
🔬 How Vaccines May Boost Broader Immunity
-
Immune activation: COVID-19 vaccines stimulate T cells, B cells, and natural killer cells, which are critical for identifying abnormal or malignant cells.
-
Cancer surveillance: This heightened immune activity may improve the body’s ability to recognize and respond to early-stage cancer cells.
-
Synergy with immunotherapy: Studies show that vaccination can sensitize tumors to immune checkpoint inhibitors, making treatments more effective.
📊 Key Research Findings
| Study | Findings | Implications |
|---|---|---|
| Nature (2025) | COVID-19 mRNA vaccines trained immune systems to kill cancer cells; improved survival in animal models and retrospective human data | Suggests vaccines may enhance cancer immunotherapy |
| Nature Cancer (2025) | Vaccines boosted immune checkpoint inhibition effectiveness in melanoma and lung cancer | Potential integration into oncology treatment |
| Clinical Briefings (2025) | Vaccination associated with improved survival in cancer patients | Supports further trials in diverse patient populations |
⚠️ Important Caveats
-
Not a cancer treatment: COVID-19 vaccines are designed to prevent viral infection, not to cure cancer.
-
Effects are subtle: Observed benefits are secondary and require larger, long-term clinical trials.
-
Individual variation: Benefits may differ depending on cancer type, patient immune status, and treatment context.
-
Duration unknown: Researchers are still studying how long these immune enhancements last.
🌍 Broader Implications
-
Routine vaccination: Could provide unexpected layers of protection beyond infectious disease prevention.
-
Public health impact: Reinforces the importance of vaccination programs for overall immune resilience.
-
Future oncology: Opens pathways for combining vaccines with personalized cancer therapies.
✅ Takeaway
COVID-19 vaccines may offer secondary immune benefits that extend beyond infection protection, potentially supporting cancer surveillance and enhancing immunotherapy. While promising, these findings remain preliminary, and more trials are needed to confirm their role in oncology. Still, they highlight the versatility of vaccines and their potential to strengthen immune resilience across multiple health challenges.
Sources:
-
Nature – Tumours sensitized to immune therapy by COVID mRNA vaccines
-
Nature Clinical Briefing – COVID vaccines and cancer survival
-
Nature Cancer – Boosting cancer immunotherapy with COVID-19 mRNA vaccines
News in the same category

