
Why Toothpaste and Baking Soda Aren’t the Answer for Wrinkles and Dark Spots – And What Might Help Instead
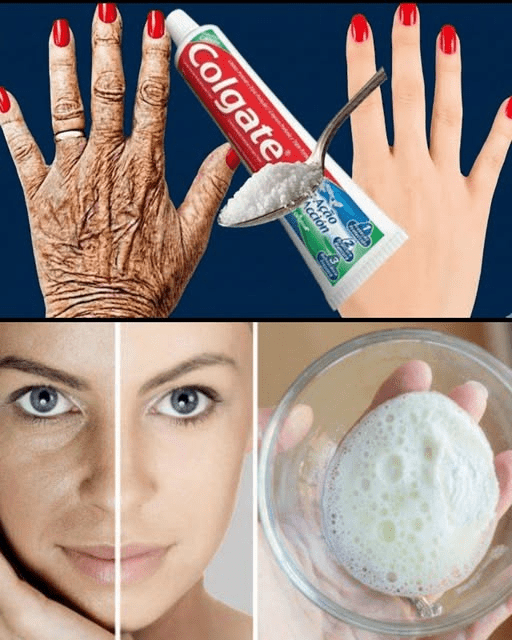

Why Toothpaste and Baking Soda Are Not Safe Solutions for Wrinkles and Dark Spots: Evidence-Based Alternatives for Healthier Skin
In recent years, social media platforms have popularized numerous “do-it-yourself” skincare hacks, many of which promote the use of household items such as toothpaste or baking soda to reduce wrinkles and dark spots. While these claims may appear appealing due to their simplicity and low cost, dermatological research consistently warns that such practices can be ineffective and potentially harmful. Understanding why these methods fail—and what science supports instead—is essential for maintaining healthy, aging skin.
Why Toothpaste and Baking Soda Can Harm Facial Skin
Toothpaste is formulated specifically for oral hygiene. It commonly contains abrasives, fluoride, menthol, and detergents designed to remove plaque and bacteria from teeth. When applied to facial skin, these ingredients can disrupt the skin’s protective barrier, leading to dryness, irritation, redness, and even chemical burns in sensitive individuals. Dermatologists emphasize that toothpaste lacks any proven benefit for treating wrinkles or hyperpigmentation (bold: American Academy of Dermatology).
Similarly, baking soda (sodium bicarbonate) poses risks due to its highly alkaline pH, which typically ranges from 8 to 9. Healthy facial skin maintains a slightly acidic pH of approximately 4.5–5.5. Applying alkaline substances can disturb this balance, weaken the skin barrier, and increase vulnerability to irritation and microbial imbalance. Research confirms that frequent exposure to high-pH substances accelerates moisture loss and inflammation (bold: International Journal of Cosmetic Science, 2018).
The Importance of Gentle, Evidence-Based Skin Care
Wrinkles and dark spots are primarily caused by ultraviolet (UV) radiation, oxidative stress, and the natural decline of collagen with age. According to bold: the American Academy of Dermatology, daily sun exposure is the leading external factor contributing to premature skin aging and hyperpigmentation.
One of the most effective and well-supported strategies for preventing wrinkles and dark spots is the consistent use of broad-spectrum sunscreen. Clinical studies show that regular sunscreen application significantly reduces photoaging and prevents the formation of new pigmentation (bold: Annals of Internal Medicine, 2013).
Hydration is another foundational element of skin health. Both internal hydration (adequate water intake) and external moisturization help maintain skin elasticity and reduce the appearance of fine lines. Well-hydrated skin reflects light more evenly, giving it a smoother, healthier appearance.
Scientifically Supported Alternatives
Several gentle, well-researched ingredients offer safer and more effective support for aging skin:
-
Vitamin C: Topical vitamin C has been shown to improve pigmentation, support collagen synthesis, and provide antioxidant protection (bold: Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology, 2017).
-
Niacinamide (Vitamin B3): Research demonstrates its ability to improve skin barrier function, reduce discoloration, and enhance overall skin tone (bold: British Journal of Dermatology, 2014).
-
Retinoids: When introduced gradually, retinoids promote cell turnover and have strong evidence supporting wrinkle reduction (bold: Archives of Dermatology, 2007).
Importantly, these ingredients require consistent, long-term use. Unlike viral “quick fixes,” their benefits accumulate gradually and safely.
Conclusion
While toothpaste and baking soda may seem like convenient skincare shortcuts, scientific evidence shows they pose unnecessary risks without offering proven benefits for wrinkles or dark spots. In contrast, gentle routines built around sun protection, hydration, antioxidants, and clinically supported ingredients provide meaningful, sustainable improvements in skin appearance. Patience, consistency, and evidence-based care remain the most reliable path to healthier, more resilient skin.
Disclaimer: This article is for educational purposes only and does not substitute professional medical advice. Individuals with sensitive skin or dermatological conditions should consult a qualified healthcare professional or dermatologist before starting new skincare routines.
News in the same category


