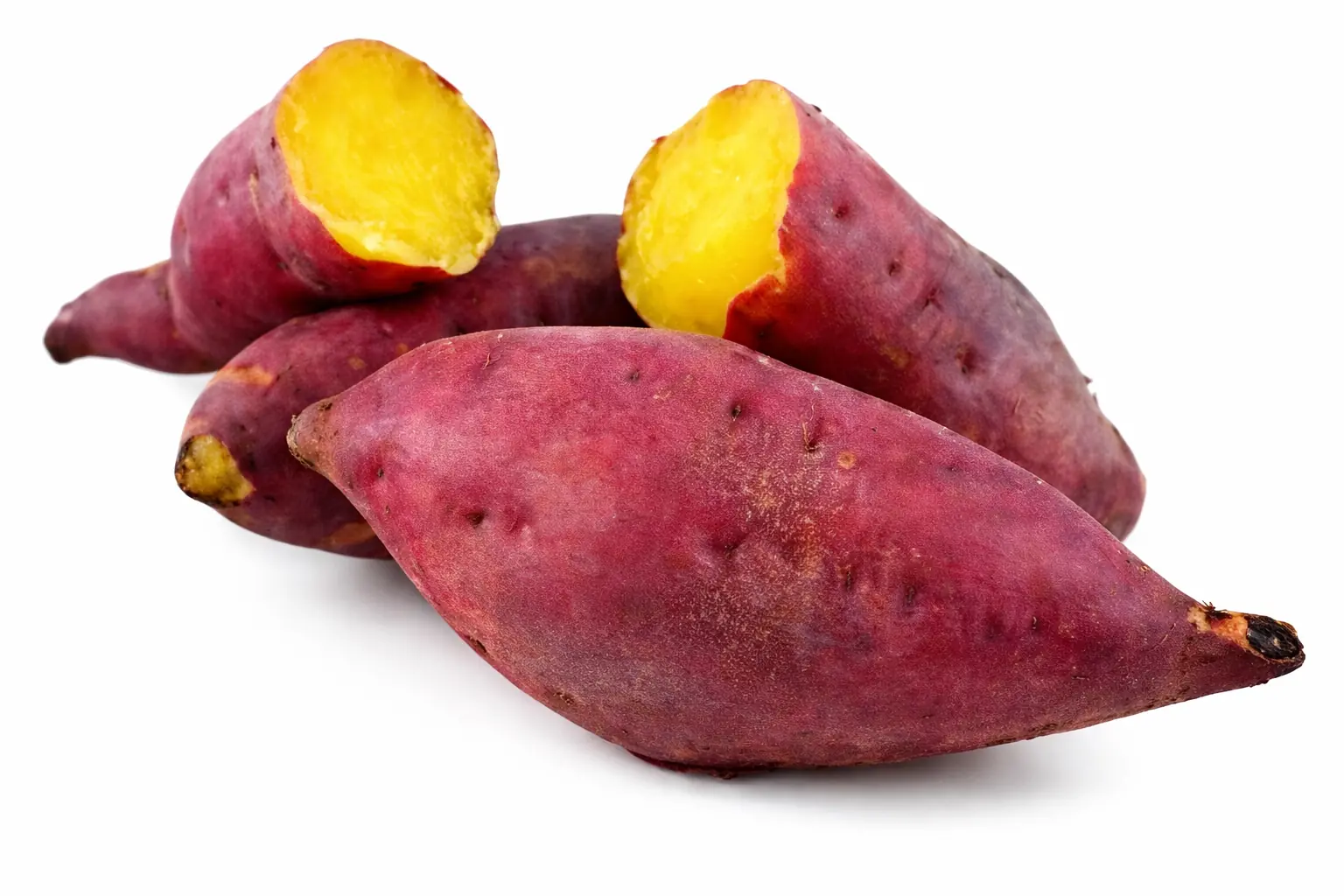
How Sweet Potatoes Fit Into a Healthy Diet
Sweet potatoes are versatile and can be prepared in numerous ways that preserve their nutritional integrity:
-
Boil or steam to retain more nutrients and maintain a lower glycemic index.
-
Bake with the skin on to maximize fiber and antioxidant content.
-
Mash or roast as a side dish or mix into soups and salads for extra texture and flavor.
Pair sweet potatoes with colorful vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats such as olive oil or nuts to create balanced meals.
Conclusion: A Nutrient Powerhouse You Can Enjoy Often
Sweet potatoes are more than just a comfort food — they are a healthy and nutrient-rich food option that provides multiple science-backed health benefits. From strengthening your immune system and protecting eye health to supporting heart function and gut health, these root vegetables deserve regular inclusion in your diet.
Whether you’re aiming for better overall health or managing specific concerns like blood sugar or digestion, sweet potatoes offer a delicious and effective way to nourish your body — one plate at a time.
News in the same category


Beets The Superfood That Actually Lives Up to the Hype

Signs and Symptoms of Thyroid Cancer

The Truth Behind White Skin Spots

Cinnamon and Vinegar: Potential Benefits, Risks, and What Science Says
Foods Commonly Linked to Parasitic Infections and How to Avoid the Risks

One Teaspoon a Day: The Health Claims Behind Honey, Lemon, Garlic, Onion, and Ginger
Can One Food Rebuild Knee Cartilage in 24 Hours? Separating Fact from Hype

What Happens to Your Body When You Eat Broccoli Regularly
Avoid These Foods to Help Prevent and Relieve Arthritis Discomfort

How to Manage Joint Pain During Menopause: Effective Tips and Treatments

This “Weed” Could Be One of the Most Valuable Plants in Your Garden

Signs and Symptoms of Parkinson's Disease

Pain on the Right Side of the Body

Here's the ideal frequency for staying healthy.

Signs and Symptoms That May Indicate High Cholesterol Levels
Why You Might Be Bruising So Easily
Garlic for Ear Infections: How to Relieve Ear Discomfort and Support Hearing Naturally

Benefits of Nettle (Urtica Dioica): 20 Health Problems You Can Treat Naturally
News Post

This carrot soup is like medicine for my stomach! Simple and delicious recipe!

Beets The Superfood That Actually Lives Up to the Hype

Signs and Symptoms of Thyroid Cancer

The Truth Behind White Skin Spots

Cinnamon and Vinegar: Potential Benefits, Risks, and What Science Says

Foods Commonly Linked to Parasitic Infections and How to Avoid the Risks

One Teaspoon a Day: The Health Claims Behind Honey, Lemon, Garlic, Onion, and Ginger

Can One Food Rebuild Knee Cartilage in 24 Hours? Separating Fact from Hype

What Happens to Your Body When You Eat Broccoli Regularly

Avoid These Foods to Help Prevent and Relieve Arthritis Discomfort

How to Manage Joint Pain During Menopause: Effective Tips and Treatments

This “Weed” Could Be One of the Most Valuable Plants in Your Garden

Signs and Symptoms of Parkinson's Disease

Pain on the Right Side of the Body

Here's the ideal frequency for staying healthy.

Signs and Symptoms That May Indicate High Cholesterol Levels

How To Remove Gas From Stomach Instantly

10 Probiotic Foods to Improve Your Gut Health Naturally