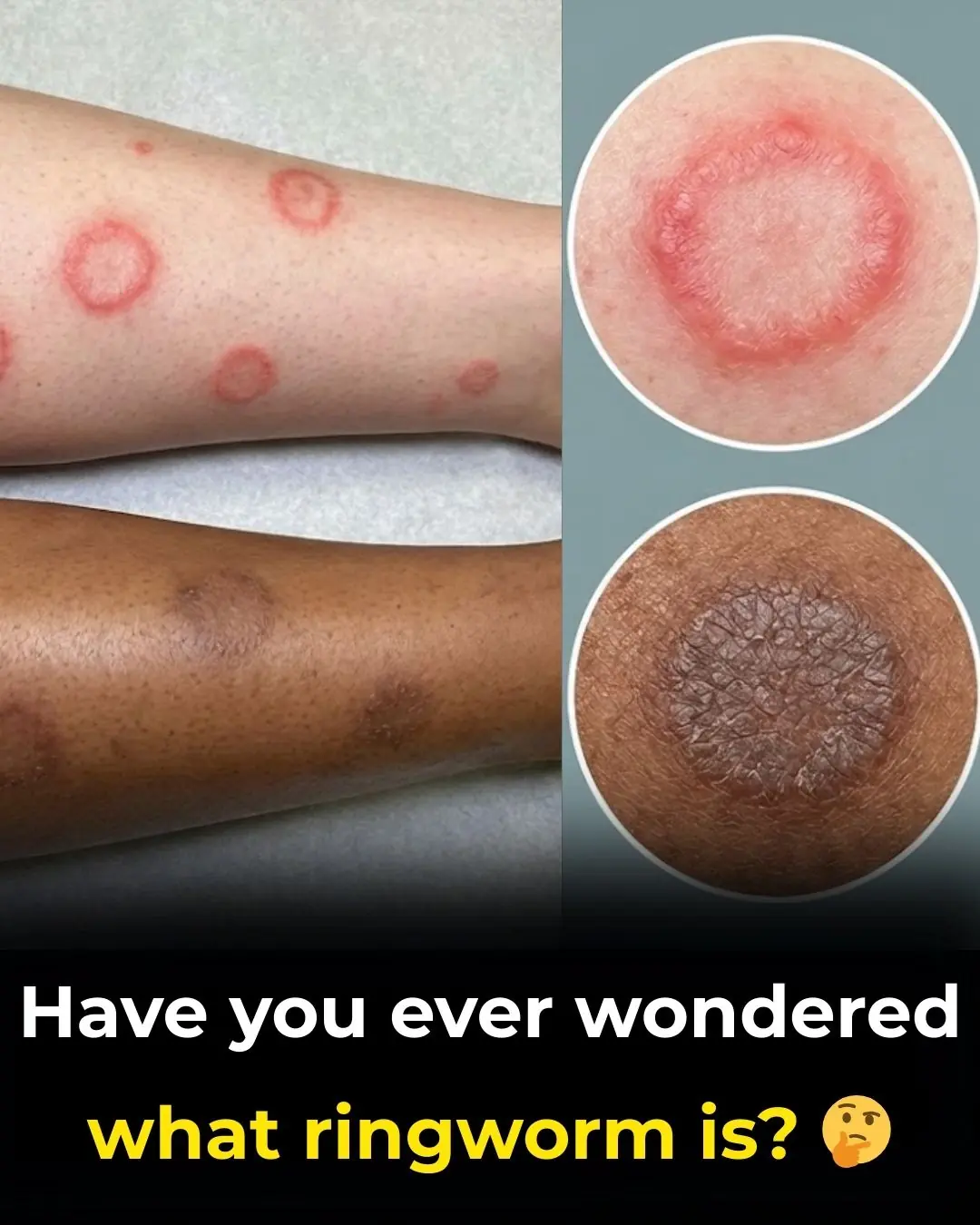
Understanding Ringworm: Causes, Symptoms, Transmission, and the Importance of Medical Evaluation
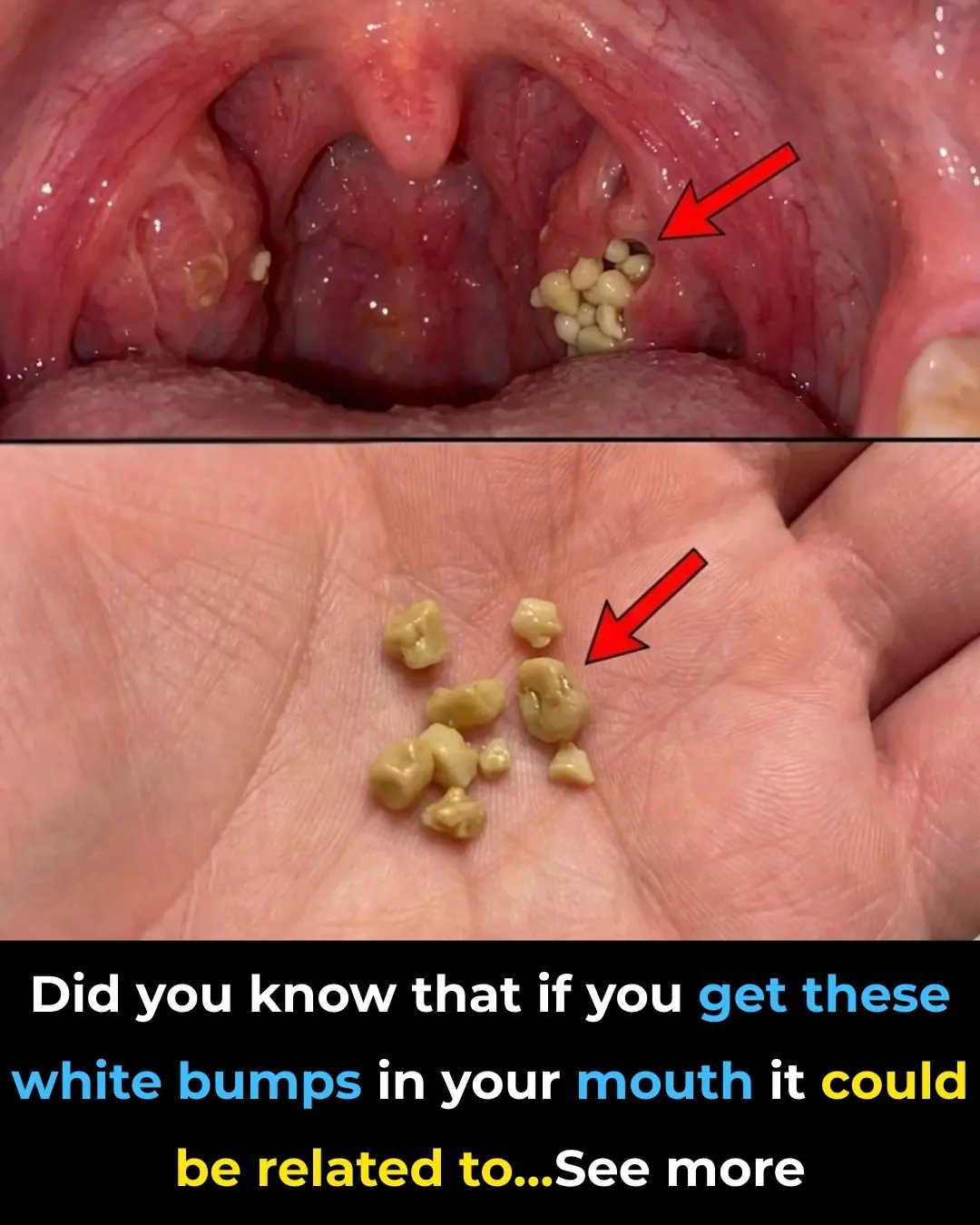
Tonsil Stones: Discover what they are, how they appear, and how to get rid of them forever.