Over 60? 10 Early Dementia Warning Signs You Must NEVER Ignore (Catch Them Before It’s Too Late)
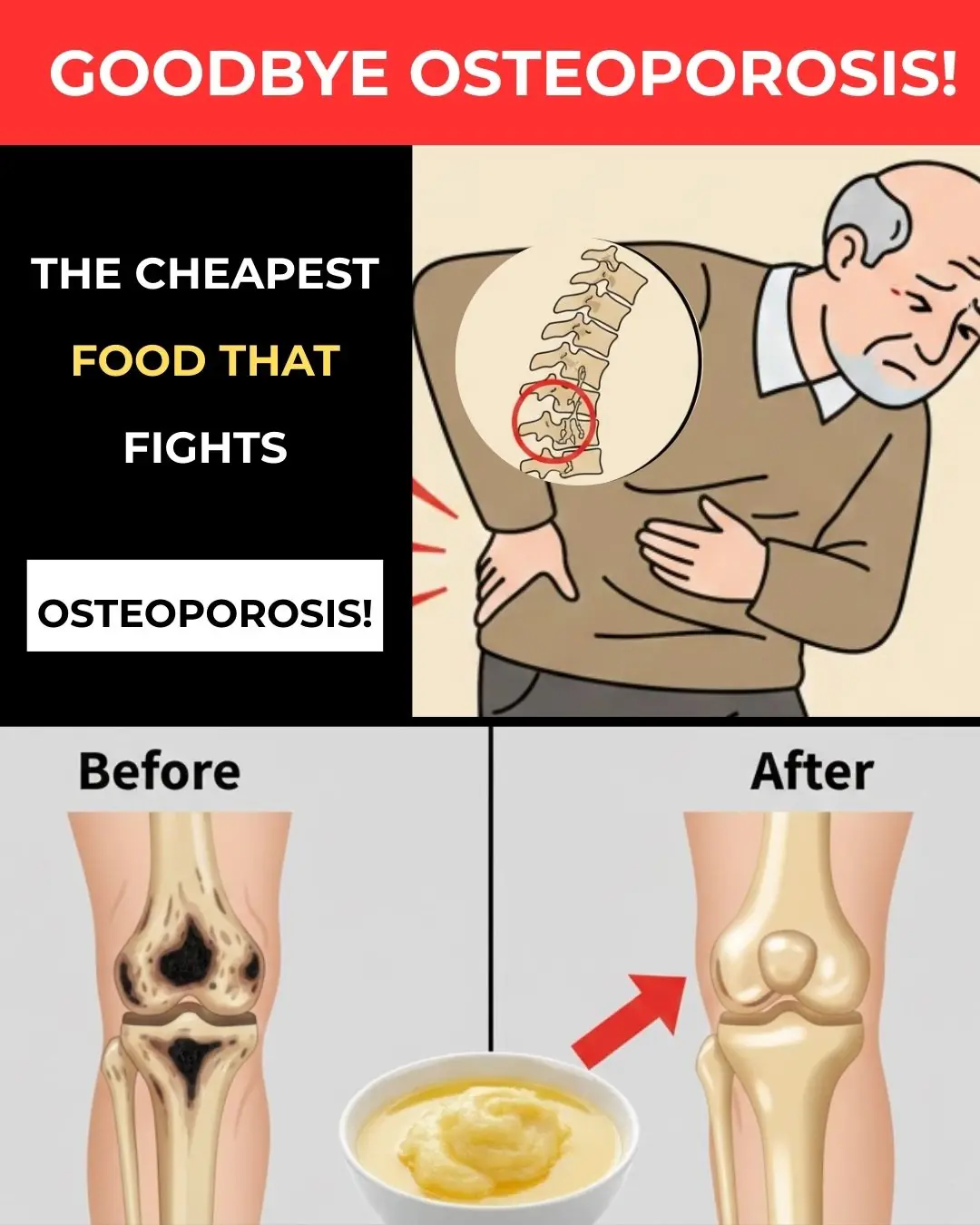
The Cheapest Superfood Most Seniors Overlook That Could Transform Bone Health After 60

