If you suffer from arthritis pain and joint aches, here's what you should know
Arthritis is not just one single disease — it’s actually a broad term used to describe over 100 different conditions that affect the joints and surrounding tissues. The word “arthritis” literally means joint inflammation, but the experience goes far beyond just swelling or stiffness.
The most common forms include osteoarthritis (OA), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and psoriatic arthritis (PsA) — each with different causes, symptoms, and treatments.
-
Osteoarthritis (OA): Often called “wear-and-tear arthritis,” it occurs when the cartilage — the protective cushion between bones — breaks down over time. This leads to friction, pain, and stiffness, most often in the knees, hips, hands, and spine.
-
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): This is an autoimmune disorder, meaning the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own joint lining (synovium). The result is chronic inflammation that can damage cartilage and bone if untreated.
-
Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA): Linked with the skin condition psoriasis, PsA causes joint inflammation and can affect both small and large joints. It may also involve swelling of the fingers and toes (dactylitis) and nail changes.
Understanding which type of arthritis you have is key to effective management and treatment, as the underlying causes and approaches differ widely.
⚠️ Common Causes of Arthritis Pain
The cause of arthritis pain depends on the specific type of arthritis but usually involves inflammation, tissue damage, or structural changes in the joints.
-
In osteoarthritis, pain comes from cartilage loss and bones rubbing directly against each other.
-
In rheumatoid arthritis, inflammation in the joint lining leads to swelling, tenderness, and eventual joint deformity.
-
For psoriatic arthritis, both immune system dysfunction and genetic factors play a role.
Risk factors include:
-
Age: The risk increases as we get older.
-
Genetics: A family history of arthritis can make you more prone.
-
Obesity: Excess weight puts added stress on weight-bearing joints.
-
Injury: Past joint injuries can trigger early degeneration.
-
Lifestyle habits: Smoking, poor diet, and certain infections may worsen inflammation.
Environmental toxins and chronic stress have also been linked to increased inflammatory responses in the body, potentially aggravating arthritis symptoms.
🔍 Recognizing Symptoms and Getting Diagnosed
Arthritis symptoms often start subtly and progress over time. Common signs include:
-
Persistent joint pain or tenderness
-
Stiffness, especially in the morning or after rest
-
Swelling around one or more joints
-
A reduced range of motion or “grinding” sensation
-
Fatigue, fever, or general malaise (especially in autoimmune arthritis)
Because symptoms can mimic other conditions, diagnosis typically involves:
-
A medical history review and physical exam
-
Imaging tests (X-rays, MRI, ultrasound) to assess joint damage
-
Blood tests to detect inflammation or specific antibodies (like rheumatoid factor or anti-CCP for RA)
Early diagnosis is critical. The sooner arthritis is detected, the more effectively it can be treated, preventing long-term joint damage.
💊 Conventional Treatments for Arthritis
Traditional medical treatments aim to reduce pain, preserve joint function, and slow disease progression.
Common options include:
-
NSAIDs (Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs): Help control pain and inflammation.
-
Corticosteroids: Potent anti-inflammatories used short-term during flare-ups.
-
DMARDs (Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs): Slow the progression of autoimmune arthritis like RA or PsA.
-
Biologic therapies: Target specific parts of the immune system for more precise control of inflammation.
-
Physical and occupational therapy: Help maintain strength, flexibility, and proper movement patterns.
-
Surgery: In advanced cases, joint replacement or arthroscopic surgery may be recommended.
These treatments can be life-changing when combined with lifestyle improvements and complementary care.
🧘 Lifestyle Changes to Manage Arthritis Pain
Lifestyle plays a major role in how arthritis develops and progresses. Even small changes can make a big difference in daily comfort and long-term joint health.
-
Stay Active: Regular low-impact exercise like swimming, yoga, or walking strengthens muscles around joints, improving stability and reducing stiffness.
-
Maintain a Healthy Weight: Every extra pound adds up to four pounds of pressure on the knees. Losing even a small amount can reduce pain significantly.
-
