Colon cancer—also known as colorectal cancer—is one of the most preventable yet deadliest cancers worldwide. It typically develops slowly over many years, often starting as small polyps that quietly grow without causing symptoms. This silent progression is why early screening is essential: the earlier colon cancer is found, the higher the chances of successful treatment and survival.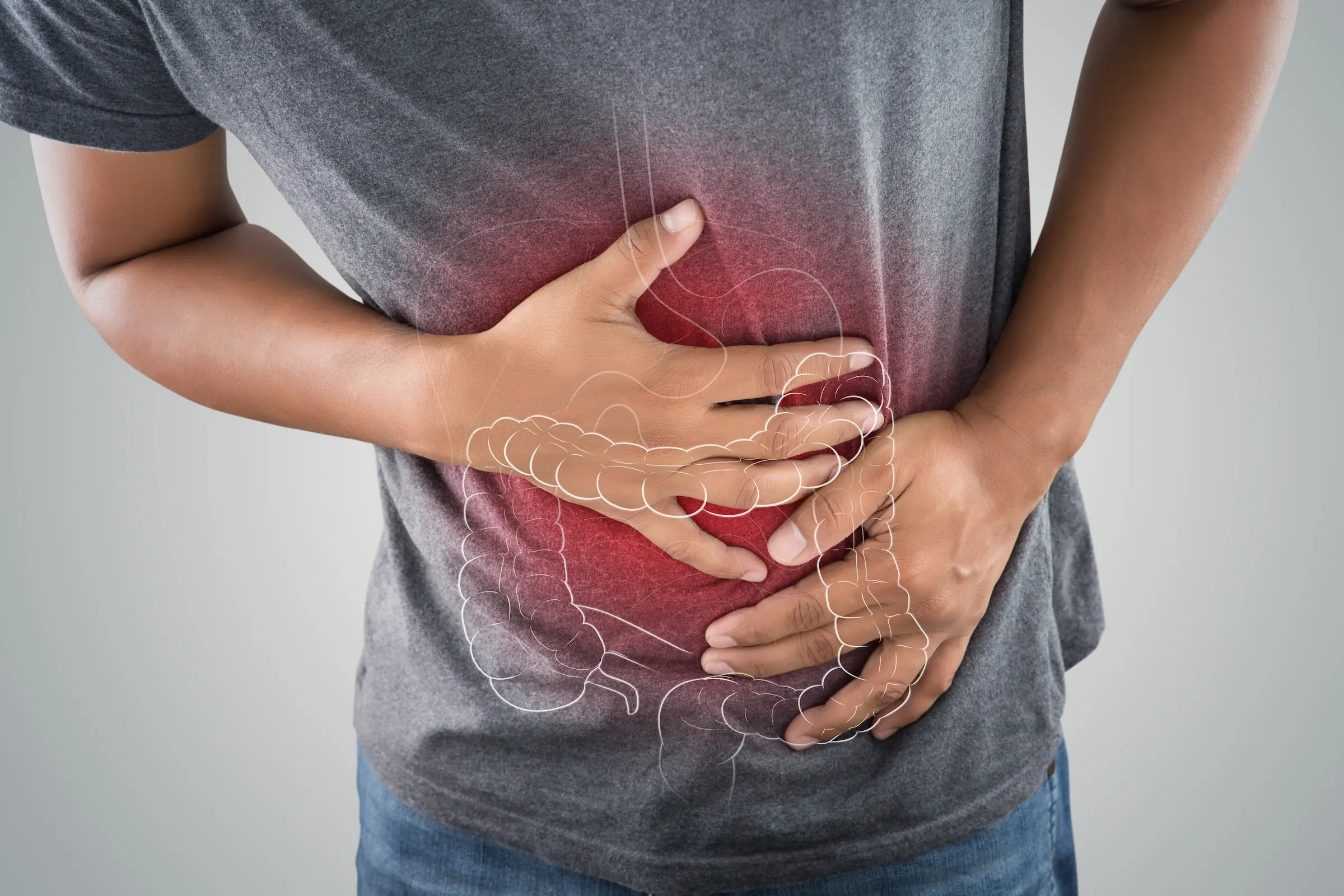
What Is Colon Cancer?