9 Hidden Garlic & Honey Benefits at Night (99% Don’t Know)

Boil Cinnamon, Cloves, Garlic, Ginger, Lemon & Onion for 15 Minutes – Your Body Will Feel the Difference by Day 3

Discover Oregano: The Golden Herb That May Gently Support Your Eye Health

How to Grow Your Nails Really Fast and Long in Just 10 Days

You don’t need complicated supplements to support digestion.
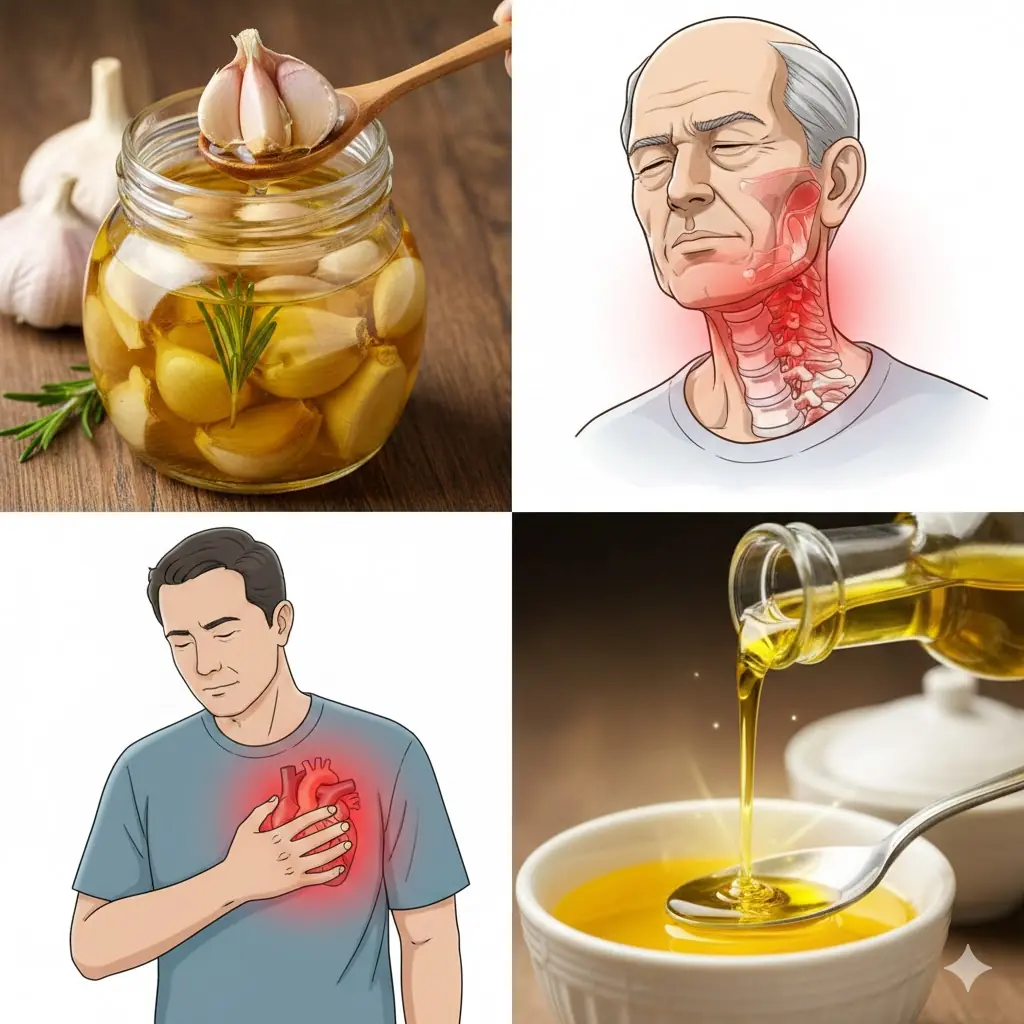
Garlic with Olive Oil Over 50: The Irreversible Body Reaction Everyone’s Talking About