Manage Stress: Stress increases inflammation. Relaxation techniques like deep breathing, meditation, or tai chi can lower stress hormones and ease pain.
-
Get Enough Rest: Joints need recovery time. Alternate activity with rest to prevent overexertion.
-
Avoid Smoking and Excess Alcohol: Both can worsen inflammation and interfere with healing.
Remember — consistency is more important than intensity. Small daily habits add up over time.
🌿 Top 10 Popular Home Remedies for Arthritis Pain
Natural remedies can provide meaningful relief when used safely and consistently. Here are ten of the most widely recognized options:
-
Hot and Cold Therapy: Heat soothes stiff joints; cold reduces swelling and inflammation.
-
Epsom Salt Baths: The magnesium in Epsom salts may ease muscle tension and joint discomfort.
-
Turmeric: Contains curcumin, a powerful anti-inflammatory compound backed by research.
-
Ginger: Works similarly to NSAIDs by blocking inflammatory compounds. Try ginger tea or capsules.
-
Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found in fish oil or flaxseed, omega-3s can reduce joint stiffness and pain.
-
Capsaicin Cream: Made from chili peppers, it temporarily blocks pain signals in nerves.
-
Acupuncture: This traditional therapy may help balance energy flow and reduce pain perception.
-
Massage Therapy: Boosts circulation, decreases stiffness, and promotes relaxation.
-
Glucosamine & Chondroitin: Supplements that may help protect cartilage and support joint repair.
-
Herbal Remedies: Boswellia (Indian frankincense) and willow bark are known for their anti-inflammatory properties.
🧴 How to Use Home Remedies Safely
Before trying new remedies or supplements:
-
Consult your healthcare provider, especially if you take medications.
-
Start small, observing for any allergic or digestive reactions.
-
Be consistent — natural remedies often take time to show results.
-
Choose high-quality products from trusted brands to ensure purity.
-
Track your symptoms to see what works best for you.
Combining natural methods with professional care usually yields the best outcomes.
🥗 Diet and Nutrition for Arthritis Relief
What you eat can either fuel or fight inflammation. A joint-friendly diet emphasizes anti-inflammatory and antioxidant-rich foods:
-
Eat more:
-
Fatty fish (salmon, sardines)
-
Leafy greens (kale, spinach)
-
Berries and citrus fruits
-
Nuts, seeds, and olive oil
-
Whole grains and legumes
-
-
Limit:
-
Processed foods and refined sugars
-
Red meat and fried foods
-
Trans fats and excessive dairy
-
Drinking plenty of water keeps joints lubricated, while herbal teas like green tea or ginger tea may provide extra anti-inflammatory support.
🏃 Exercises and Physical Therapy for Joint Health
Physical activity remains one of the most effective non-drug treatments for arthritis.
-
Low-impact exercises: Swimming, cycling, and walking protect joints while improving flexibility.
-
Strength training: Builds supportive muscles around affected joints, reducing strain.
-
Stretching: Keeps ligaments flexible and prevents stiffness.
-
Physical therapy: A therapist can tailor exercises to your needs, ensuring safety and effectiveness.
Start slowly and progress gradually — it’s about movement, not performance.
🩺 When to Seek Professional Help
You should see a doctor if you notice:
-
Persistent joint pain or swelling
-
Stiffness lasting more than 30 minutes in the morning
-
Redness, warmth, or visible joint deformity
-
Pain that interferes with sleep or daily tasks
If pain worsens despite home remedies or over-the-counter medication, or if you experience sudden, severe joint pain, seek medical evaluation promptly. Early treatment can prevent permanent damage.
🔬 Emerging Research and Future Directions
Arthritis research is advancing rapidly. Scientists are exploring:
-
Genetic and molecular triggers to personalize treatments
-
Biologic therapies that precisely target immune pathways
-
Stem cell and regenerative medicine for repairing cartilage
-
3D-printed implants and improved joint replacement materials
The future of arthritis care is moving toward personalized, regenerative, and less invasive therapies, giving hope to millions of people affected worldwide.
🌟 Final Thoughts
Arthritis can be challenging, but it’s not the end of an active life. With a mix of medical treatment, lifestyle changes, and natural support, you can reduce pain, protect your joints, and regain mobility.
Knowledge is power — the more you understand about your condition, the better equipped you are to manage it effectively. Start small, stay consistent, and celebrate every improvement along the way.
Your joints — and your future self — will thank you. 💪
News in the same category


