
Revolutionary Surgery-Free Kidney Stone Treatment Using Magnetic Micro-Robots"
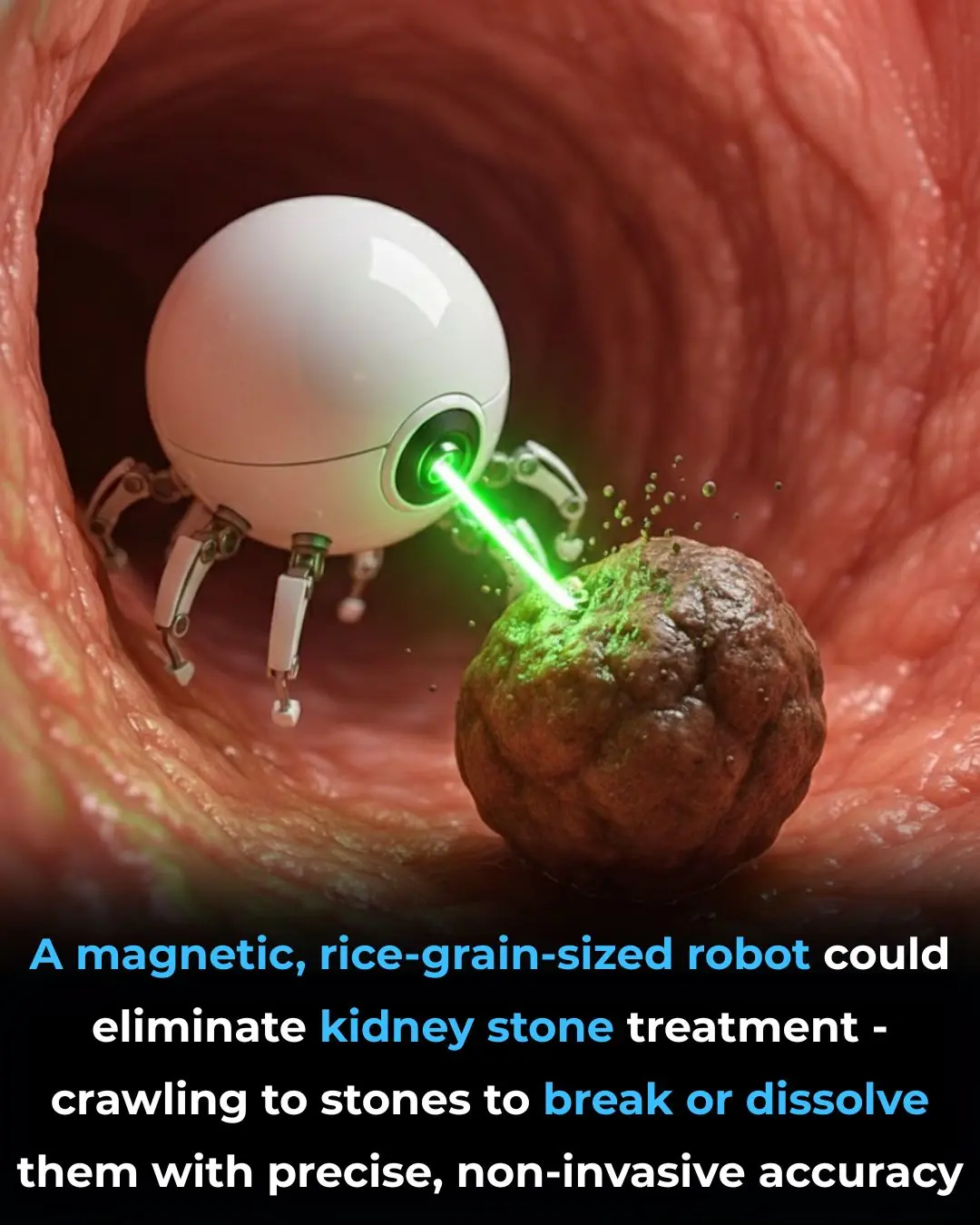
Surgery-Free Kidney Stone Treatment May Be Just Around the Corner
Imagine a world where kidney stones can be treated without the need for painful procedures, surgical cuts, or extended recovery periods. This may soon be a reality thanks to groundbreaking advancements in medical technology. Scientists are developing tiny magnetic micro-robots, each no larger than a grain of rice, that are capable of navigating through the human body to locate and eliminate kidney stones with remarkable precision.
These micro-robots, controlled by external magnetic fields, can travel through the urinary tract and attach themselves to kidney stones. Once in place, they can either drill into or dissolve the stones, eliminating the need for invasive incisions. Inspired by nature’s own design, these robots are made from soft, flexible materials that allow them to move safely through the body's tissues and fluids without causing harm.
The revolutionary technology is being developed by a team of researchers at the Max Planck Institute, in collaboration with leading medical professionals across Europe and Asia. If successful, this innovation could replace traditional kidney stone surgeries, offering a non-invasive and highly effective alternative.
Kidney stones are a common and often excruciating condition that affect millions of people worldwide. Traditionally, the treatment for large or problematic stones involved invasive surgeries such as lithotripsy or nephrolithotomy. These methods not only involve significant pain but also carry risks of complications and long recovery times. The development of micro-robots presents a promising new approach, potentially reducing both the physical burden on patients and the medical risks associated with current treatments.
These robots work by being guided through the body by external magnets. Once they reach the stone, they can either use mechanical force to break it apart or employ chemical agents to dissolve it entirely. Their small size allows them to access areas of the body that would otherwise be difficult to reach using traditional surgical tools, ensuring a higher level of precision in treatment.