Understanding Menstrual Cramps: Causes, Symptoms, and When to Seek Medical Help

🧪 The Breakthrough Procedure

🔬 How mRNA Cancer Therapy Works

🧪 Historical Context: Sugar vs. Fat in Nutrition Science

🧪 The Breakthrough in Switzerland

Pineapple and Cucumber: A Natural Gut Health Remedy

Lyme disease: causes, natural treatment, and how to effectively prevent it
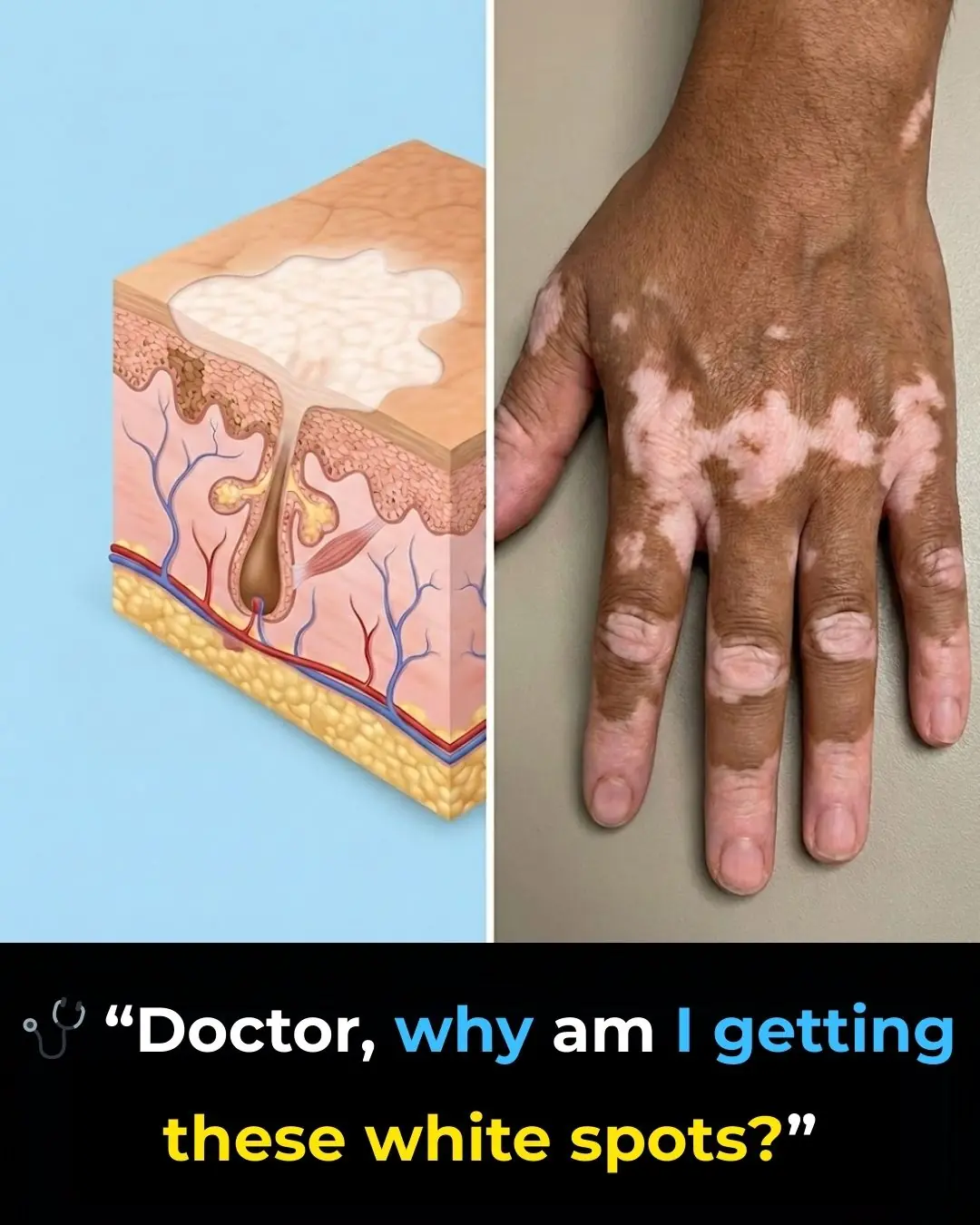
Understanding Vitiligo: Causes, Diagnosis, and the Importance of Medical Evaluation
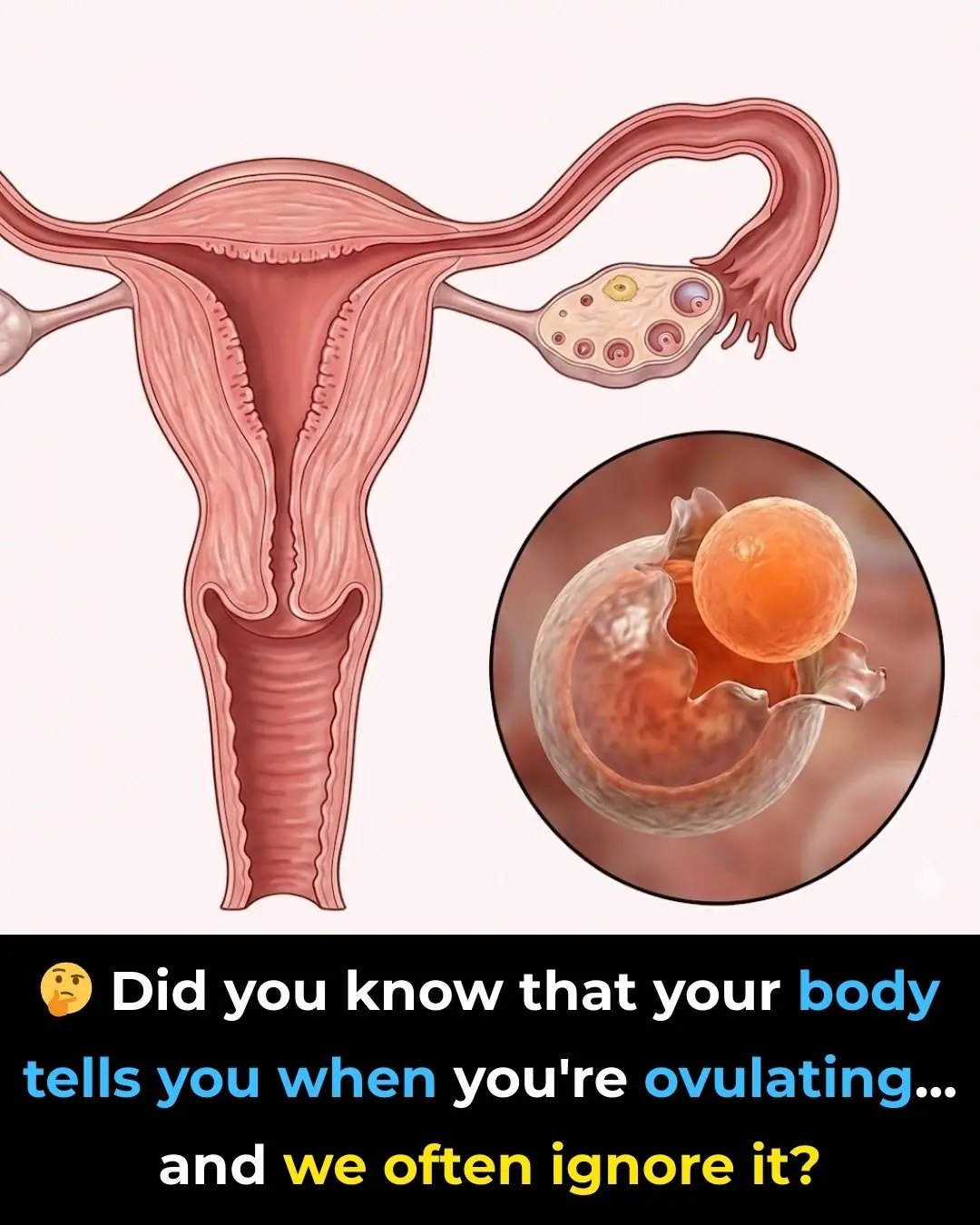
Understanding Ovulation: Key Signs Your Body Sends and Why They Matter

