
The Top 5 Viruses and Bacteria Linked to Cancer Today
Many cancers associated with viral or bacterial infections may take years to develop symptoms, making early detection difficult. Below are five viruses and bacteria that are currently considered major contributors to cancer risk worldwide.
1. Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) – Stomach Cancer
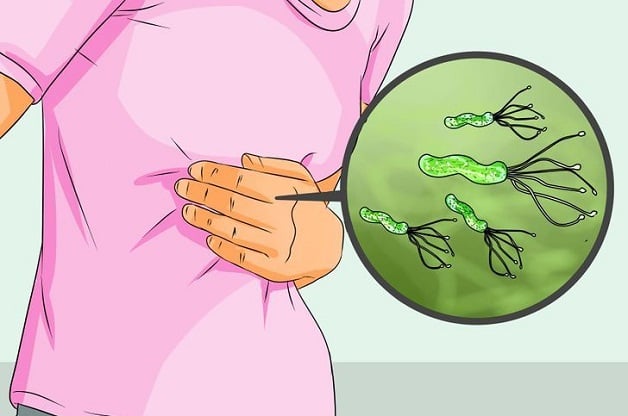
Helicobacter pylori is a bacterium that can survive in the highly acidic environment of the stomach. It is a major cause of chronic gastritis, gastric ulcers, and is strongly associated with stomach cancer.
Medical experts emphasize that persistent H. pylori infection significantly increases the risk of gastric cancer. People infected with this bacterium are advised to undergo regular health check-ups, including testing for H. pylori and endoscopic examinations, to detect abnormalities in the stomach at an early stage.
2. Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) and Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) – Liver Cancer
Liver cancer is one of the most common cancers in Vietnam and many other countries. The leading causes are chronic infections with Hepatitis B virus (HBV) and Hepatitis C virus (HCV).
Long-term hepatitis infection can lead to liver inflammation, cirrhosis, and eventually liver cancer. Early screening, monitoring, and appropriate treatment of hepatitis infections are crucial to reducing cancer risk.
3. Human Papillomavirus (HPV) – Cervical Cancer
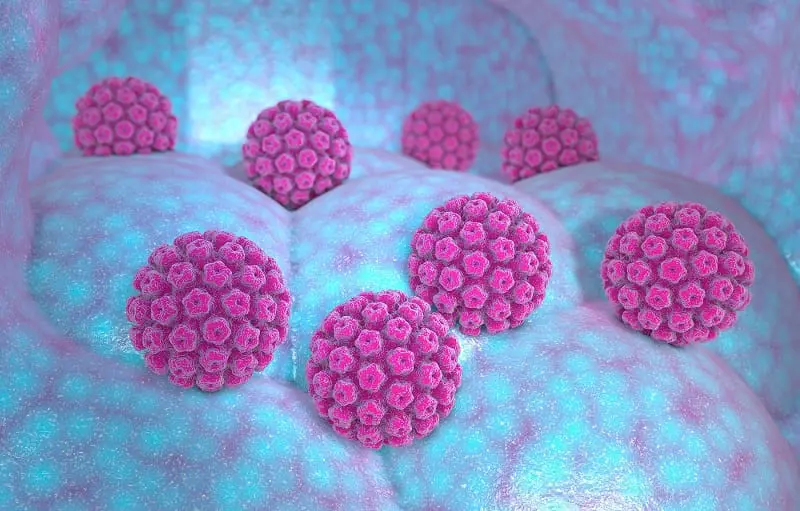
Human Papillomavirus (HPV) is a large group of related viruses, each identified by a specific type number. Certain high-risk HPV types are known to cause cancer, most notably cervical cancer in women.
HPV infection is very common and often asymptomatic, but persistent infection with high-risk strains can lead to the development of cancer over time. Regular screening and vaccination play a key role in prevention.
4. Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV) – Nasopharyngeal Cancer
Numerous studies have demonstrated a strong association between Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV) and nasopharyngeal cancer. Elevated levels of EBV antibodies are commonly found in patients with undifferentiated nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
EBV is transmitted through bodily fluids, particularly saliva, and can spread through close contact such as kissing, sharing food or drinks, and oral sexual contact. Because of this, illnesses caused by EBV are sometimes referred to as “the kissing disease.”
5. Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) – Immune-Related Cancers
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) weakens the immune system, reducing the body’s ability to fight infections and abnormal cell growth. HIV infection is associated with several cancers, including non-Hodgkin lymphoma, Hodgkin lymphoma, and Kaposi’s sarcoma.
HIV can also stimulate abnormal proliferation of certain immune cells, increasing the risk of genetic mutations that may lead to cancer. Practicing safe sex and preventive measures are essential to reduce the risk of HIV transmission.
News in the same category


Fig Leaves: A Valuable Medicinal Plant in the Home Garden

4 Foods People Swear Prevent Hangovers—What Science Says

Signs and Symptoms of Influenza (Flu)
Are You Up to Date on Migraine Prevention?

Radiation and Targeted Cancer Therapy Combination Shows Low Risk of Serious Side Effects

Can Metformin Protect Premature Infants After Antenatal Steroid Exposure?
Vaccines and Healthy Aging: Benefits That Go Beyond Infection Prevention

Drink Coconut Water for 7 Consecutive Days and Notice Remarkable Health Benefits

11 Fruits Rich in Iron That Help Improve Blood Health Naturally
Beyond Stroke, This Dangerous Disease Surges During Cold Weather

Why Do Older People Often Have More Age Spots on Their Skin?

Surprise Finding: How the Immune System May Prevent Us From Burning Fat

What Role Do Methanogens Play in the Gut Microbiome?

The Best Times to Drink Coffee for Optimal Health Benefits

The Best Time to Drink Pomegranate Juice for Blood Pressure and Muscle Recovery

Why Your Cat Chooses to Sleep With You

10 Conditions Ginger Can Help Manage Naturally

How Often Do You Poop? New Research Shows Bowel Movement Frequency Linked to Overall Health
News Post

Fatal Mountain Lion Attack in Colorado Prompts Trail Closures and Public Safety Warnings

Honoring Sourabh Raaj Jain: The Actor Who Brought Lord Krishna to Life 🌸✨🙏

Kate Winslet: Redefining Human Limits 🌊🏆✨

Vidushi Deeksha V Creates History with Bharatanatyam ✨🏆💃

Salai Arun: The Farmer Who Traveled 80,000 KM to Save India’s Seeds 🌾🇮🇳

India’s Latest Internet Crush: A German Woman in a Saree 🌍🇮🇳💫

Back From the Brink: The Blue Macaws That Inspired Rio Return to the Wild After 20 Years

Flying Hope After Dark: How a Restaurant Owner Uses Drones to Reunite Lost Pets with Their Families

France Bans the Use of Wild Animals in Circuses, Marking a Turning Point for Animal Welfare

After 80 Years of Suffering, a Rescued Elephant Lies Down for the First Time

How to Soften Rock-Hard Frozen Meat in Just Minutes for Easy Cooking

How to Identify Fish Contaminated with Urea: No Matter How Cheap, Don’t Buy It

Fig Leaves: A Valuable Medicinal Plant in the Home Garden

The Invisible Resident: How a Baby Octopus Lived Undetected in a Public Aquarium for Months

Belgium Bans Dolphin Captivity, Marking a Major Victory for Marine Animal Welfare

Draymond Green confronts fan over 'Angel Reese' chant

Nicki Minaj’s diplomatic moment, explained

Entertainment duo the Kessler twins die by assisted suicide at 89 on same day
