
Lecanemab (Leqembi): A Breakthrough Treatment for Early Alzheimer’s That Targets the Disease at Its Source
Lecanemab (Leqembi): A Breakthrough Treatment for Early Alzheimer’s That Targets the Disease at Its Source
Lecanemab, marketed under the name Leqembi, made global headlines in 2023 when it became the first fully FDA-approved treatment proven to slow the progression of early Alzheimer’s disease. This major medical milestone applies to patients experiencing mild cognitive impairment (MCI) or mild dementia caused by Alzheimer’s. Unlike older treatments that simply manage symptoms, Lecanemab stands out because it targets the underlying biology of the disease, marking a major shift in how Alzheimer’s can be treated.
Alzheimer’s disease is driven in part by the buildup of amyloid-beta plaques, toxic protein clusters that disrupt brain cell communication and contribute to memory decline. According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and the Alzheimer’s Association, removing these plaques is a critical step in slowing the disease’s progression.

How Lecanemab Works: Targeting Toxic Amyloid-Beta Plaques
Clinical research published in the New England Journal of Medicine shows that Lecanemab is designed to bind and remove amyloid-beta plaques from the brain, reducing one of the key drivers of nerve cell damage. This mechanism directly addresses the biological cause of Alzheimer’s rather than simply masking symptoms, which is why the FDA classified it as a disease-modifying therapy.
In the large, global Clarity AD Phase 3 clinical trial, patients treated with Lecanemab showed:
-
Significant reduction of amyloid-beta plaques in brain imaging
-
Slower deterioration in memory and cognitive abilities
-
Better preservation of daily functioning and independence
These results offer new hope to families and patients facing early-stage Alzheimer’s.
Sources:
-
U.S. Food & Drug Administration (FDA)
-
National Institute on Aging (NIA), NIH
-
New England Journal of Medicine (Clarity AD Trial)
Benefits for Patients: Slowing Cognitive Decline Over 18 Months
Over an 18-month period, patients receiving Lecanemab demonstrated a notable slowdown in memory loss and cognitive decline compared to those given a placebo. This translates into meaningful real-world benefits, such as:
-
Maintaining communication skills longer
-
Retaining problem-solving abilities
-
Needing less assistance with daily tasks
-
Prolonging independence and overall quality of life
Even though the treatment does not stop or cure Alzheimer’s, these improvements can make a profound difference for patients and families navigating the early stages of the disease.
Global Medical Approval: A Milestone in Alzheimer’s Care
Following the FDA’s full approval, several countries—including the European Union, Japan, South Korea, and the United Arab Emirates—approved Lecanemab for early Alzheimer’s treatment. This worldwide acceptance underscores its status as one of the most promising and scientifically supported Alzheimer’s therapies to date.
Experts from leading organizations such as the Alzheimer’s Association, EMA, and Japan’s Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) describe the approval of Lecanemab as a historic turning point in neurology and brain-health innovation.
Not a Cure—But a Game-Changing Step Forward
Medical specialists emphasize that while Lecanemab is not a cure, it represents a transformational advancement. No previous therapy has shown such consistent evidence in targeting amyloid-beta plaques and slowing clinical decline.
Researchers continue to explore:
-
Next-generation immunotherapies
-
Neuroprotective treatments
-
Combination therapies to protect brain cells
-
Earlier detection of Alzheimer’s biomarkers
These scientific efforts aim to further reduce cognitive deterioration and improve long-term outcomes.
Conclusion: A New Era of Hope for Alzheimer’s Patients
Lecanemab (Leqembi) marks the beginning of a new chapter in Alzheimer’s treatment—one where the root cause of the disease can finally be confronted. For patients in the early stages, it offers extended independence, improved quality of life, and renewed hope for the future.
As research continues, the approval of Lecanemab stands as one of the most significant breakthroughs in modern neuroscience, signaling major progress toward more effective treatments for Alzheimer’s disease worldwide.
News in the same category


8 Mind-Bending Optical Illusions That Test Your Level of Self-Awareness

When Humor Meets Heritage: The Risks of Defacing Public Art

A Heartbreaking Act of Heroism: The Selfless Sacrifice of Matthew Daines

Physicists Find Evidence Of A Fifth Force Of Nature Hiding Inside Calcium Atoms

People Are Only Just Discovering What Really Happened To First Dog Sent To Space And It's Heartbreaking

Japan's Heated Benches: A Heartfelt Innovation for the Homeless

Greenland Shark: Earth's Longest-Living Vertebrate Gliding Through Four Centuries of History

Solar Impulse 2: The Plane That Circled the Globe Using Only Solar Power

Grounding: The Science, the Skepticism, and the Emerging Promise of Earth-Based Wellness

Here's how often should you wash your hair, according to a dermatologist

The Solar Flower: France’s Elegant Fusion of Art, Innovation, and Renewable Power

Kipekee: The World’s Only Spotless Giraffe and a Powerful Symbol for a Species in Decline
AI-Driven Cellular Reprogramming: South Korea’s Groundbreaking Step Toward Restorative Cancer Therapy

Live Music Therapy: A Gentle Breakthrough Transforming Dementia Care in NHS Wards

3 Colors You Should Never Wear to a Funeral—and What to Choose Instead

Microbiome-Based Therapeutic Foods: A New Hope in the Fight Against Childhood Malnutrition

