You’re Storing Your Batteries Wrong — Here’s How to Do It Right
Batteries keep our world running — from remote controls and flashlights to smartphones and even cars. But here’s the problem: most of us are storing them incorrectly. Improper storage can shorten their lifespan, cause leaks, and even create safety hazards. The good news? A few simple changes can make a big difference.
In this guide, we’ll uncover the science behind battery storage, debunk common myths, and share proven ways to keep your batteries safe, efficient, and long-lasting.
1. Why Battery Chemistry Matters
Not all batteries are created equal. Alkaline, lithium-ion, and nickel-metal hydride batteries each have different chemical makeups — and therefore, different storage needs.
-
Alkaline batteries (the ones in remotes and toys) can leak in high humidity.
-
Lithium-ion batteries (in phones and laptops) degrade faster in heat.
-
NiMH rechargeable batteries prefer moderate temperatures and partial charge.
Temperature, humidity, and storage method all affect how well these batteries hold power. Understanding the chemistry helps you prevent damage before it happens.
2. Always Keep Battery Ends Separate
Those little metal tips — the positive and negative terminals — can cause trouble if they touch. When they do, the battery can short-circuit, heat up, or even start a fire.
The safest option? Keep batteries in their original packaging or use a plastic battery organizer where each battery fits snugly in its own slot. This is especially crucial for 9-volt batteries, which have terminals close together and are more prone to shorting.
3. The Best Temperature: Room Temperature
Batteries like the same temperatures we do — not too hot, not too cold. A range between 20°C and 25°C (68°F–77°F) is ideal.
Extreme heat speeds up chemical breakdown, while freezing temperatures reduce capacity. For instance:
-
Alkaline batteries lose charge below 0°C (32°F).
-
Lithium-ion batteries can permanently lose capacity if stored above 30°C (86°F) for long periods.
Store your batteries somewhere cool, dry, and stable — like a closet, not a garage or car.
4. Avoid Metal Containers — Choose Plastic Instead
Metal and electricity don’t mix. Storing batteries in a metal tin or drawer can cause terminals to touch the metal surface and short-circuit.
Instead, use plastic bins or containers with dividers. They’re non-conductive, safe, and help you keep batteries organized by size and type.
5. Stop Storing Batteries in the Fridge
One of the most common myths is that batteries last longer in the refrigerator. While it’s true that cooler temperatures slow chemical reactions, the humidity in a fridge causes condensation — leading to corrosion, rust, and leakage.
Instead, choose a cool, dry cabinet away from direct sunlight and heat. That balance keeps your batteries fresh and safe.
6. How to Spot and Recycle Expired Batteries
Old batteries can leak or bulge — a clear sign that their internal chemicals have broken down. Don’t toss them in the trash!
Take used or expired batteries to a recycling drop-off center or local hazardous waste facility. Proper recycling prevents toxic metals from seeping into the environment. Many electronics stores and supermarkets also have battery recycling bins.
7. Never Mix Different Battery Types
Mixing alkaline, lithium, or rechargeable batteries in one device is a recipe for trouble. Each type discharges at a different rate, causing the weaker one to overwork — which can lead to leakage or damage.
Always use matching batteries — same brand, type, and age — for consistent performance.
8. Keep Batteries in Their Original Packaging
Manufacturers design packaging to protect batteries from dust, humidity, and short-circuits. If possible, keep unused batteries sealed until needed. The packaging also helps you easily track expiration dates and battery types.
9. Rechargeable Battery Storage Tips
Rechargeables need a bit of extra care. Before storing them, charge them to about 40–60%, not full or empty.
-
Fully charged? They degrade faster over time.
-
Fully drained? They risk permanent capacity loss.
Store rechargeables in a cool, dry drawer, and check their charge every few months.
10. Myths vs. Facts About Battery Storage
Let’s bust a few myths:
❌ Myth: Fully discharge batteries before recharging.
✅ Fact: Modern lithium-ion batteries prefer shallow charge cycles — don’t drain them completely.
❌ Myth: Refrigerating batteries makes them last longer.
✅ Fact: Condensation can damage them. Keep them dry and cool instead.
11. Viral Battery “Hacks” — What Works and What Doesn’t
Social media is full of battery hacks, but not all are safe. Some good advice includes placing silica gel packets (those “do not eat” bags) with stored batteries to absorb moisture.
But avoid trendy freezer tricks — cold and humidity don’t mix well with battery chemistry. Always double-check advice against scientific or manufacturer sources before trying it.
Final Thoughts
Proper battery storage is simple but essential. Keep them cool, dry, and separate. Avoid metal, heat, and humidity. Recycle old ones responsibly, and your batteries will last longer, perform better, and stay safer.
A little care now means fewer leaks, less waste, and more reliable power when you need it most.
News in the same category


