Chronic Gastritis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
Chronic gastritis is a long-term inflammatory condition that affects the lining of the stomach. Unlike acute gastritis, which develops suddenly and often resolves quickly, chronic gastritis progresses slowly over months or years. Over time, the persistent inflammation can damage the stomach lining, reduce stomach acid production, interfere with nutrient absorption, and increase the risk of ulcers and even stomach cancer.
Because the symptoms can be subtle or appear only intermittently, many people overlook early warning signs. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatment options is essential to preventing long-term complications.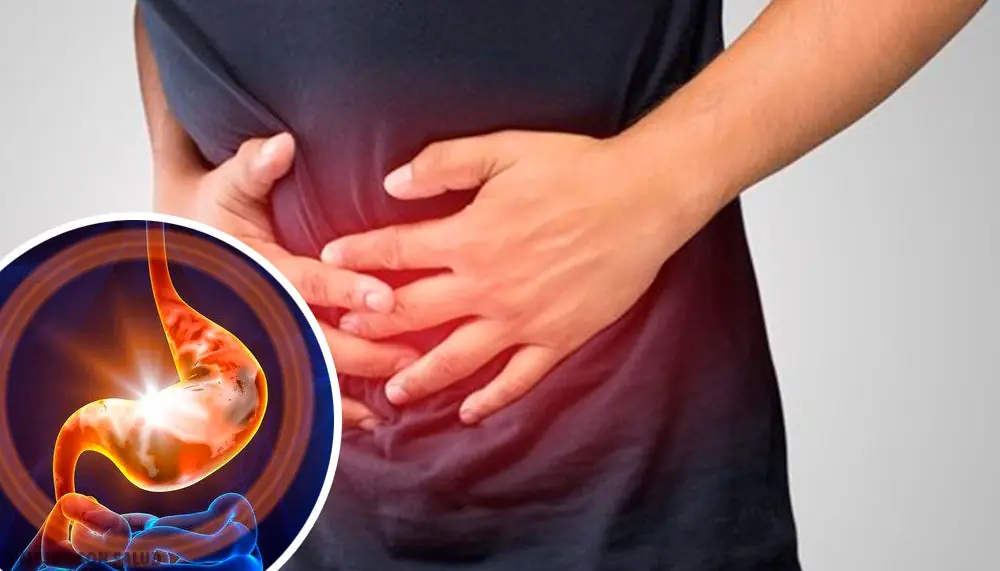
What Is Chronic Gastritis?
The stomach lining contains specialized cells responsible for producing mucus, stomach acid, and digestive enzymes. In chronic gastritis, these cells become damaged due to persistent inflammation. If the damage continues, the stomach lining can thin out (a condition called atrophic gastritis), reducing its protective function.
This condition is common across all age groups but becomes more frequent as people get older. Many cases remain undiagnosed because the symptoms can mimic common digestive issues.
Common Causes of Chronic Gastritis
Several underlying factors can trigger long-term inflammation in the stomach:
1. Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection
This bacteria is the leading cause of chronic gastritis globally. H. pylori weakens the protective mucus layer, allowing acid to irritate the stomach lining. Without treatment, the infection can persist for decades.
2. Long-term use of NSAIDs
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen, aspirin, and naproxen are known to irritate the stomach lining. Overuse reduces the stomach’s ability to produce protective mucus, leading to chronic inflammation.
3. Excessive alcohol consumption
Alcohol acts as a stomach irritant and can inflame the lining when consumed regularly or in large amounts.
4. Autoimmune disorders
Autoimmune gastritis occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks the stomach lining. This type is often linked to vitamin B12 deficiency and can lead to anemia.
5. Stress and lifestyle factors
Long-term stress, irregular eating habits, smoking, and high caffeine consumption can all contribute to chronic irritation and inflammation.
6. Older age
As people age, the stomach lining naturally becomes thinner and more vulnerable to inflammation.
Symptoms of Chronic Gastritis
Symptoms vary based on the severity of the inflammation and the underlying cause. Some people experience constant discomfort, while others feel symptoms only after meals.
Common signs include:
-
Persistent upper abdominal pain or burning
-
Bloating or feeling overly full after eating
-
Nausea and occasional vomiting
-
Loss of appetite
-
Burping and acid reflux
-
Black or tarry stools (indicating bleeding)
-
Fatigue (usually due to anemia)
-
Unexplained weight loss
Because these symptoms overlap with other digestive conditions, proper medical evaluation is essential.
Potential Complications
If left untreated, chronic gastritis can gradually worsen and lead to serious complications:
-
Peptic ulcers
-
Vitamin B12 deficiency
-
Iron-deficiency anemia
-
Stomach polyps
-
Atrophic gastritis
-
Higher risk of stomach cancer
The good news: early treatment significantly reduces these risks.
Diagnosis of Chronic Gastritis
Doctors use several methods to diagnose this condition:
1. Endoscopy
A thin tube with a camera is inserted into the stomach to inspect the lining for redness, thinning, or bleeding.
2. H. pylori testing
This may include blood tests, stool samples, breath tests, or biopsies.
3. Blood tests
These check for anemia, vitamin deficiencies, and immune system activity.
4. Stool tests
Used to detect blood or infection in the digestive tract.
Treatment Options
Effective treatment depends on the cause:
1. Treating H. pylori
When bacteria is present, doctors prescribe a combination of antibiotics and acid-reducing medications to eradicate it.
2. Reducing stomach acid
Medications include:
-
Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs)
-
H2 blockers
-
Antacids
These help protect the stomach lining and promote healing.
3. Lifestyle and dietary changes
-
Avoid spicy, fried, or acidic foods
-
Limit alcohol and caffeine
-
Eat smaller, more frequent meals
-
Reduce stress
-
Quit smoking
4. Supplements
Vitamin B12 or iron supplements may be necessary for those with deficiencies.
When to Seek Medical Help
You should consult a doctor if you experience:
-
Severe or persistent stomach pain
-
Blood in stool or vomit
-
Sudden unexplained weight loss
-
Symptoms lasting more than two weeks
Conclusion
Chronic gastritis is a slow-progressing condition that can significantly impact your digestive health if left unmanaged. The key lies in early detection, proper diagnosis, and consistent lifestyle adjustments. With the right treatment, most people recover fully and avoid long-term complications.
News in the same category