One of the key advantages of this robotic technology is its ability to function without causing any tissue damage. The soft materials from which the robots are made allow them to move through the body’s delicate tissues with minimal risk of injury. Furthermore, because the robots are designed to operate remotely, the need for anesthesia and recovery time is significantly reduced, making this a far less invasive alternative to traditional methods.
Researchers from the Max Planck Institute, alongside medical experts from institutions across Europe and Asia, have made significant strides in perfecting this technology. The teams are currently working on fine-tuning the robots’ capabilities to ensure they can effectively navigate the body and perform their tasks with maximum efficiency. Early studies have shown promising results, and experts believe that the technology could be ready for wider clinical use within the next few years.
The potential impact of this innovation is substantial. If successful, it could revolutionize the way kidney stones are treated worldwide. Patients would no longer have to endure long recovery times or invasive surgeries. Instead, they could benefit from a simple, non-invasive procedure that requires minimal recovery, all while maintaining the same level of effectiveness as traditional methods.
In conclusion, the development of magnetic micro-robots offers a future in which kidney stone treatments are safer, faster, and less invasive. With promising results from ongoing research, we may soon see a shift away from traditional surgeries, making these high-tech robots the future of kidney stone treatment. This breakthrough could have far-reaching implications not only for kidney stone patients but for the medical field as a whole, paving the way for the use of robotic technology in treating other conditions as well.
Sources:
-
Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems (https://www.is.mpg.de/)
-
European Urology Association (https://www.uroweb.org/)
-
National Kidney Foundation (https://www.kidney.org/)
News in the same category