The Ultimate Healing Tonic: A Powerful Natural Drink for Swollen Feet, Diabetes & Poor Circulation

Reverse diabetes and insulin resistance fast—4 hacks doctors don’t tell you!
4 powerful remedies to eliminate parasites—#2 will surprise you!
Top 7 peripheral neuropathy creams that actually STOP nerve pain fast!

The Real Health Benefits of Papaya Seeds: A Tiny Powerhouse Worth Trying

15 Things That Women Will Always Notice About A Man Over 50

Marathon Runner Diagnosed With Terminal Cancer Warns Against Ignoring Small Symptoms
PANCREATIC CANCER NEEDS CATCHING EARLY. THE SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS TO LOOK OUT FOR
Woman diagnosed with stage four colon cancer warns people about 5 symptoms she ignored

1 cup to protect the pancreas (and reduce blood sugar)

Eliminate Excess Water and Prevent Hand and Foot Swelling with These Effective Recipes

MARATHON RUNNER DIAGNOSED WITH TERMINAL CANCER URGES PEOPLE NOT TO DISMISS SMALL SYMPTOM HE EXPERIENCED

4 Powerful Foods That Naturally Boost Collagen and Repair Your Body from Within
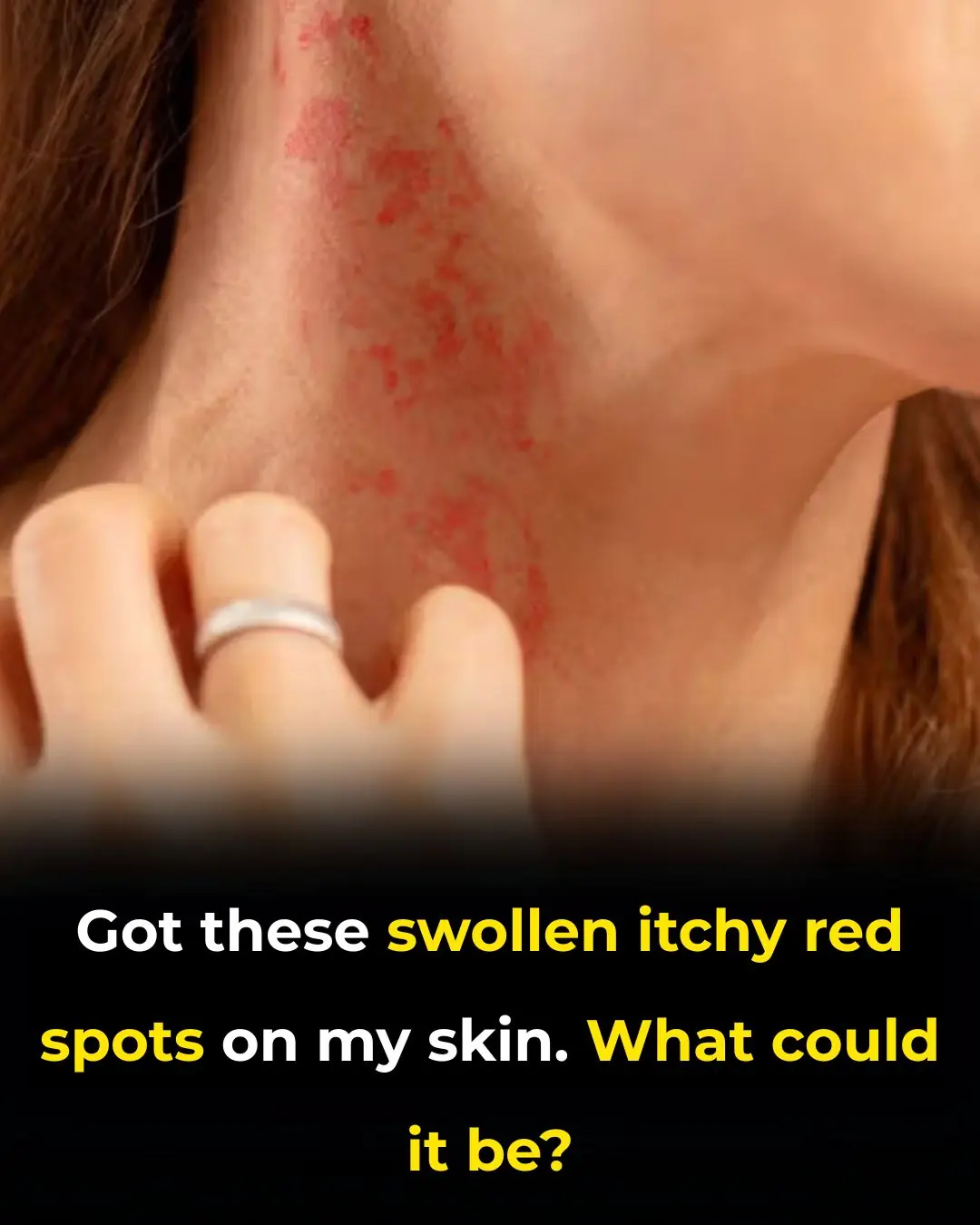
Ugh, these so annoying
1 Teaspoon in Your Morning Coffee Could Stop Insulin Resistance Within Minutes
7 silent signs your heart could be in trouble – don’t ignore these!