Lung Cancer: 8 Common Symptoms Often Misdiagnosed

Type 2 Diabetes: Early Symptoms and Effective Ways to Control It

Winter Vomiting Disease On Uptick In Midwest
A Potentially Fatal New Covid-related Syndrome Has Emerged
The FIRST Sign of VITAMIN B12 DEFICIENCY Is…

Your Body Is Lacking Magnesium If…

Two handfuls of peanuts daily boost memory in 4 months
Fatty Liver Disease: What Doctors Want You to Know Early
Silent Kidney Disease: Symptoms, Causes, and Prevention Tips
10 Warning Signs of Heart Disease Most People Ignore

Doctors reveal that eating beets causes...

People with heart problems should avoid these 4 things to reduce stimulation to the heart
12 Bizarre Symptoms of Vitamin D Deficiency You Need to Know
Natural Remedies and Prevention Strategies for Bunions: What Really Works
Natural Scar Remedies: How Scars Form and the Most Effective Evidence-Based Treatments to Help Them Fade
Eight Digestive Red Flags You Should Never Ignore: Causes, Risks, and When to Seek Medical Care
A Complete Guide to Bulging Veins: Causes, Complications, and Care

The Myth of “Safe” Smoking Debunked: How Minimal Tobacco Use Still Damages the Body
News Post