Is Your Toilet Sitting Position Causing Constipation? Here’s How to Fix It Naturally
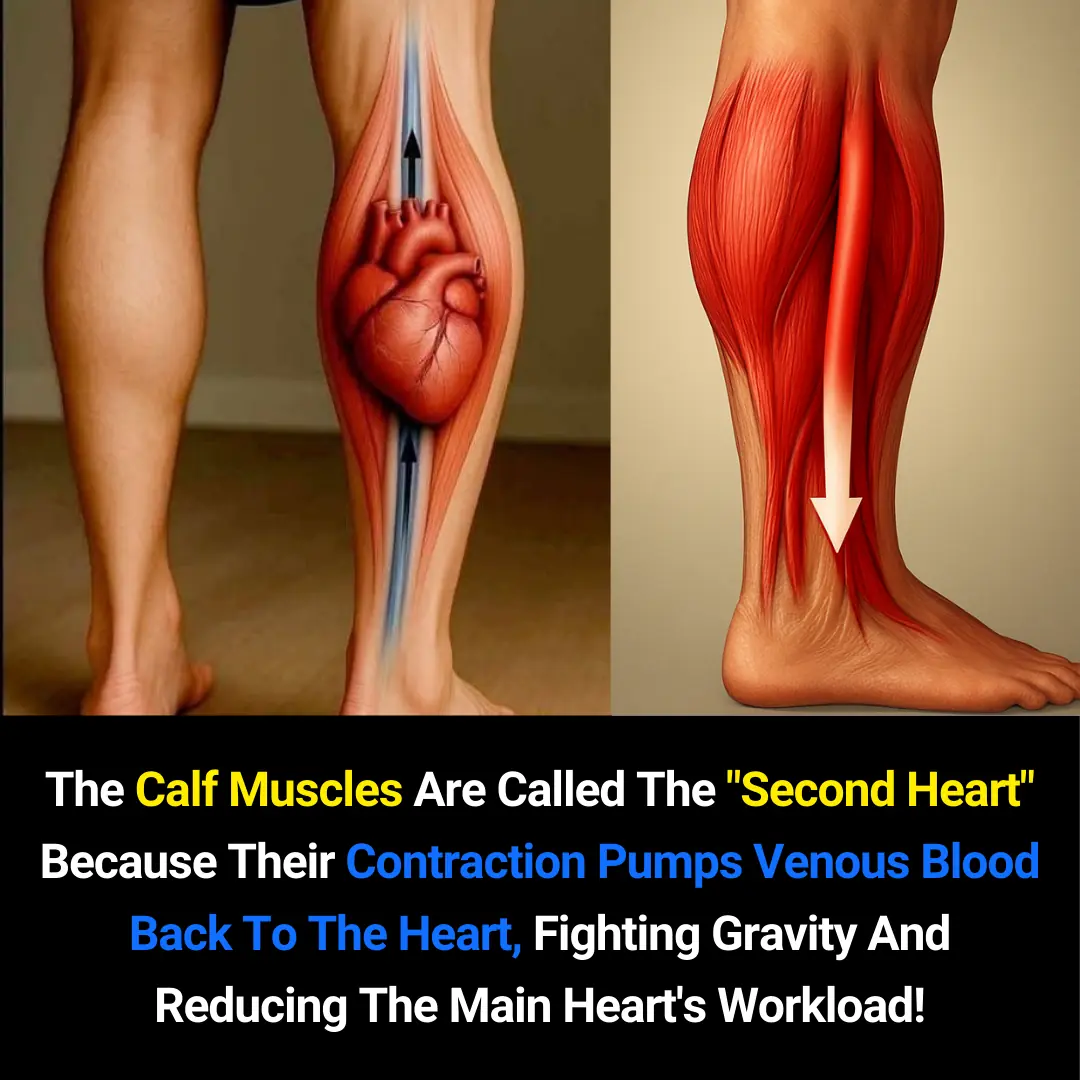
The Calf Muscles: Why They Are Known as the Body’s “Second Heart”