Thyme Essential Oil Shows Promise in Killing Lung, Oral, and Ovarian Cancer Cells
7 Warning Signs of a Heart Attack You Should Never Ignore
News Post

Rock Star’s Family Devastated As Common Symptom Leads To ER Visit And Aggressive Cancer Diagnosis

Tammy Slaton Shocks Fans With Stunning Weight Loss Photos—Inside Her Transformation

Doctors Feared Baby Had a Mouth Tumor—But the Real Cause Left Everyone Stunned

31-Year-Old Father Warns Others After Subtle Symptoms Lead to Colon Cancer Diagnosis

35-Year-Old Man Dubbed the “Modern Dorian Gray” Reveals His Unusual Secrets for Staying Youthful

7-Eleven Manager Allegedly Suffocates Employee During Shift—Victim Dies Days Later

Take This Before Bed — and Wake Up Transformed

The Ultimate Healing Tonic: A Powerful Natural Drink for Swollen Feet, Diabetes & Poor Circulation

Stop This Dangerous Habit Before Your Phone Explodes!

Women Who Age Quickly & Have Shorter Lifespans Often Do These 4 Things at Night — How Many Are You Guilty Of?

Eating Fish “for Ultimate Strength” — 30-Year-Old Woman Diagnosed with Premature Ovarian Failure, Body Full of Mercury

42-Year-Old Man Dies of Stroke Despite No Smoking or Alcohol — Doctor Warns: “How Dare You Eat This Every Day!”

“Doctor warns: 3 beauty habits you might think are harmless — but that could speed up cancer development!”

