
More Than 300 Kidney Stones: A Startling Warning About Sugary Drinks and Dehydration
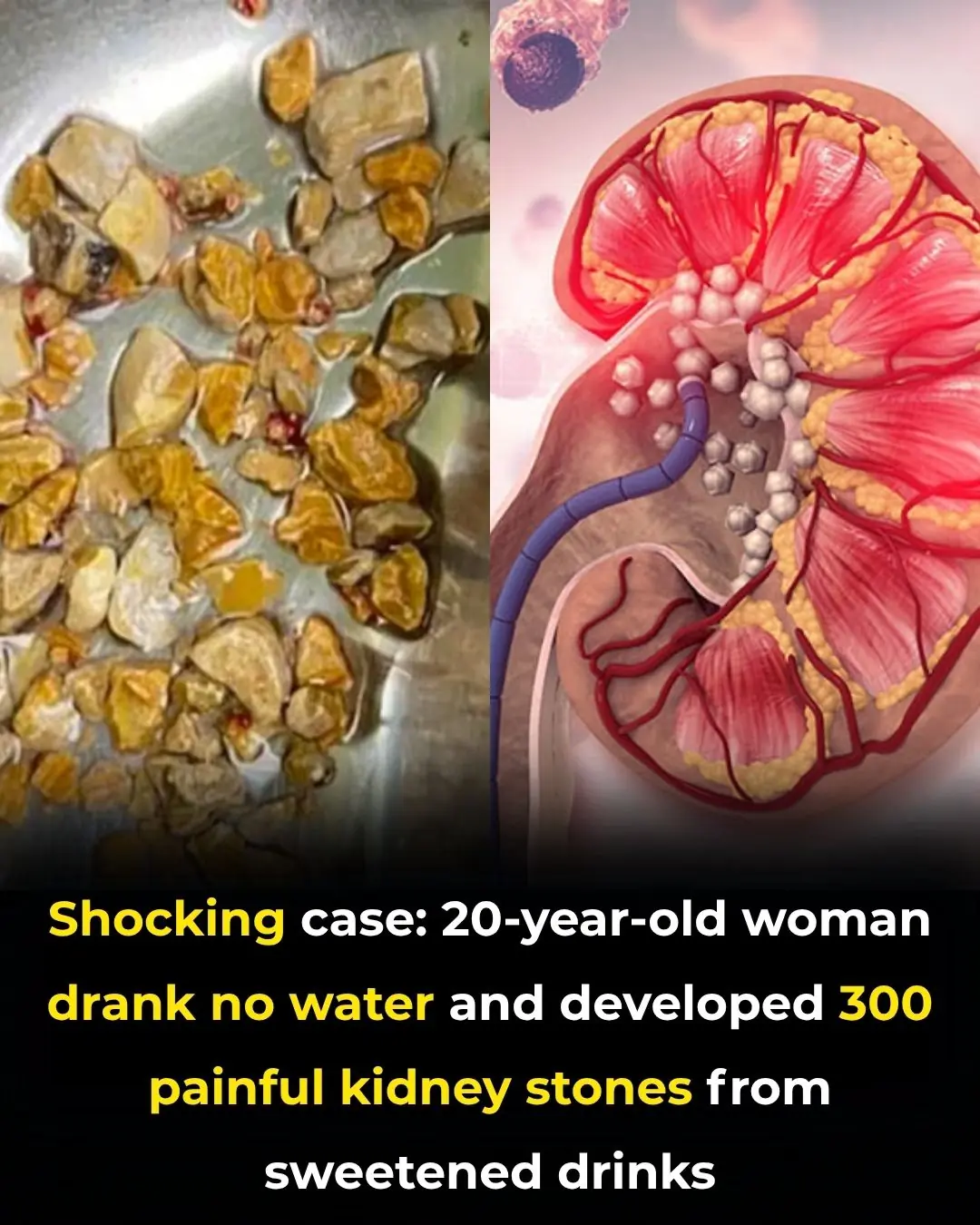
A Shocking Medical Case: Over 300 Kidney Stones Found in a Young Woman Who Avoided Water for Years
In a medical case that has stunned both doctors and the public, a 20-year-old woman was found to have more than 300 kidney stones after years of avoiding plain water and relying exclusively on sugary beverages for hydration. Her daily routine—filled with sodas, sweetened juices, and energy drinks—had finally pushed her body past its limit.
She arrived at the hospital in severe distress, reporting intense abdominal pain, persistent nausea, and increasing difficulty urinating. Imaging scans revealed a staggering number of stones scattered throughout her kidneys and urinary tract. According to her medical team, the underlying causes were clear: chronic dehydration and excessive consumption of high-sugar drinks, both of which can drastically alter the body’s mineral balance and promote stone formation.
Kidney stones develop when minerals such as calcium, oxalate, or uric acid become overly concentrated in the urine. Under normal circumstances, adequate water intake dilutes these substances and helps them pass harmlessly through the kidneys. But without water, these minerals crystallize, clump together, and harden—leading to excruciating pain, recurrent infections, and, if left untreated, permanent kidney damage.
Health authorities like the World Health Organization (WHO) and the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) emphasize that proper hydration is essential for maintaining kidney function and preventing stone formation.
Doctors had no choice but to perform emergency interventions to remove the stones and prevent further organ damage. Multiple procedures were required to clear the urinary tract, and the patient underwent close monitoring to stabilize her kidney function. Her medical team also delivered a critical warning: hydration is not optional—it is a fundamental requirement for survival.
This case serves as a powerful reminder, particularly for young people who frequently substitute water with sodas, bottled teas, flavored coffees, and energy drinks. Research from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and the Mayo Clinic shows that high sugar intake—especially from fructose-sweetened beverages—increases the risk of kidney stones by elevating urinary calcium and uric acid levels. Meanwhile, dehydration further concentrates these minerals, creating the perfect conditions for stones to form.
Your kidneys are remarkable organs, filtering nearly 150 liters of blood each day to remove toxins and regulate fluid balance. But they need clean, adequate hydration to do their job effectively. Neglecting water doesn’t just lead to discomfort—it can result in long-term, irreversible damage.
The message is simple but vital:
Your body doesn’t just need fluids; it needs water. Pure, uncomplicated, life-sustaining water. And no sugary drink in the world can replace it.
Trusted Sources:
-
World Health Organization — Hydration & Health Guidelines
-
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) — Kidney Health & Chronic Dehydration
-
National Institutes of Health (NIH) — Kidney Stone Research
-
Mayo Clinic — Causes and Prevention of Kidney Stones
-
National Kidney Foundation — Dietary Risk Factors for Kidney Stones
News in the same category