Little Pocket in Women’s Underwear

A Decade of Struggle: The Inspiring Journey from Wrongful Conviction to Legal Triumph

Rise Tower: Saudi Arabia's 2,000-Meter Megastructure Set to Redefine the Future of Urban Living
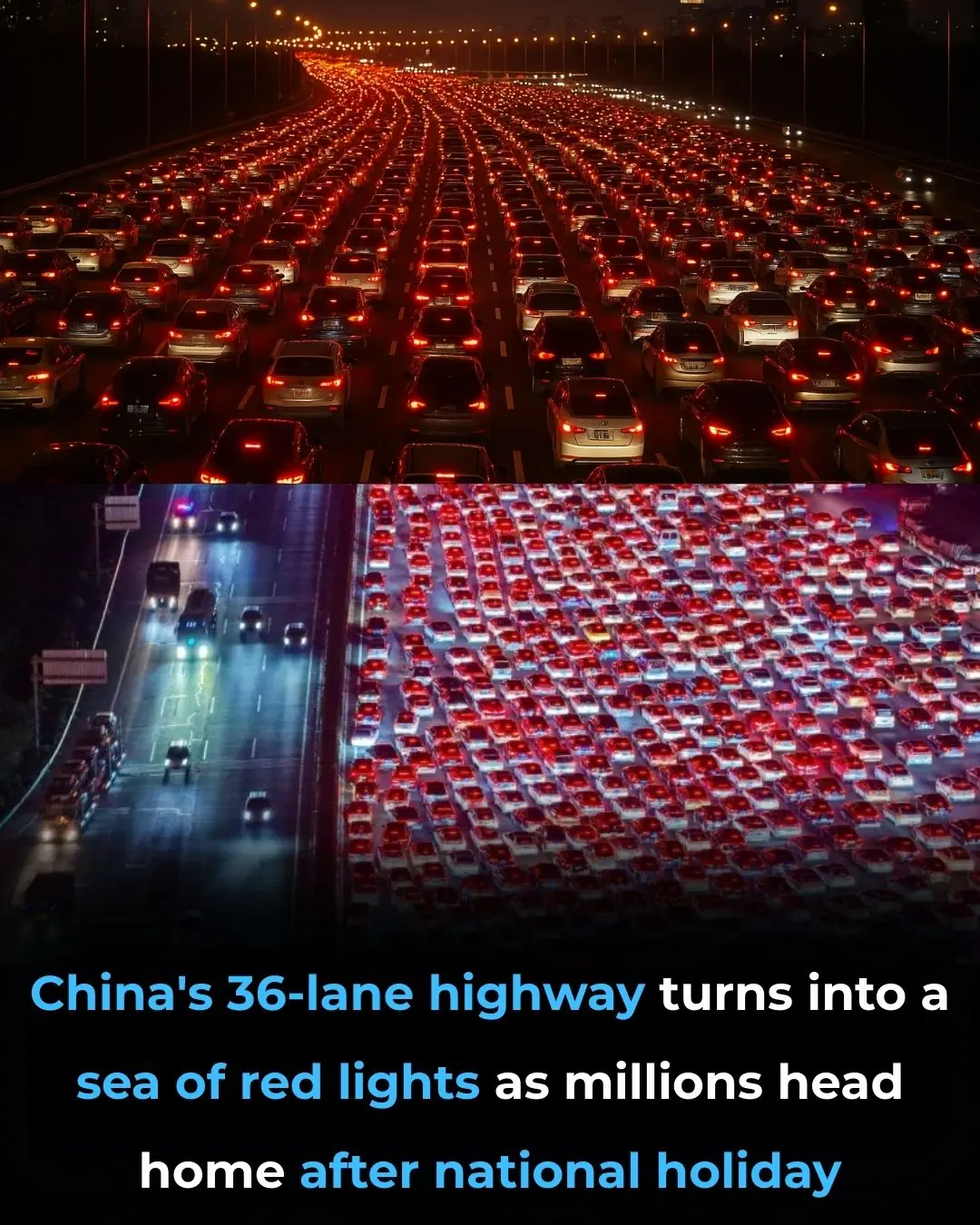
The Wuzhuang Toll Station Traffic Jam: A Glowing Sea of Red Lights and China's Growing Highway Crisis

Single Dad Dresses as Mother for Daughter's School Celebration, Showing Unconditional Love

Effective Natural Remedies for Everyday Ailments: Quick and Easy Hacks

Six-Year-Old Boy from Mizoram Shows Pure Compassion by Saving Injured Chick

The Natural Remedies That Preceded Modern Medications

The Mysterious Creator of Bitcoin and a Silent Billionaire
Green Dot On Your Phone

A Sustainable Approach to Reducing Space Debris

Scientists Restore Hearing in People Born Deaf Through Groundbreaking Gene Therapy

For The First Time In Decades, Antarctica Gained Over 100 Billion Tons Of Ice In A Single Year Instead Of Losing It

Baking Soda Solution Proven to Remove Up to 96% of Pesticides From Fruits More Effectively Than Vinegar or Plain Water