5 Phrases That Reveal When a Man’s Heart Is Already Leaving
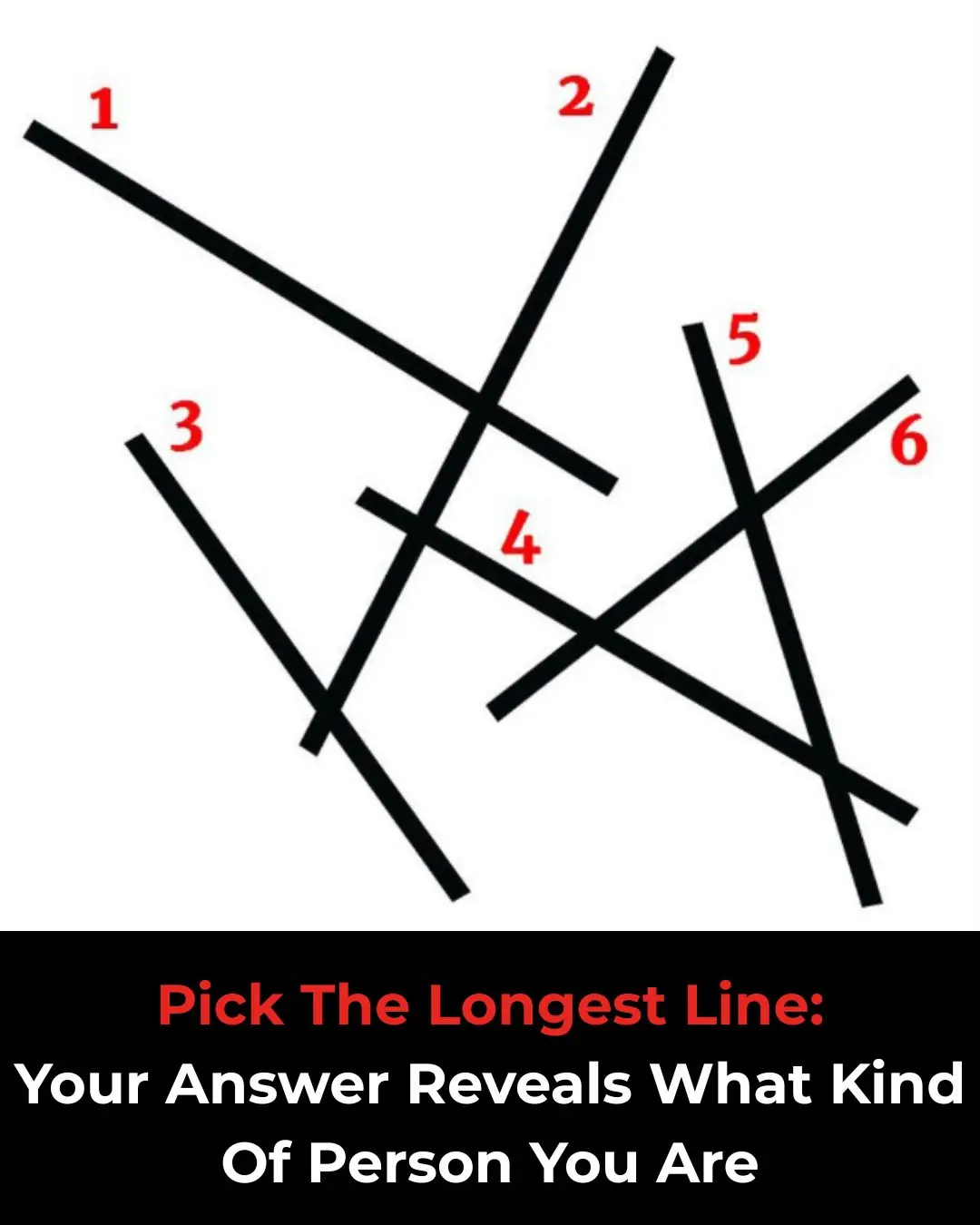
Choose the Longest Line

The Real Reason Public Toilet Seats Have That Weird Gap
News Post

10 Heartbreaking Reasons Children Stop Visiting Parents

8 Mind-Bending Optical Illusions That Test Your Level of Self-Awareness

Baking Soda and Castor Oil Can Treat More than 20 Health Problems
The one thing 98.7% of people do to lower blood pressure without medication

The 1-cup bedtime drink that stops you from waking up at 3 AM

Pokeweed (Phytolacca americana): Why You Should Keep Your Distance from These Toxic Plants
The Hidden Power of Common Lantana (Lantana camara): What You Can Safely Do with It at Home

11 Little-Known Secrets of Purslane: A Wonder Plant in Disguise

When Humor Meets Heritage: The Risks of Defacing Public Art

Never Clean Your Light Switches with Water! Here’s a Safe Trick to Make Them Spotless

Tips for Boiling Pork to Perfectly White, Odor-Free Meat

A Heartbreaking Act of Heroism: The Selfless Sacrifice of Matthew Daines

Tips to Restore White Clothes That Have Turned Yellow or Dull

Storing Meat by Freezing It Right After Buying Is a Mistake: A Butcher Shares a Method That Keeps Pork Fresh for Up to a Year

Don’t Just Water Your Chili Plants — Use This to Make Them Produce Heavily With Bigger, Healthier Fruits

10 signs you're not drinking enough water
You can gain up to 5 pounds of water weight per day. Here's how to shed the excess

🧼 Whoa, Had No Clue About This! 6 Safe & Smart Cleaning Hacks That Actually Work

Physicists Find Evidence Of A Fifth Force Of Nature Hiding Inside Calcium Atoms
