
The Vegetable Known as a “Natural Calcium Pill”: Containing Three Times More Calcium Than Milk and Seven Times More Than Eggs

Carrot leaves are not only a nutritious vegetable but are also considered a true “natural calcium pill” in the plant world. The calcium content in carrot leaves is remarkably high—up to three times that of milk and seven times that of eggs. Specifically, 100 grams of carrot leaves contain approximately 394 mg of calcium, compared to 125 mg in milk and 55 mg in chicken eggs.
In addition to being rich in calcium, carrot leaves are an excellent source of vitamins, particularly vitamin A and carotene, which help protect eye health and improve vision. Consuming carrot leaves not only supports bone strength but also provides essential nutrients for maintaining good eyesight.
Carrot leaves have a pleasant aroma and can be prepared in a variety of dishes, such as steamed vegetables, stir-fried dishes with meat, or even savory cakes. Including carrot leaves in daily meals is a simple way to enhance both bone and eye health.
Suggested Dish: Steamed Carrot Leaves
Step 1: Cut the leaves from the carrot roots and rinse them thoroughly several times under running water to remove any dirt.
Step 2: Drain the leaves well, then mix them with one tablespoon of cooking oil to retain moisture.
Step 3: Add one tablespoon of flour to the leaves and mix evenly.
Step 4: Steam the carrot leaves in boiling water for about five minutes.
Step 5: Prepare a sauce by finely chopping garlic and chili, then mixing them with light soy sauce, sesame oil, salt, and sugar to taste.
Step 6: Place the steamed carrot leaves on a plate, drizzle with the sauce, and serve.
Another Calcium-Rich Vegetable: Malabar Spinach
Besides carrot leaves, Malabar spinach is also a highly nutritious vegetable. It contains a wide range of beneficial compounds, including vitamins, dietary fiber, glucans, mucopolysaccharides, β-carotene, and organic acids. Consuming Malabar spinach during the summer can help cool the body, relieve heat, support digestion, and reduce blood pressure.
Malabar spinach is particularly notable for its high calcium content, providing approximately 166 mg of calcium per 100 grams, which is about three times higher than that of regular spinach.
Moreover, Malabar spinach contains low levels of oxalic acid, making it suitable for all age groups—especially the elderly and children. It supports calcium absorption and promotes healthy digestion.
A simple dish such as stir-fried Malabar spinach with garlic is not only flavorful but also beneficial for digestive health, making it especially suitable for middle-aged and older adults.
News in the same category