14 Warning Signs of Low Magnesium Levels and What to Do About It (Science Based)
Top 10 Foods to Heal Knee Pain and Boost Cartilage Naturally

Blood Type O Diet: What to Eat and What to Avoid
7 nutrients that actually repair nerves

This one vitamin could help stop you from waking up to pee every night

The Cold Room Sleep Trick That Can Transform Your Health

Why You Keep Waking Up at Night

Research reveals the #1 vitamin for eye protection
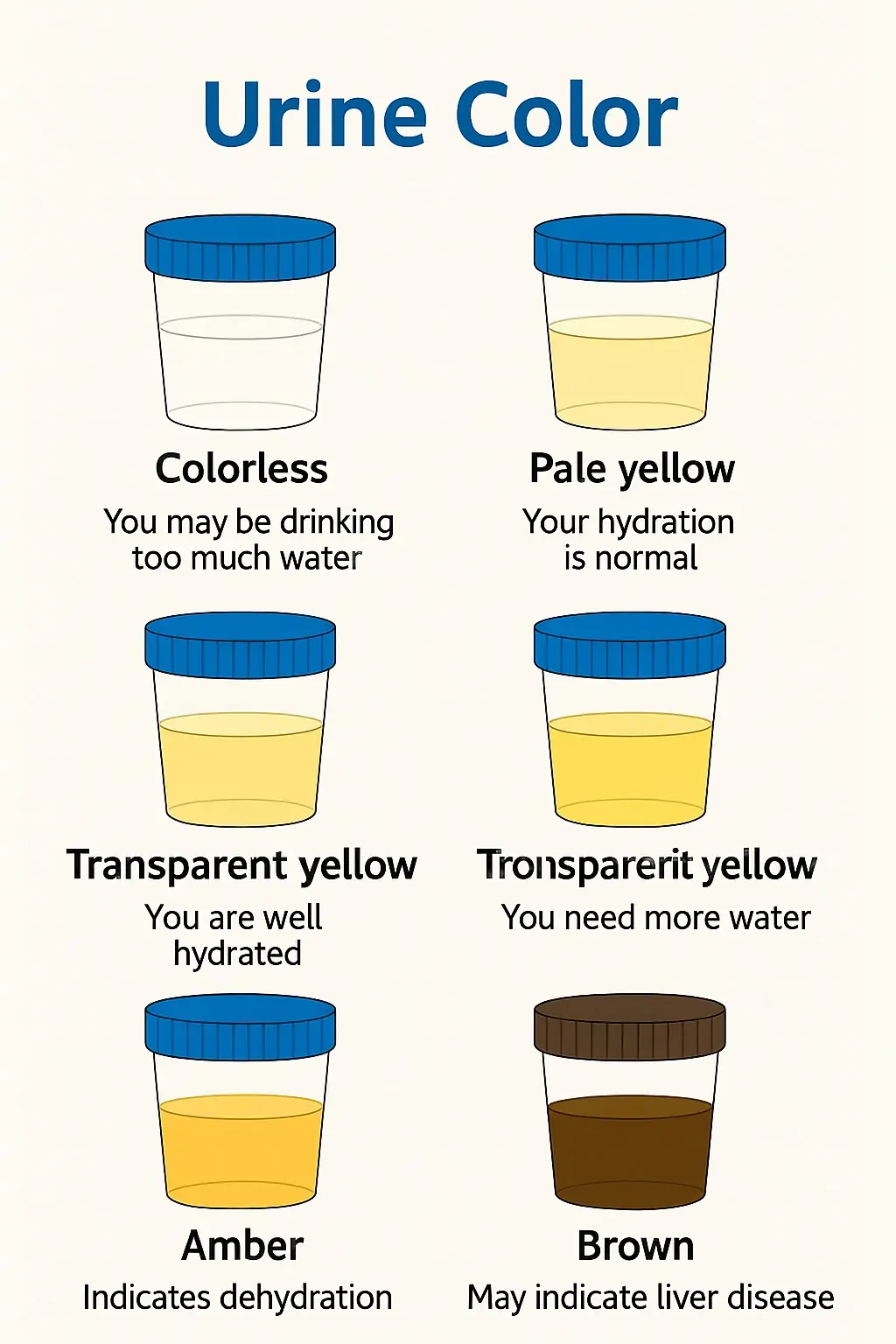
What Your Urine Color May Be Telling You (Gently & Naturally)

Soothe Leg Pain Naturally: Garlic & Clove Remedy for Joints, Circulation, and Comfort
Eat Garlic — But Avoid This Common Mistake! | 95% of People Don’t Know This Simple Trick
Home Remedies For Kidney Stones – 21 Remedies For Effective Pain Relief
Eat One Clove of Garlic Every Morning on an Empty Stomach – and Watch These 12 Health Benefits Unfold!

Never do this when flying; many people have ruined their lives because they didn’t know better

Public Health Experts Stress Vaccination as Key to Preventing Severe and Long COVID
People who are about to be affected by cancer often show three unusual signs in the neck; even having just one of them can be a warning for your health
4 vitamins to reverse neuropathy and damaged nerves – relieve foot & hand pain fast!

8 Amazing Foods To Clean Out Your Toxic Liver