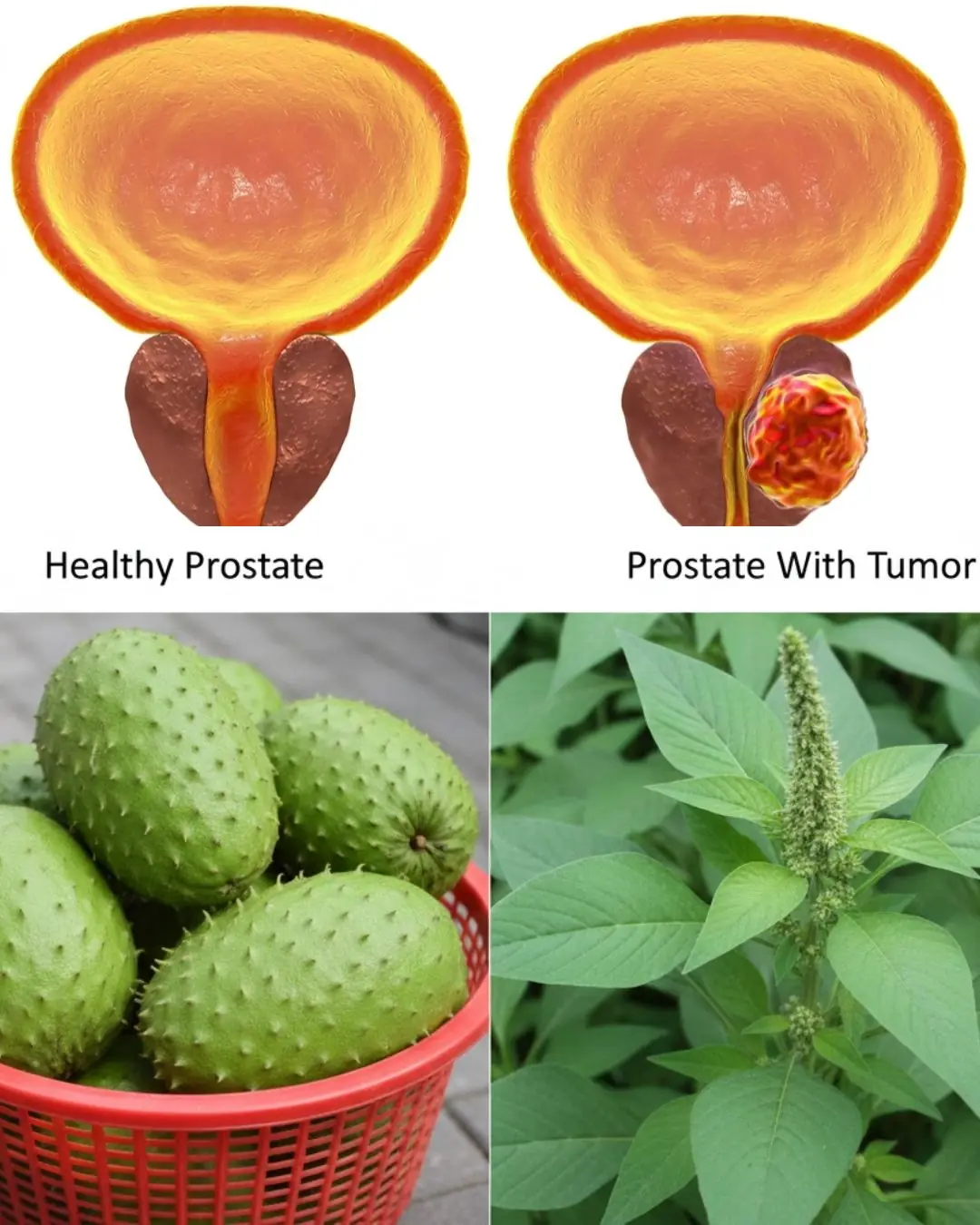
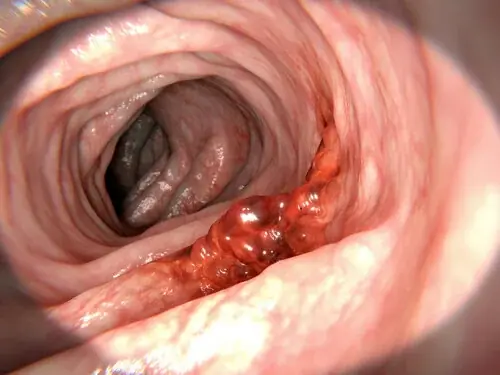
Colon cancer begins in the large intestine (colon), usually forming from clusters of abnormal cells called polyps. Not all polyps turn into cancer, but certain types, especially adenomatous polyps, have a higher risk.
