Could Your Magnesium Supplement Be Causing Side Effects?
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Health-GettyImages-1583213828-c3ac84a4664e42a9bea9c901b1a4ba5b.jpg)
Magnesium supplements can cause side effects, most commonly affecting the digestive system. Diarrhea, nausea, and stomach pain are especially likely when magnesium is taken in doses above 350 milligrams per day. At much higher amounts, magnesium can lead to more serious reactions, including symptoms of toxicity such as low blood pressure and muscle weakness.
Common Side Effects of Magnesium
Gastrointestinal (GI) issues are the most frequently reported side effects associated with magnesium supplementation. These reactions are more likely to occur when intake exceeds 350 milligrams daily, which is the recommended upper limit for supplemental magnesium in adults.
Gastrointestinal Symptoms
The most common digestive side effects include diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, stomach pain, and abdominal cramping. Magnesium is often used as a treatment for constipation because it draws water into the intestines. This softens stool and makes bowel movements easier. However, this same mechanism can also lead to loose stools and digestive discomfort when too much magnesium is consumed.
Certain forms of magnesium are more likely to cause diarrhea and other GI symptoms. These include magnesium carbonate, magnesium chloride, magnesium oxide, and magnesium gluconate. The likelihood and severity of side effects increase as the dose rises.
Taking magnesium supplements with food may help reduce stomach irritation and lower the risk of nausea or cramping.
Magnesium Toxicity
Extremely high doses of magnesium—typically more than 5,000 milligrams per day—can result in magnesium toxicity. This occurs when blood magnesium levels rise above the normal range of 0.75–0.95 millimoles per liter and reach levels between 1.74 and 2.61 millimoles per liter.
Symptoms of magnesium toxicity may include:
-
Low blood pressure (hypotension)
-
Facial flushing or redness
-
Confusion or mental changes
-
Difficulty urinating
-
Fatigue or extreme drowsiness
-
Muscle weakness
-
Trouble breathing
-
Slow, fast, or irregular heartbeat
-
Heart failure
-
Coma
-
Cardiac arrest
Magnesium toxicity is rare and most often occurs when magnesium is administered intravenously in a medical setting. However, very high doses of oral magnesium supplements can still cause toxicity, particularly in people with reduced kidney function.
Who Is at Higher Risk for Side Effects?
Certain individuals are more likely to experience side effects from magnesium supplements. This includes people with kidney disease, reduced kidney function, or a history of kidney failure. Those receiving dialysis and older adults are also at increased risk, as kidney function naturally declines with age.
Additionally, some forms of magnesium—such as magnesium oxide or magnesium sulfate—are more likely to cause digestive discomfort compared to other formulations.
What Is a Safe Magnesium Dose?
For adults, the upper safe limit for magnesium from supplements alone is 350 milligrams per day. This limit does not include magnesium obtained naturally from food sources such as leafy green vegetables, whole grains, nuts, seeds, and legumes.
The recommended daily intake of magnesium from both food and supplements varies by age, sex, and life stage:
-
Men:
-
Ages 14–18: 410 mg
-
Ages 19–30: 400 mg
-
Ages 31 and older: 420 mg
-
-
Women:
-
Ages 14–18: 360 mg
-
Ages 19–30: 310 mg
-
Ages 31 and older: 320 mg
-
-
Pregnant individuals:
-
Ages 14–18: 400 mg
-
Ages 19–30: 350 mg
-
Ages 31 and older: 360 mg
-
-
Breastfeeding individuals:
-
Ages 14–18: 360 mg
-
Ages 19–30: 310 mg
-
Ages 31 and older: 320 mg
-
When to See a Doctor
If you are taking magnesium supplements and develop symptoms such as severe weakness, breathing difficulty, confusion, or low blood pressure, stop taking the supplement and seek medical care immediately.
You should also contact a doctor right away if you notice blood in your stool or black, tarry stools after taking magnesium, as this may indicate gastrointestinal bleeding.
Before starting any supplement, it is always best to consult a healthcare provider to make sure it is safe, appropriate, and dosed correctly for your individual health needs.
News in the same category


One Person Washes the Dishes, the Whole Family Faces Cancer Risk?

Rising Stroke Rates: Doctors Warn Against Overusing Four Common Foods
Aspirin May Help Stop Cancer From Spreading, Study Finds

A 53-Year-Old Man Diagnosed With Liver Cancer: Doctors Warn About the Top 3 Behaviors That Severely Damage the Liver

Top 10 signs of a gallbladder attack

MIT Researchers Develop Injectable Gel That Regenerates Damaged Nerves
Are Biologic Therapies Safe in Patients With Psoriasis and Cancer?

Smoking and Dementia: A Critical Link You Can’t Ignore

Which Fruits Should Cancer Patients Avoid and Which Should They Eat?
Advancing Clinical Excellence in IgA Nephropathy
What To Know About Chronic Kidney Failure
Why Thick Toenails Happen, And How To Get Rid of Them

The military sleep method that can help you fall asleep in just two minutes

Surprising Health Benefits of Purslane (Portulaca oleracea)
Rising Deaths From Stomach Cancer: Doctors Warn — See These 4 Abdominal Signs and Seek Medical Care Immediately

Australia is replacing animal testing with smarter, humane science

Cracked Egg in Your Carton? Here’s When It's Safe to Eat—And When to Toss

Scientists Restore Natural Hearing Using Stem Cells in a Historic Medical Breakthrough
News Post