Why we help waiters: The psychology behind a simple act of kindness

A natural wonder: the woodpecker’s tongue
News Post
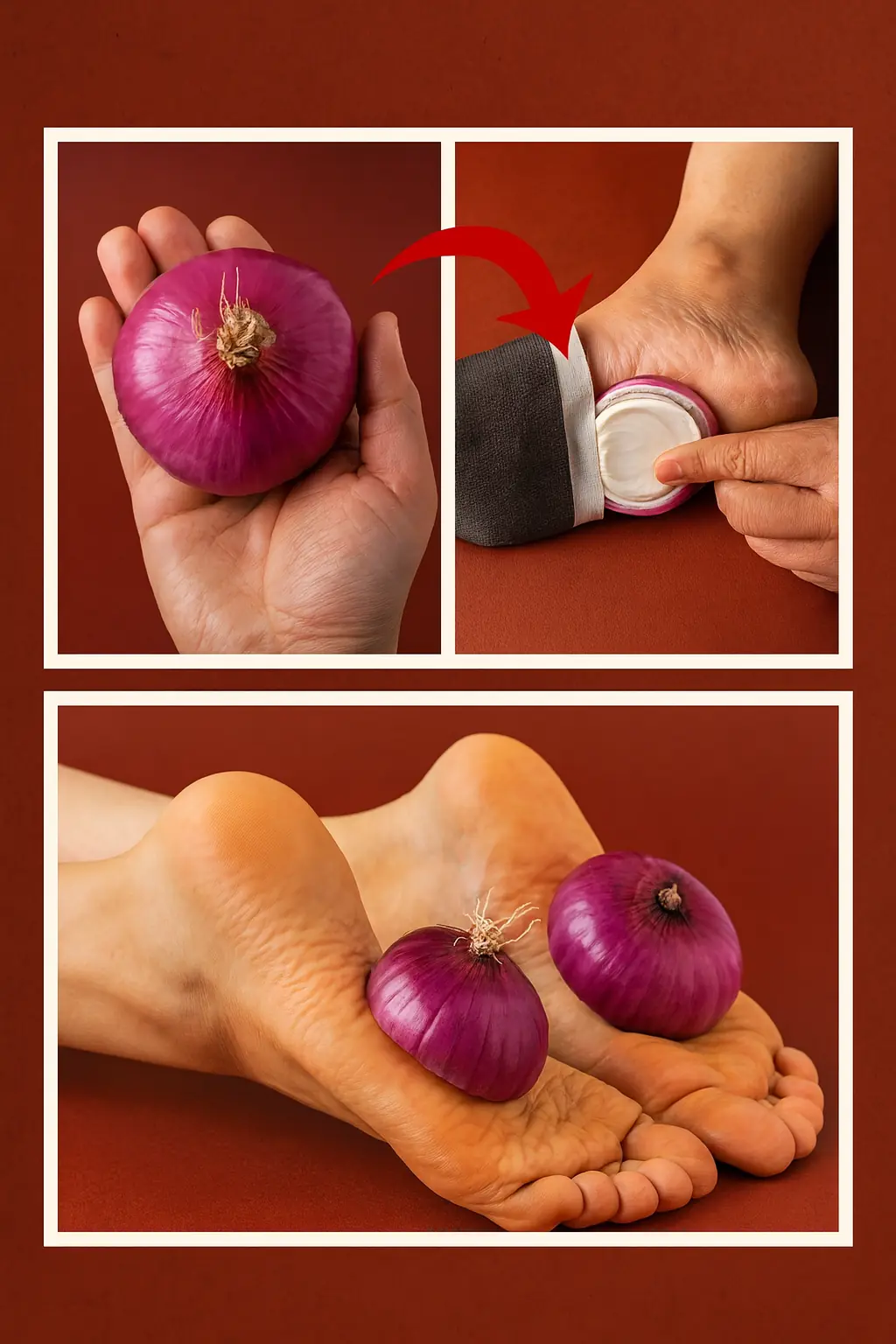