Boil Perilla Leaves with a Few Stalks of Lemongrass — Your Body Gets These 7 Excellent Benefits

Everyone Fears Diabetes — But Diabetes “Fears” These 5 Foods the Most

Objects That May Be Harming Your Health Without You Noticing

Drinking Plantain Leaf Tea: 5 Powerful Health Benefits for Your Body

Drink Roasted Black Bean and Ginger Tea for 7 Days — Your Body Will Thank You with 3 Amazing Benefits
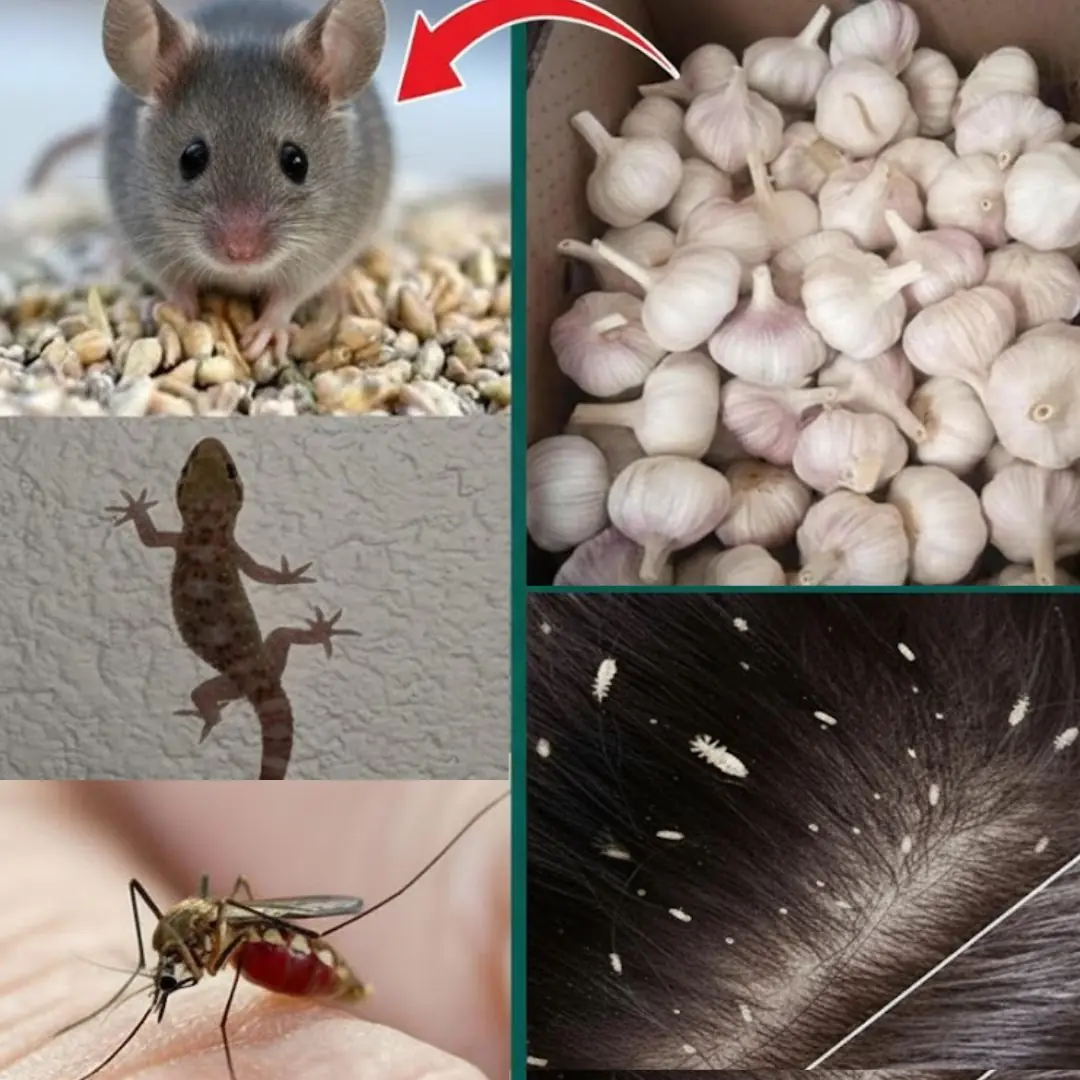

Garlic: The Natural Weapon Against Pests You Probably Forgot About