Discover How Baking Soda Could Transform Your Skin’s Appearance in Minutes – Even After 70!
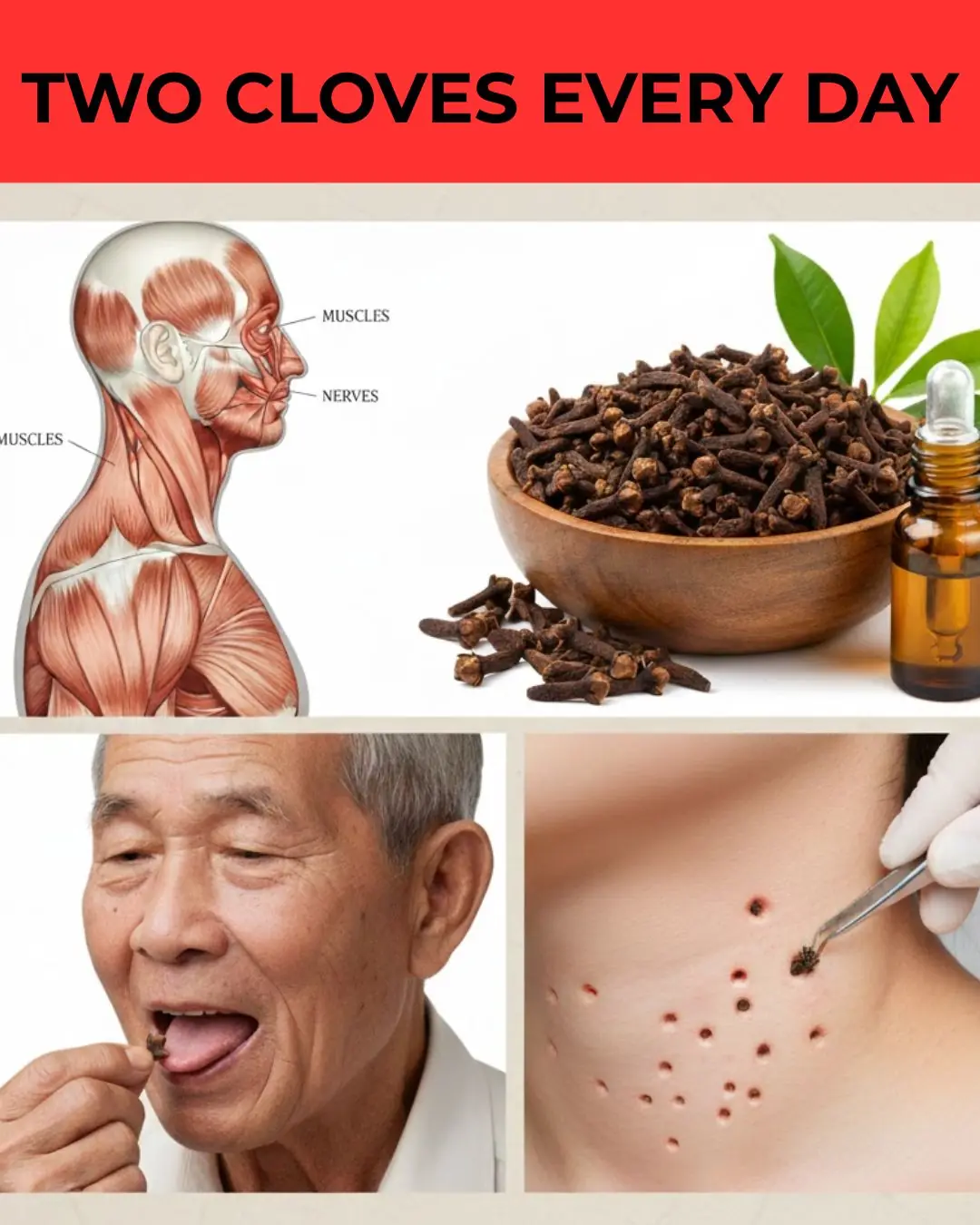
What Happens When You Add Just 