Why Do Men Lose Their Hair? The Story Behind Every Follicle

Muña vs. Gastritis: Peruvian scientist demonstrates its power against the Helicobacter pylori bacteria

Early Menopause: Recognizing the Signs, Understanding the Risks, and Steps You Can Take
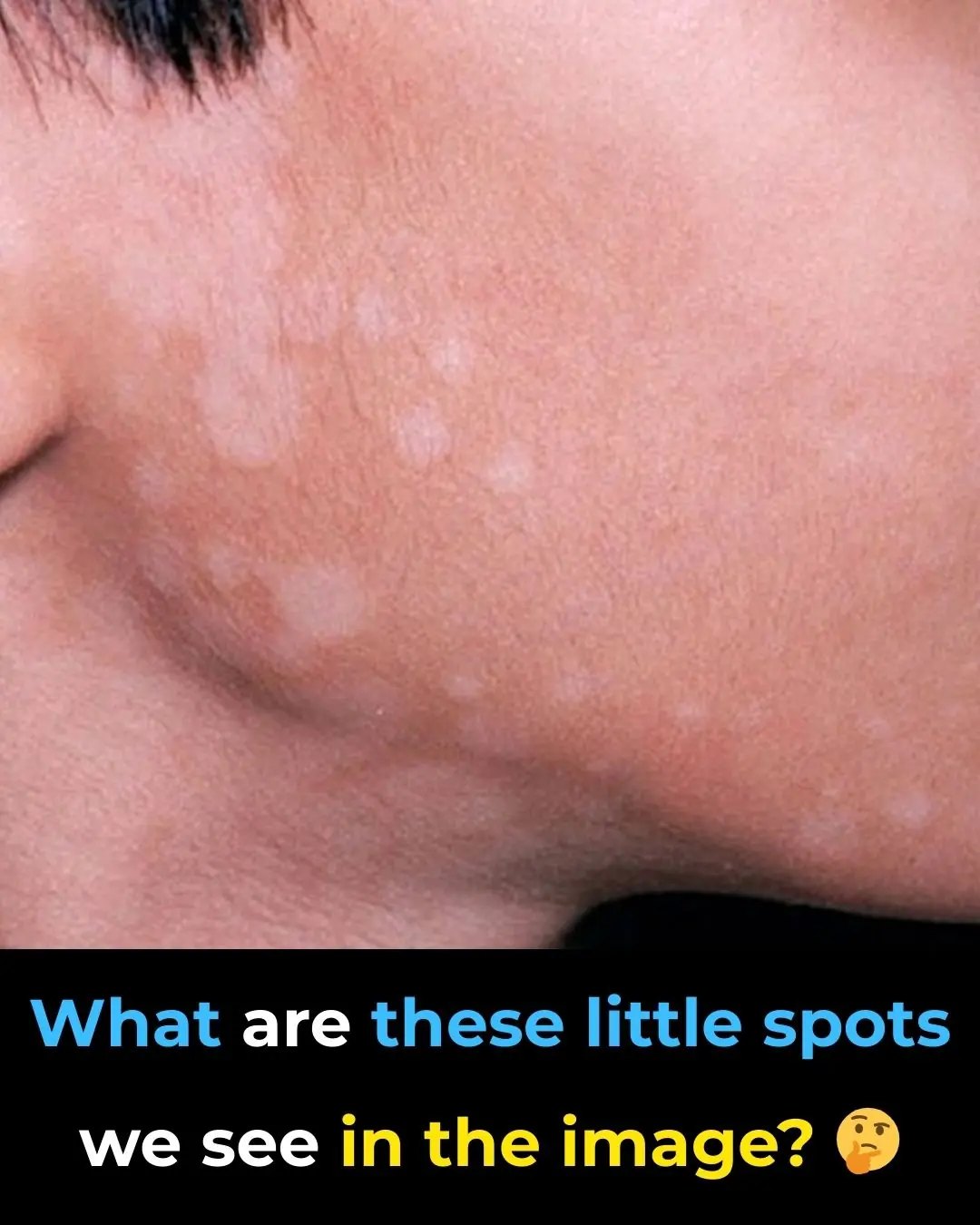
"What Are These Spots in the Image? 🤔"
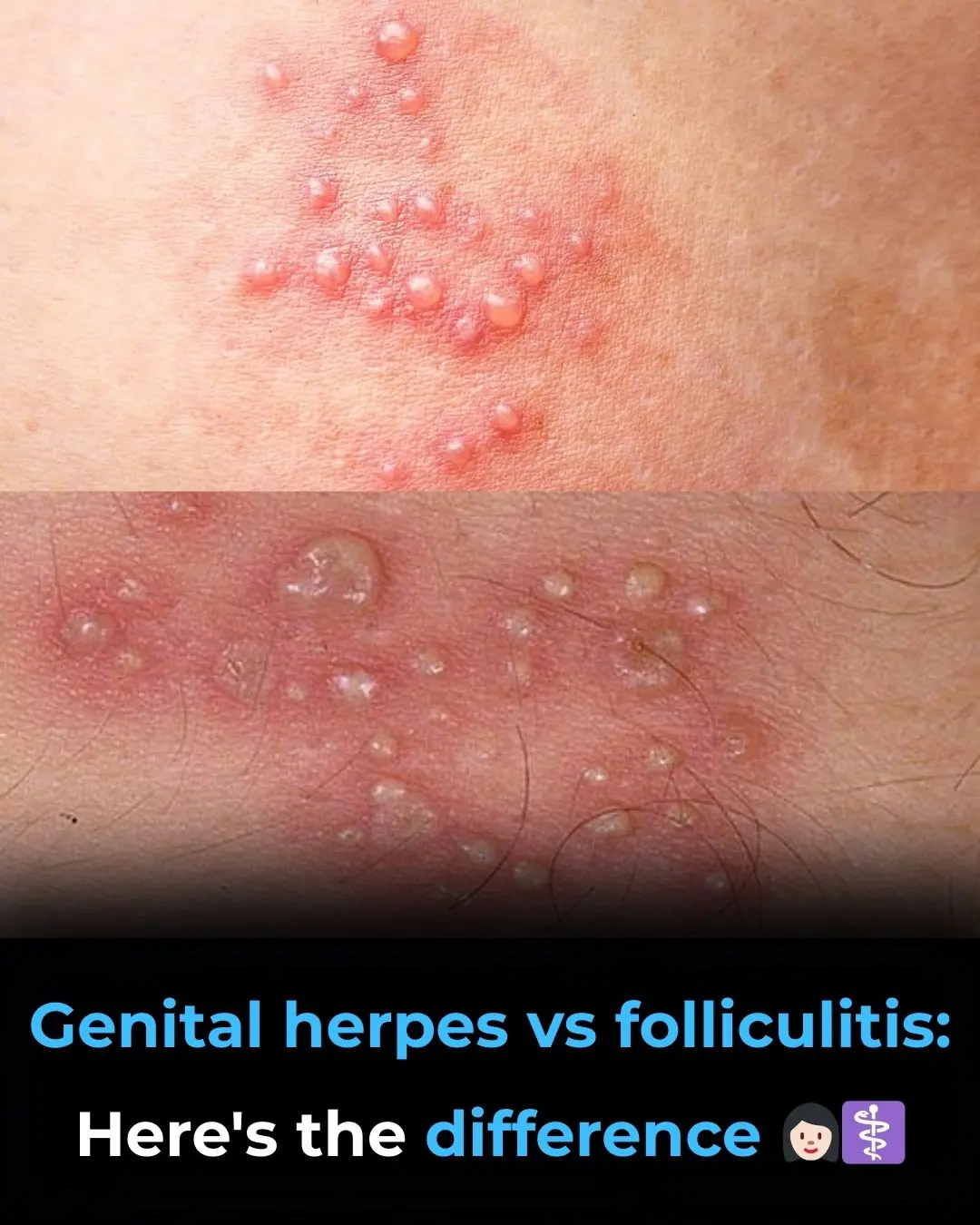
Genital Herpes vs Folliculitis: Understanding the Difference 👩🏻⚕️
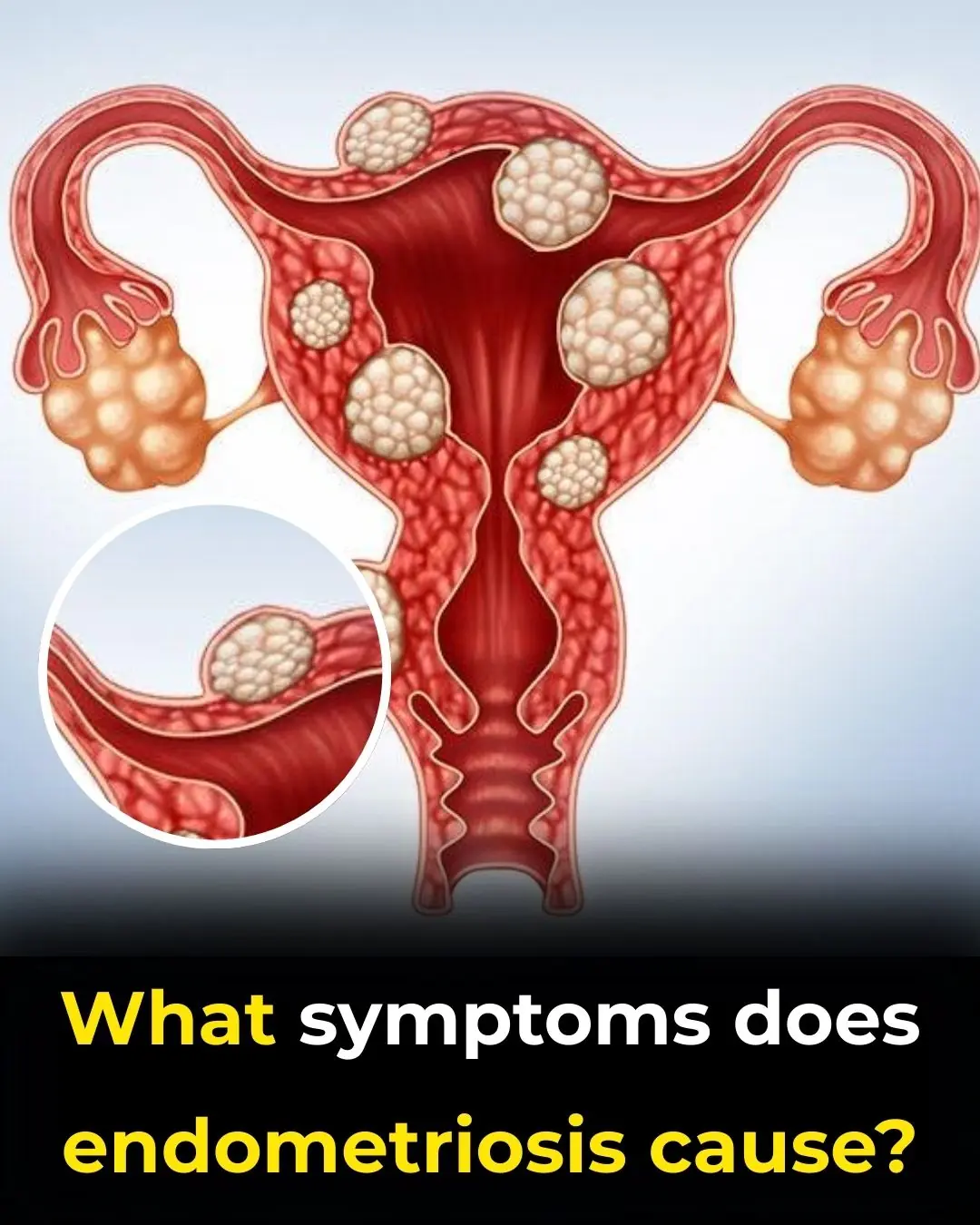