The Lasting Power of Soulful Connection: How Kindness Leaves an Eternal Imprint

Olympian Gus Kenworthy Rescues 90 Dogs From South Korean Meat Farm, Turning Compassion Into Action

Crush Papaya Leaves Every Night – Your White Hair May Start Turning Dark and Growing Like Crazy by Morning
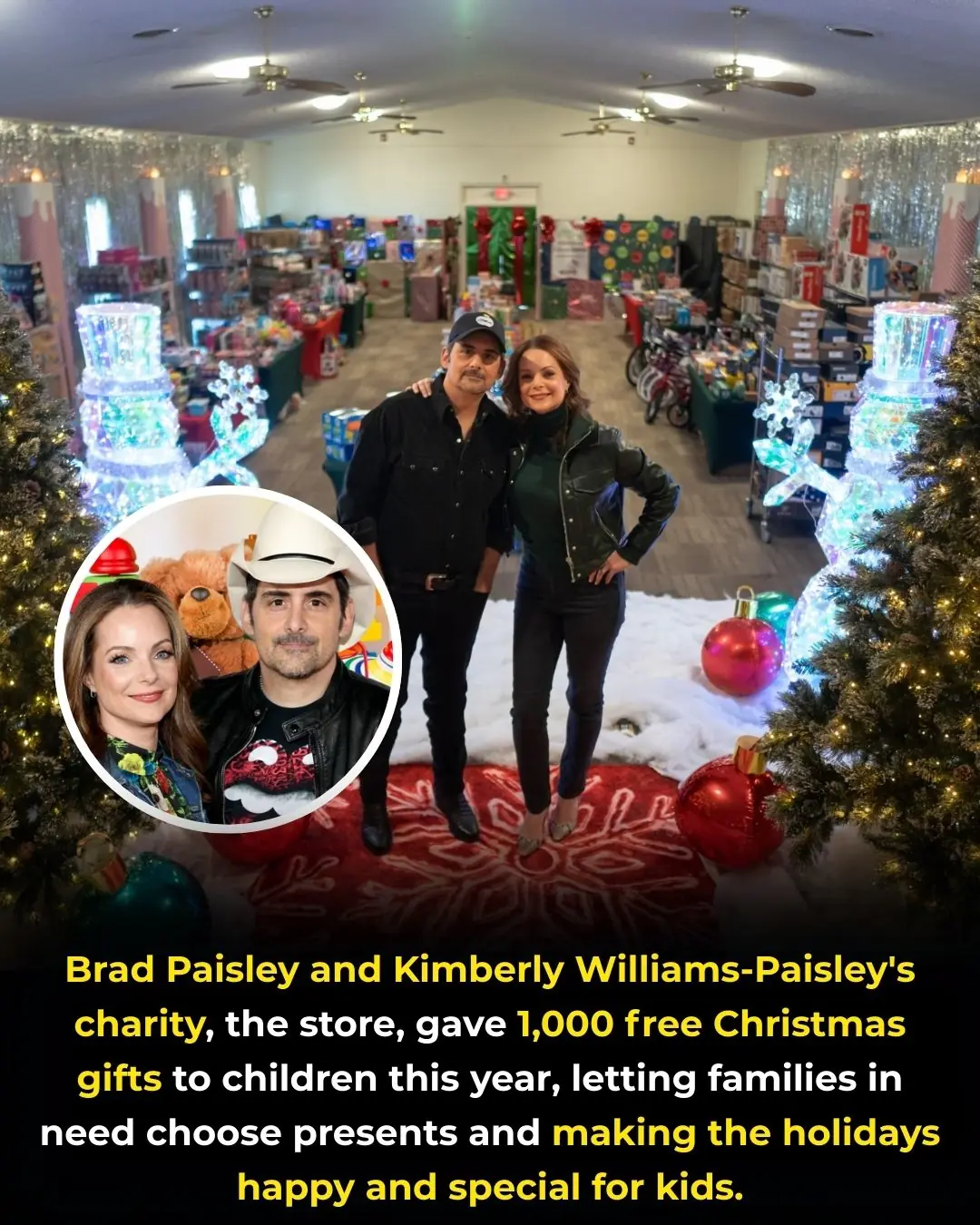

Brad Paisley and Kimberly Williams-Paisley Spread Holiday Joy by Giving 1,000 Christmas Gifts to Children in Need

Over 60? 10 Early Dementia Warning Signs You Must NEVER Ignore (Catch Them Before It’s Too Late)
The Cheapest Superfood Most Seniors Overlook That Could Transform Bone Health After 60

9 Hidden Garlic & Honey Benefits at Night (99% Don’t Know)

Boil Cinnamon, Cloves, Garlic, Ginger, Lemon & Onion for 15 Minutes – Your Body Will Feel the Difference by Day 3

Discover Oregano: The Golden Herb That May Gently Support Your Eye Health

The Cardiovascular Benefits of Pomegranate Juice: Scientific Evidence and Mechanisms

How to Grow Your Nails Really Fast and Long in Just 10 Days

You don’t need complicated supplements to support digestion.

This Flight Landed Before It Took Off — Thanks to Time Zones

The Legendary 2004 Harvard–Yale Prank That Outsmarted the Crowd and Made History

Behind the Mask: How a Mexican Priest Fought in the Ring to Protect Orphans

Arlington Mom Welcomes Giant Baby Boy

Trump Orders Transgender Male Inmates to Be Housed in Men’s Prisons, Sparking Nationwide Debate

Yurok Tribe Reclaims 47,000 Acres of Ancestral Land in Historic California Land-Back Deal

A First-Class Act of Kindness at 30,000 Feet