What makes colon cancer dangerous is that it can grow silently for years before any symptoms appear. By the time clear symptoms develop, the disease may already be advanced.
Why Screening Is Critical
1. Early detection saves lives
When caught early, colon cancer has a 90% survival rate. But late-stage colon cancer has a survival rate below 15%.
2. Screening prevents cancer—not just detects it
During colonoscopy, doctors can remove polyps before they become cancerous.
3. Screening identifies silent internal bleeding
Small polyps may bleed slowly without noticeable symptoms. Detecting hidden blood early can reveal serious disease.
4. Screening catches cancer before it spreads
Once cancer spreads to the liver or lungs, treatment becomes more difficult and survival drops sharply.
Who Should Get Screened?
1. Adults age 45 and older
Colon cancer rates are rising in younger adults, so guidelines now recommend screening starts at 45.
2. People with a family history of colon cancer
A parent, sibling, or child with colon cancer increases your risk dramatically.
3. Individuals with chronic bowel diseases
Ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s disease raise the risk over time.
4. People with lifestyle-related risks
-
Obesity
-
Smoking
-
Low-fiber diet
-
Sedentary lifestyle
-
Excess red or processed meat
Symptoms of Colon Cancer
Many patients do not experience symptoms until the cancer is advanced. However, the following warning signs should never be ignored:
1. Changes in Bowel Habits
-
Persistent constipation
-
Chronic diarrhea
-
Narrow “pencil-like” stools
2. Blood in the Stool
Bright red or dark brown stool may indicate hidden bleeding.
3. Unexplained Weight Loss
Cancer cells consume energy, causing weight loss even with normal eating.
4. Persistent Abdominal Pain
Cramping, discomfort, or a feeling of fullness can occur.
5. Fatigue and Weakness
Caused by low red blood cells from internal bleeding.
6. Feeling of Incomplete Bowel Movements
Even after using the toilet.
Types of Screening Tests
1. Colonoscopy
The gold standard. Detects and removes polyps during the same procedure.
2. Stool Tests (FIT or FOBT)
Detect hidden blood in stool. Done yearly.
3. CT Colonography
A virtual colonoscopy using imaging.
4. Sigmoidoscopy
Examines only the lower colon.
Your doctor will recommend the most suitable test based on age, risk level, and symptoms.
How Colon Cancer is Treated
1. Surgery
Most early-stage cancers are removed surgically.
2. Chemotherapy
Used when cancer has spread or carries high-risk features.
3. Radiation Therapy
More common for rectal cancers.
4. Targeted Therapy and Immunotherapy
Used for advanced cases to attack cancer cells more precisely.
How to Reduce Your Risk
-
Eat a high-fiber diet
-
Incorporate fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
-
Limit red and processed meats
-
Exercise regularly
-
Maintain a healthy weight
-
Avoid smoking and heavy alcohol use
-
Get screened as recommended