Understanding Endometriosis: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and the Importance of Early Detection with Dr. Pau Zúñiga
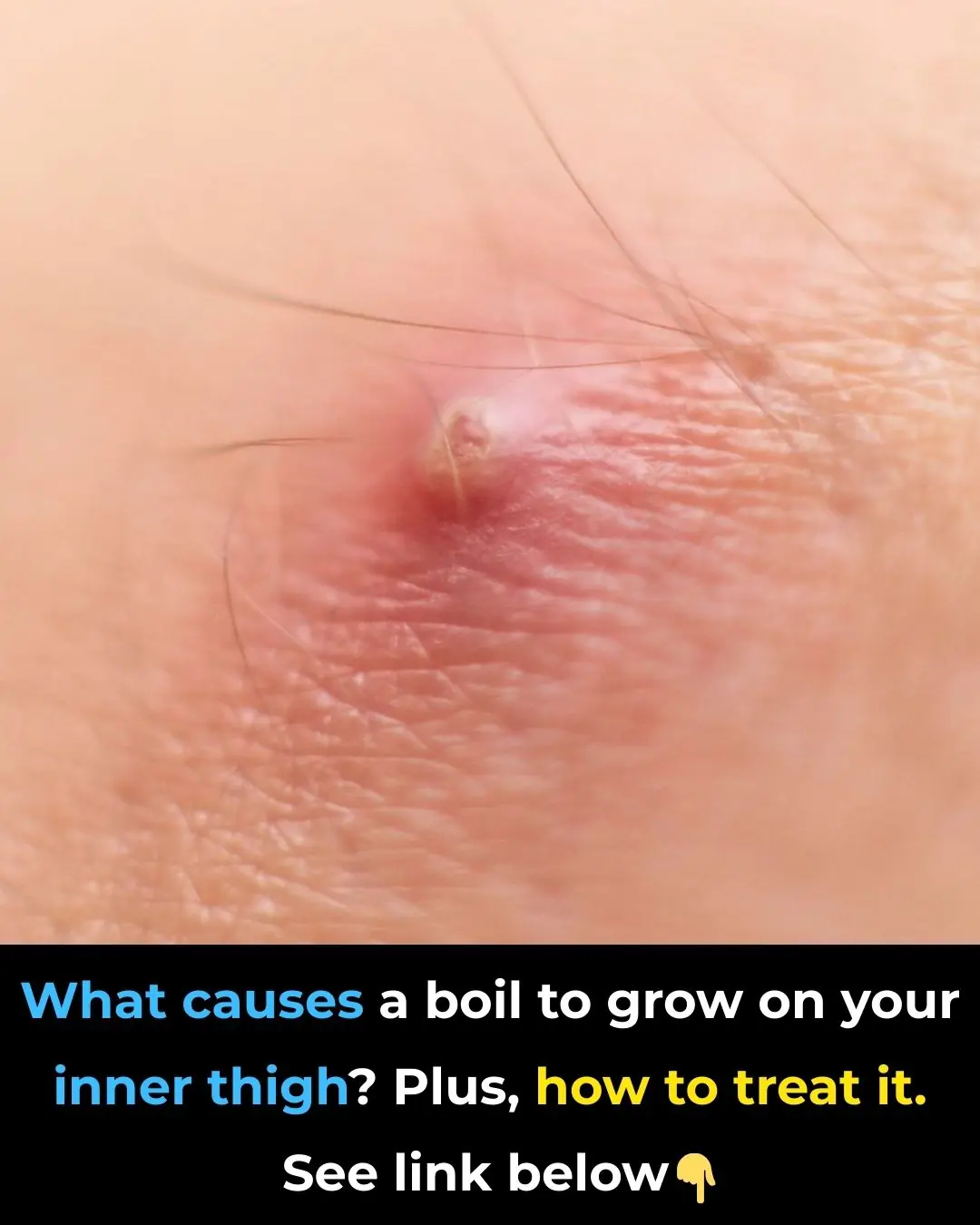
Boil on Inner Thigh: Symptoms and Treatment Options
News Post