Gordon Ramsay shares health update as he reveals why he "had to come clean" over cancer diagnosis

KIM KARDASHIAN FAILS THE CALIFORNIA BAR EXAM
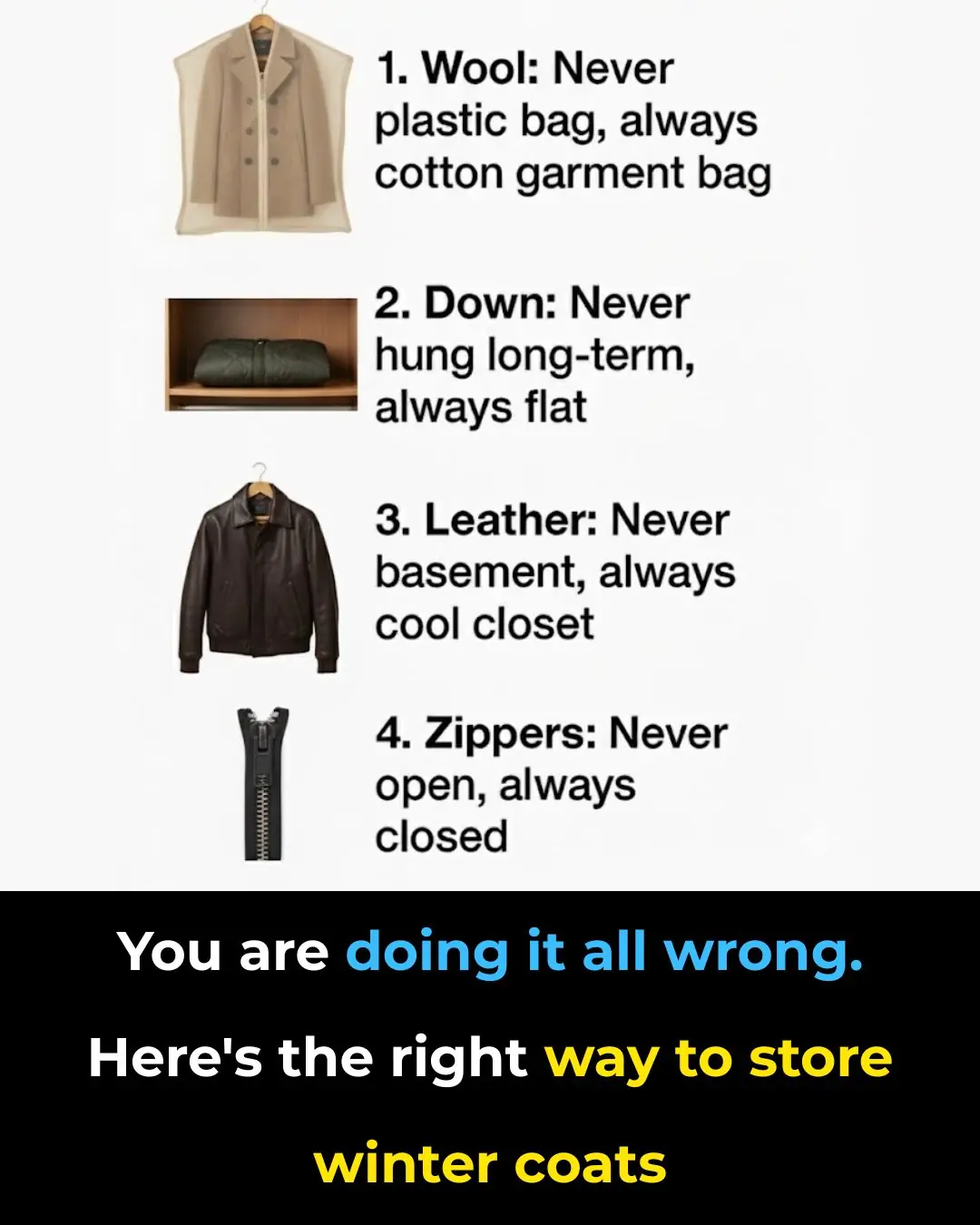
You’re Storing Your Winter Coats All Wrong — Here’s How to Do It Right