Cocklebur Uncovered: The Surprising Healing Potential of Xanthium Strumarium

The Secret Lemon and Nopal Drink That Can Transform Your Wellness Routine
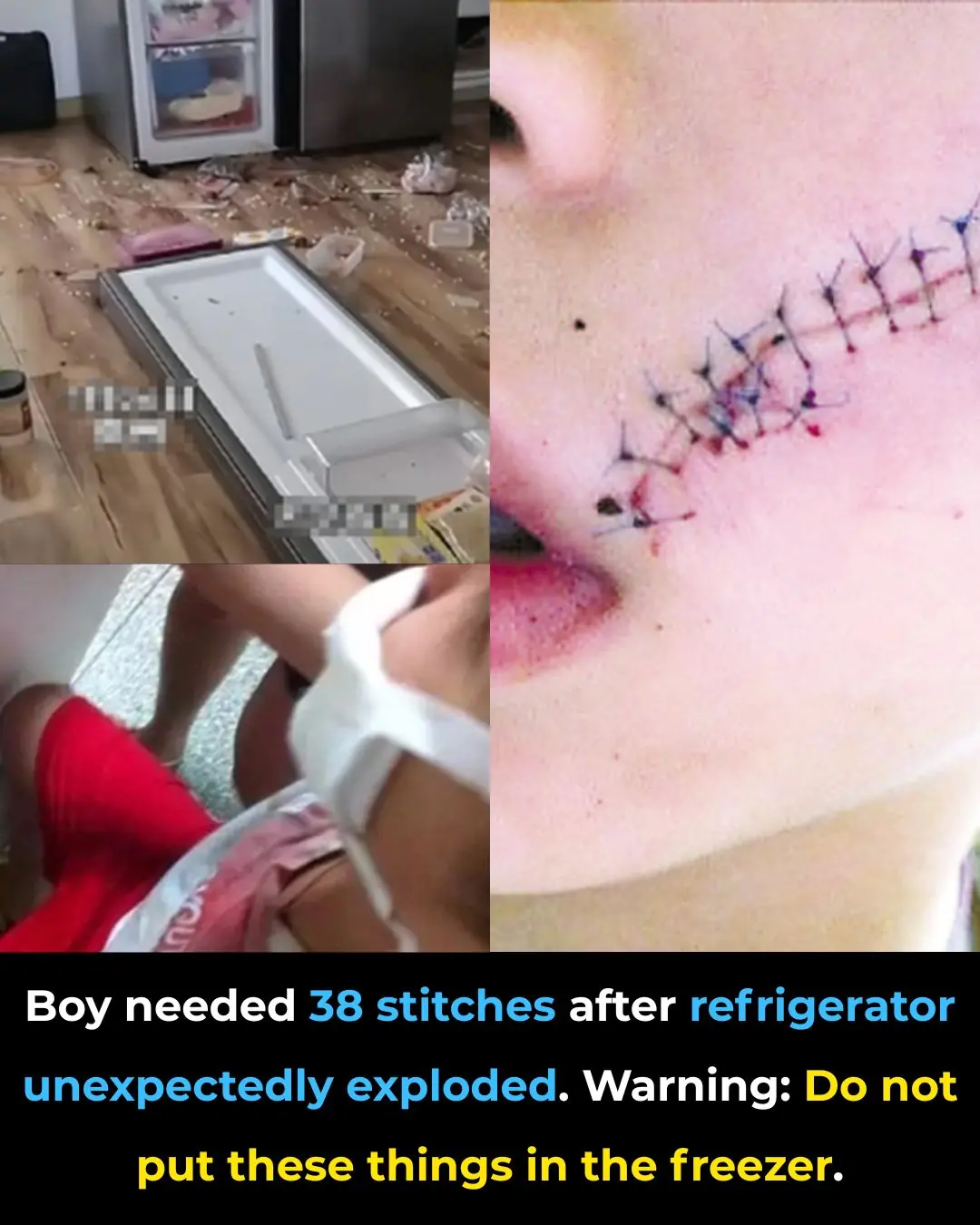
Boy Receives 38 Stitches After Refrigerator Explosion: Warning Against Storing These Items in the Freezer

Check This Spot on a Crab’s Shell to Ensure Sweet, Meaty Flesh Every Time

Want to Cut Back on Starches Without Feeling Hungry? Add These 6 Nutritious Vegetables to Your Diet

Natural Energy Booster: Ginger and Tomato for All-Day Vitality

The Nightly Choice That Could Protect or Endanger Your Brain
What Really Happens to Your Liver During Dry January