A Powerful Woman Pushes a Child into a Puddle — But the Birthmark on His Hand Leaves Her Stunned…

Health Benefits of Coffee

The Lack of This Mineral Is Causing Age Spots: Discover the Solution

Warning For Pink Slime Found in Your Bathroom

Understanding Ringworm: Causes, Symptoms, Transmission, and the Importance of Medical Evaluation

The Helmet That Started Breathing at Night

Tonsil Stones: Discover what they are, how they appear, and how to get rid of them forever.

Understanding Menstrual Cramps: Causes, Symptoms, and When to Seek Medical Help

Black CEO Removed from VIP Seat for White Passenger – 5 Minutes Later The Entire Crew Gets Fired

Morgan Freeman Slams Unauthorized AI Voice Use, Says His Lawyers Are “Busy”

Beloved Florida pastry chef, 71, killed in freak accident with bread-making machine

He Left His Wedding to Save a Country

He Erased His Wife from the Billionaire Gala—Until the Entire Room Rose When She Walked In

Meghan Markle and Prince Harry reunite with Hollywood PR firm after 11th publicist quit

🥊 What Mary Kom Said

🕊️ The Incident

NFL fines Texans’ Azeez Al-Shaair for wearing ‘stop the genocide’ eye black

🏆 Mohanlal’s Achievement

🐾 What Mika Singh Announced