2 Garlic Cloves a Day to Your Routine – Even After 50!
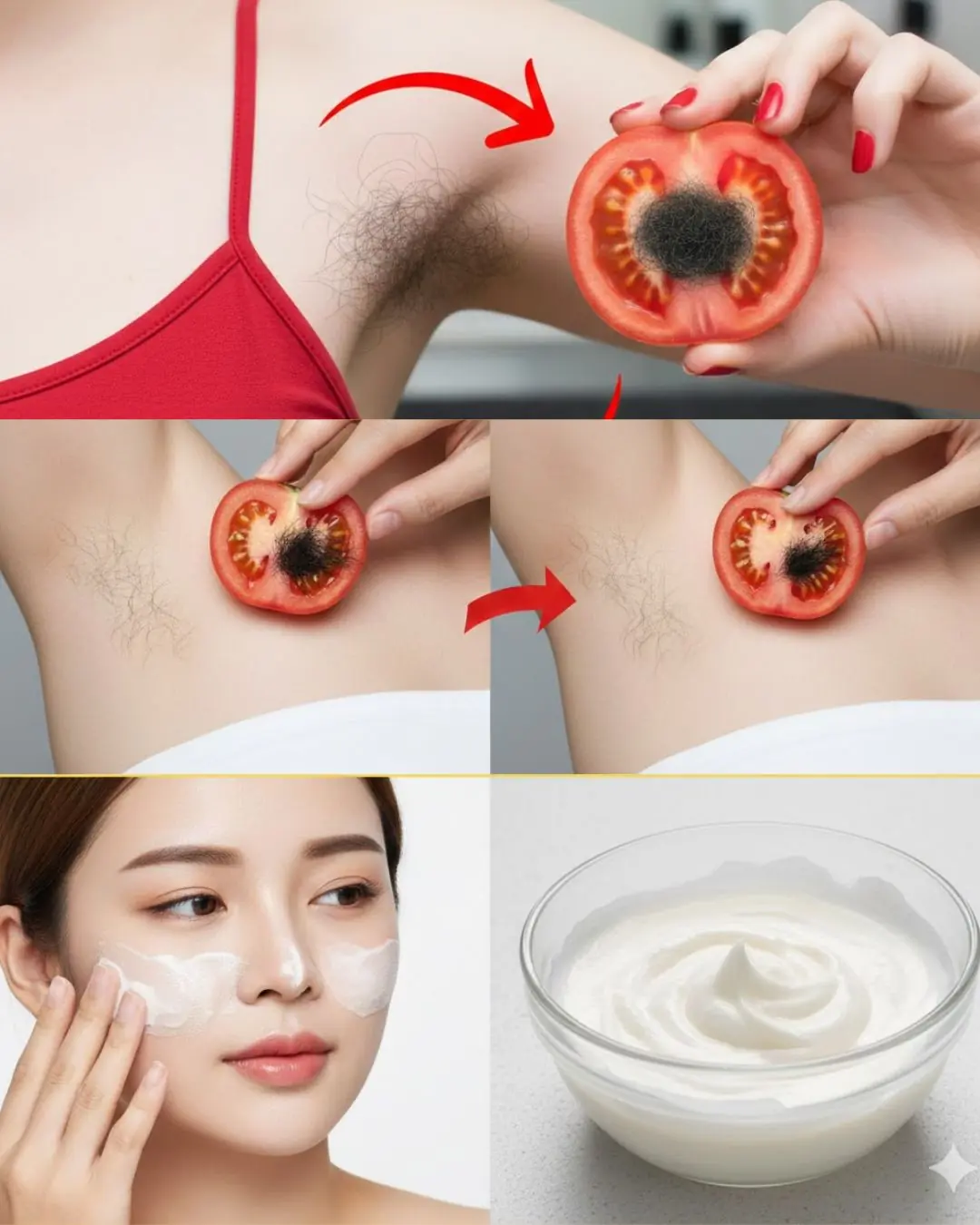
Stop Shaving? Exploring Popular Home Remedies for Hair Removal