Stem Cell Breakthrough Offers New Hope for Reversing Diabetes in Early Human Trials
News Post

How I Exp0sed My Husband’s Li es: A Cheating Anniversary He'll Never Forget

THE CAT THAT BR0KE ALL THE RULES: A POLICE OFFICER'S UNEXPECTED MISSION

Mullein: Exploring the Benefits of Leaves, Flowers, and Roots

Airport X-Ray Scanners Upgrade: Shocking Level of Details

From White Hair to Naturally Darker Hair: Fast Home Remedies & Growth Tips

Teen told he just had ‘growing pains’ dies day after diagnosis

7 Ways To Use Vaseline For Wrinkle Free, Flawless Skin

EVERYTHING JAMES FRANCO SAID ABOUT BEING ‘CAST OUT’ FROM HOLLYWOOD DURING HIATUS

The #1 seed that makes bones & muscles strong—how to use it!

14 Warning Signs of Low Magnesium Levels and What to Do About It (Science Based)

Strictly Come Dancing star eliminated from competition on their birthday

Top 10 Foods to Heal Knee Pain and Boost Cartilage Naturally

Blood Type O Diet: What to Eat and What to Avoid

7 nutrients that actually repair nerves

Coronation Street's Lucy Fallon shows off huge ring as she announces engagement

MAFS UK’s ‘strongest’ couple split after romantic display at reunion

The Versatility and Benefits of Orange Peel Powder

The Hidden Power of the Honey Locust Tree (Gleditsia triacanthos): Health, Healing, and Everyday Uses

This one vitamin could help stop you from waking up to pee every night