Why Bath Towels Have Lines — And What They Actually Do

Prince Harry and Meghan Markle roasted over deleted Kris Jenner birthday photos as fans speculate ‘embarrassing’ reasons why

The Right Way to Clean and Care for Your Winter Boots

Why You Should Regularly Clear Cookies on Your Smartphone

The One Show’s Alex Jones in tears as she makes emotional announcement: ‘We are all so proud of you

Paris Fury talks being a grandma after daughter Venezuela engaged at 16

Tom Fletcher ‘excited’ to perform with son Buzz for ‘truly special’ moment on Children in Need

WENDY WILLIAMS DOES NOT HAVE FRONTOTEMPORAL DEMENTIA

‘Broke My Heart!’: Arkansas Woman Drove Hours to Confront Pastor She Was Having an Affair with, Then Shot Him Dead in Front of His Wife

‘Had Security Called on Me 13 Times’: White Fans Tried to Get Black Woman Removed from Floor Seats at Jonas Brothers Concert Then It Backfired
‘Do You Have That Same Smoke? I’m Sick Of It’: Stephen A. Smith Believes His Rebuttal To Michelle Beadle and Cari Champion Is Giving Them The ‘Attention’ They Seek

5 Early Cancer Symptoms You Must Not Overlook

Angus T. Jones, Who Played Jake Harper, Left The Show “Two And A Half Men” 9 Years Ago – This Is Him Today

I'm A Celebrity's Joel Dommett announces wife's pregnant with second child

Hollywood icon Sally Kirkland, 84, enters hospice after dementia diagnosis
News Post

Add a drop of essential oil to an onion and no matter how many mosquitoes and insects it has, they will disappear

Shower Head Clogged After Long Use? Try This Method to Clean It Easily Without Spending Money

Why You Shouldn’t Wash Rice Inside the Electric Rice Cooker: A Common Mistake Many People Don’t Know

Add This Ingredient to Your Coffee: No More Yellow Teeth or Bad Breath

Don’t Eat Tofu Right Away After Buying It: Freezing It in the Fridge Has Amazing Benefits

Don’t Rush to Store Lemons in the Fridge — Do This Instead to Keep Them Fresh All Year Without Bitterness

Too Many Ripe Tomatoes? Try These 5 Preservation Methods to Enjoy Them All Year — Without Spending on Fresh Ones

The “Miracle” Termite Prevention Methods for Wooden Furniture

Kelvin Fletcher and wife Liz share update as they reveal they're expecting 'new arrivals'

Don’t Clean a Dirty Rice Cooker with Plain Water: Use This Trick and It’ll Shine Like New in Just 5 Minutes

Gordon Ramsay shares health update as he reveals why he "had to come clean" over cancer diagnosis

KIM KARDASHIAN FAILS THE CALIFORNIA BAR EXAM

You’re Storing Your Winter Coats All Wrong — Here’s How to Do It Right

Why Bath Towels Have Lines — And What They Actually Do

Prince Harry and Meghan Markle roasted over deleted Kris Jenner birthday photos as fans speculate ‘embarrassing’ reasons why

The Right Way to Clean and Care for Your Winter Boots

Why You Should Regularly Clear Cookies on Your Smartphone

The One Show’s Alex Jones in tears as she makes emotional announcement: ‘We are all so proud of you