Discover the Hidden Power of Ginger Oil: Why Women Over 65 Are Seeing Thicker, Darker Hair Naturally

Top 10 Foods That May Help Reduce Frequent Nighttime Urination (Nocturia)

Top Superfoods That Could Support Your Kidney Health in Just 30 Days – The Natural Boost You’ve Been Missing!

Top 10 Simple Exercises to Improve Circulation & Blood Flow in Your Feet and Legs (Seniors Must Try!)
Cancer Hates These 6 Seeds: Seniors, Add Them Daily for Natural Antioxidant Support!
11 Bedtime Drinks That Help LOWER Creatinine & Repair Your Kidneys Overnight (Starting Tonight!)
News Post

The Lasting Power of Soulful Connection: How Kindness Leaves an Eternal Imprint

Olympian Gus Kenworthy Rescues 90 Dogs From South Korean Meat Farm, Turning Compassion Into Action

Crush Papaya Leaves Every Night – Your White Hair May Start Turning Dark and Growing Like Crazy by Morning
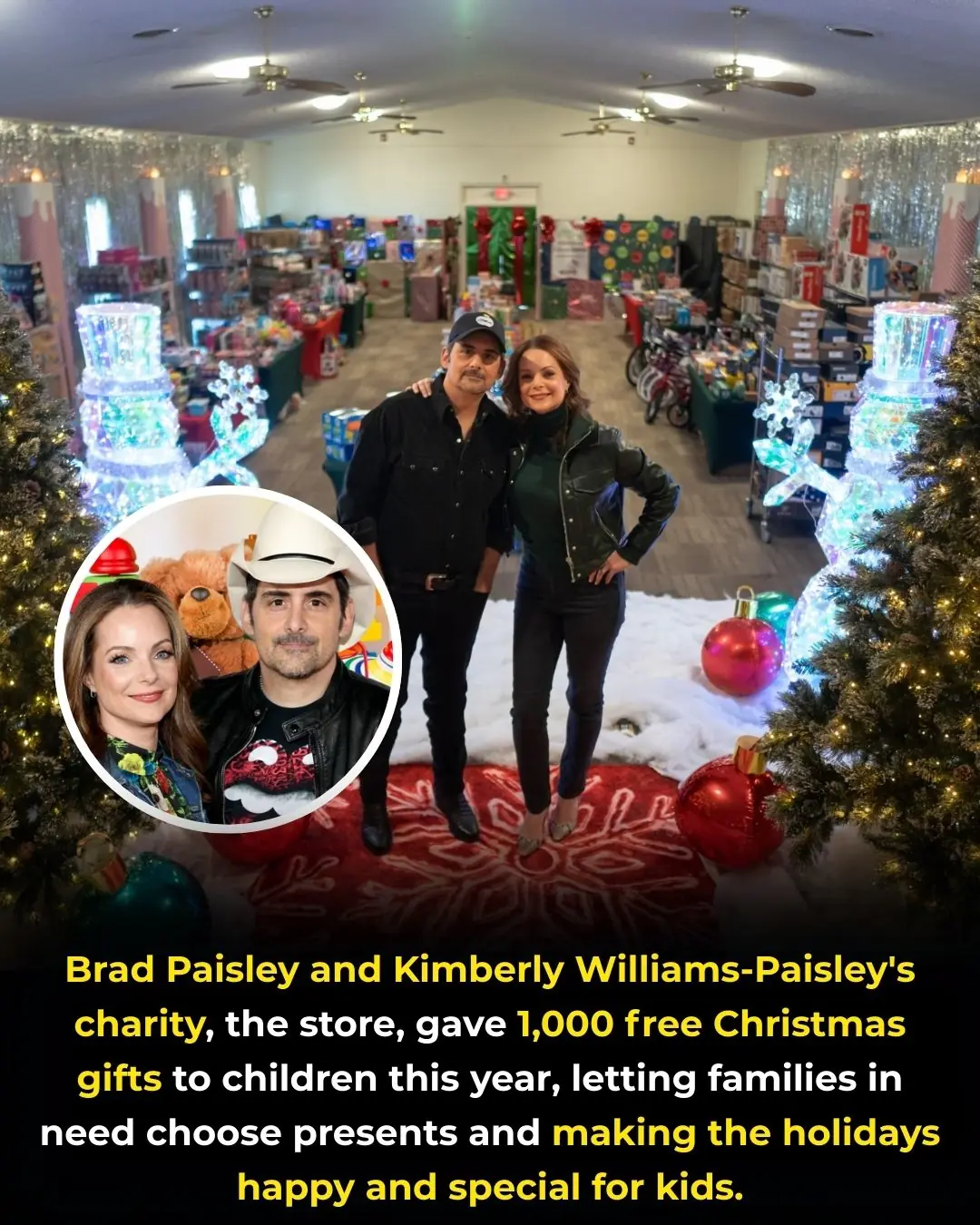

Brad Paisley and Kimberly Williams-Paisley Spread Holiday Joy by Giving 1,000 Christmas Gifts to Children in Need

Over 60? 10 Early Dementia Warning Signs You Must NEVER Ignore (Catch Them Before It’s Too Late)

The Cheapest Superfood Most Seniors Overlook That Could Transform Bone Health After 60

9 Hidden Garlic & Honey Benefits at Night (99% Don’t Know)

Boil Cinnamon, Cloves, Garlic, Ginger, Lemon & Onion for 15 Minutes – Your Body Will Feel the Difference by Day 3

Discover Oregano: The Golden Herb That May Gently Support Your Eye Health
The Cardiovascular Benefits of Pomegranate Juice: Scientific Evidence and Mechanisms

How to Grow Your Nails Really Fast and Long in Just 10 Days

You don’t need complicated supplements to support digestion.

This Flight Landed Before It Took Off — Thanks to Time Zones

The Legendary 2004 Harvard–Yale Prank That Outsmarted the Crowd and Made History

Behind the Mask: How a Mexican Priest Fought in the Ring to Protect Orphans

Arlington Mom Welcomes Giant Baby Boy

Trump Orders Transgender Male Inmates to Be Housed in Men’s Prisons, Sparking Nationwide Debate

Yurok Tribe Reclaims 47,000 Acres of Ancestral Land in Historic California Land-Back Deal

A First-Class Act of Kindness at 30,000 Feet