15 autoimmune warning signs your doctor keeps dismissing as stress or aging

Why You Keep Waking Up With a Dry Mouth

🌿 What Rosemary Can Actually Do
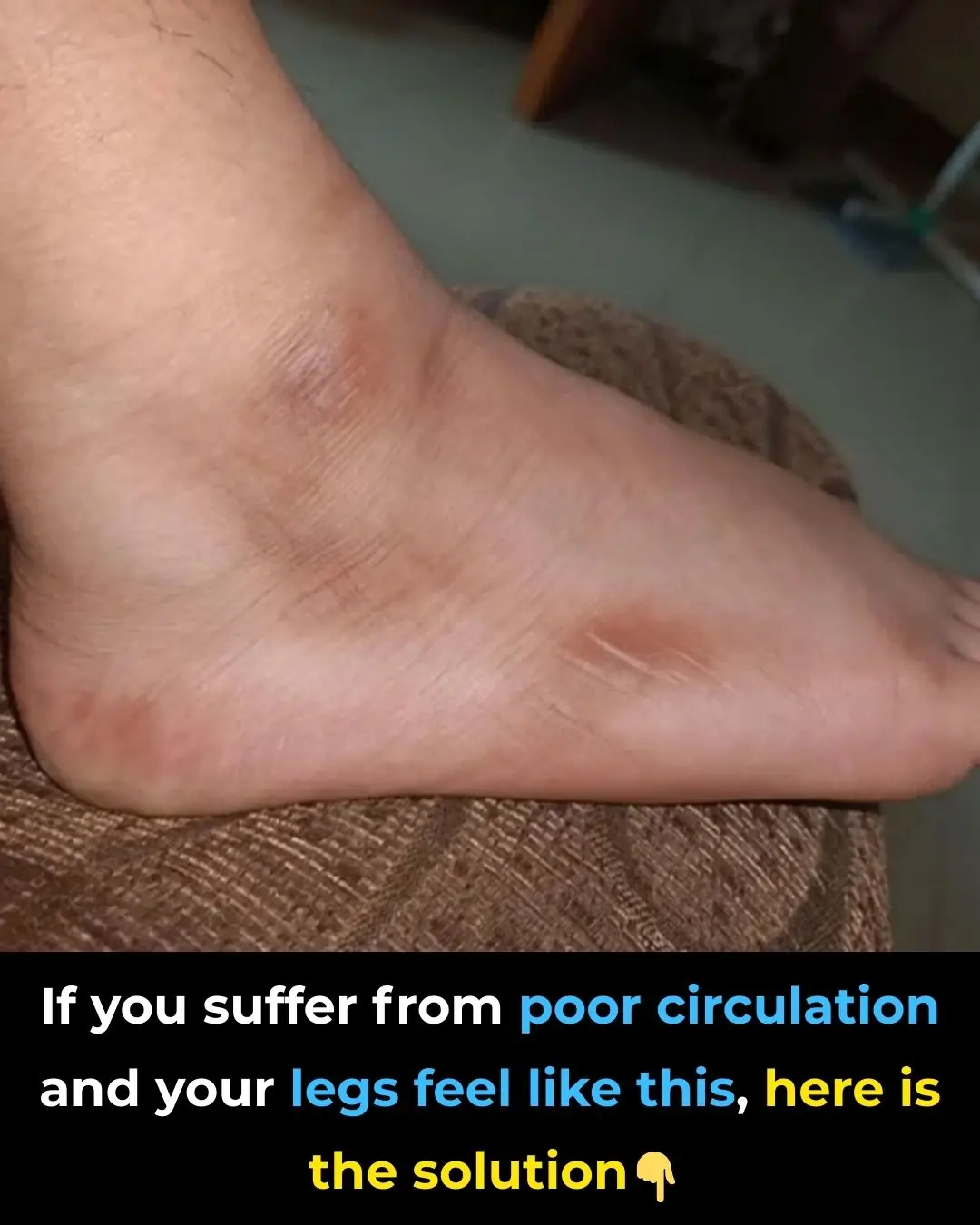
🩺 If Your Legs Feel Heavy, Cold, or Tingly—Here’s What It Means (And How to Improve Circulation Naturally)

What Does an Itchy Left Hand Mean

Four Types of Vegetables That Cancer Cells “Fear”: Doctors Recommend Eating Them Regularly for Better Health

The Biggest “Invisible Killers” in the Kitchen: These Three Things Can Be More Harmful Than Dirty Cooking Oil — Keep Them Away From the Elderly and Children

How to Identify Fish Contaminated with Urea: No Matter How Cheap, Don’t Buy It

Fig Leaves: A Valuable Medicinal Plant in the Home Garden
The Top 5 Viruses and Bacteria Linked to Cancer Today
News Post

He Took His Mistress to a Candlelit Dinner. I Brought Her Husband.

He Arrived With His Lover. The Judge Ruled Everything Belonged to Her

My Husband Left Me in the Snow for Being Infertile. A Widowed CEO Found Me That Night.

Six Weeks After I Gave Birth to Triplets, My CEO Husband Served Me Divorce Papers — Then Introduced His 22-Year-Old Mistress

My Husband Filed for Divorce — Then Our Daughter Played a Video That Changed Everything

Restoring Brain Energy Reverses Advanced Alzheimer’s Pathology in Preclinical Models

Too Many Ripe Tomatoes to Eat? Try These 5 Simple Ways to Preserve Them All Year Round—No Grocery Costs Needed

The Natural Remedy Everyone Aged 30–75 Should Try

Cocklebur Uncovered: The Surprising Healing Potential of Xanthium Strumarium

The Secret Lemon and Nopal Drink That Can Transform Your Wellness Routine

Simple and Effective Ways to Clean Your Phone Speaker at Home

Boy Receives 38 Stitches After Refrigerator Explosion: Warning Against Storing These Items in the Freezer

Check This Spot on a Crab’s Shell to Ensure Sweet, Meaty Flesh Every Time

Want to Cut Back on Starches Without Feeling Hungry? Add These 6 Nutritious Vegetables to Your Diet

Effective Natural Ways to Control Slugs in Home Vegetable Gardens

Natural Energy Booster: Ginger and Tomato for All-Day Vitality

Most do this wrong. Here’s how often to actually vacuum

Browns' Shedeur Sanders debuts after Dillon Gabriel concussion