Sleeping with Onion Slices in Your Socks: A Curious Wellness Trend Explained
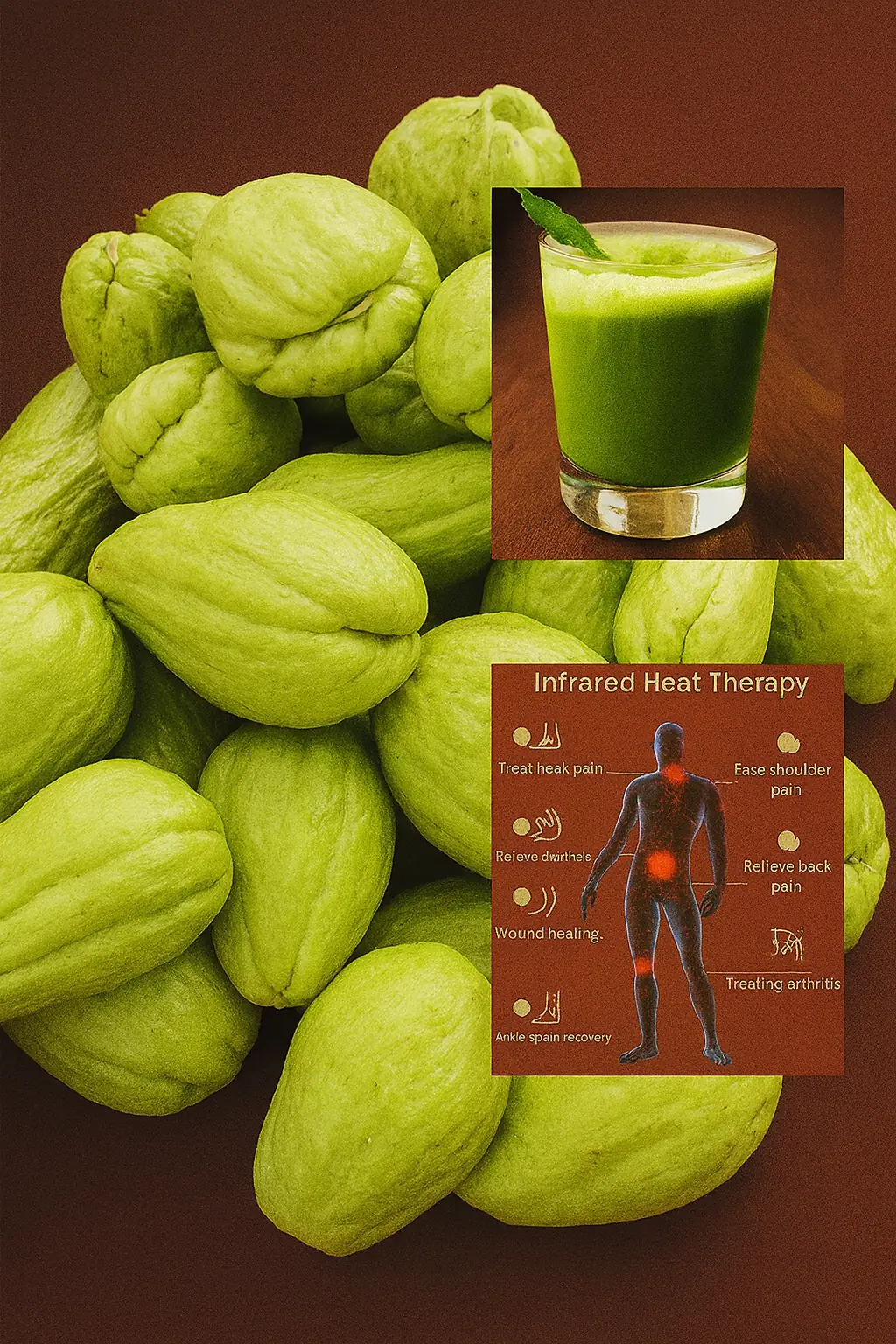

Discover the Gentle Power of Chayote: A Simple Plant with Surprising Health Benefits

The 3-Ingredient Morning Elixir That May Help Your Body Reset Naturally

Onion Juice for Hair Growth and Gray Hair: Does It Really Work?

18 Powerful Benefits of Cloves for Women (and How to Use Them Effectively)

How to Apply Lemon on Your Face with Vaseline: A Simple Brightening Cleanser That Really Works

Bay Leaves and Salt: The Powerful Home Remedy Hidden in Your Kitchen

Not Just the Fruit! Fascinating Facts About Carambola Leaves You’ll Wish You Knew Sooner

Tips for cleaning mold from your washing machine drum using inexpensive, familiar items without vinegar or bleach.

Adding a few slices of fresh lemon to your boiled eggs: Amazing benefits many people are unaware of.

Is Your Refrigerator Running Louder Than Usual? Dirty Condenser Coils Could Be the Reason

Fabric Softeners and Indoor Air Quality: Hidden Health Risks You Should Know

Is Your Toilet Sitting Position Causing Constipation? Here’s How to Fix It Naturally

The Calf Muscles: Why They Are Known as the Body’s “Second Heart”

10 Signs You’re Eating Too Much Sugar

Little Pocket in Women’s Underwear

A Decade of Struggle: The Inspiring Journey from Wrongful Conviction to Legal Triumph

Rise Tower: Saudi Arabia's 2,000-Meter Megastructure Set to Redefine the Future of Urban Living

The Wuzhuang Toll Station Traffic Jam: A Glowing Sea of Red Lights and China's Growing Highway Crisis