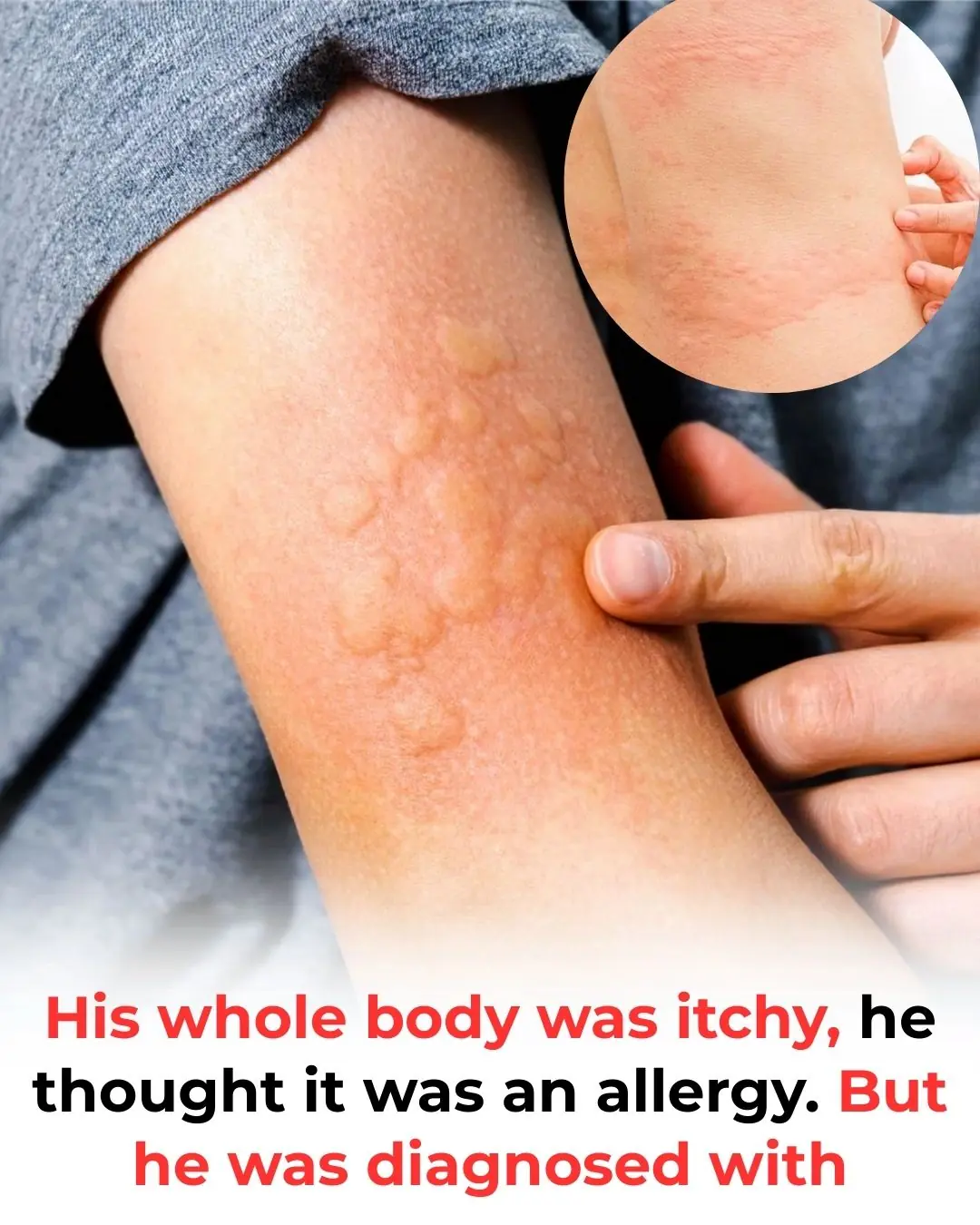
His whole body was itchy, he thought it was an allergy but then he was diagnosed

Lung Cancer: 8 Common Symptoms Often Misdiagnosed

Type 2 Diabetes: Early Symptoms and Effective Ways to Control It

Winter Vomiting Disease On Uptick In Midwest

A Potentially Fatal New Covid-related Syndrome Has Emerged
Stroke in Young Adults: Why It’s Becoming More Common

The FIRST Sign of VITAMIN B12 DEFICIENCY Is…

Your Body Is Lacking Magnesium If…

Two handfuls of peanuts daily boost memory in 4 months

Fatty Liver Disease: What Doctors Want You to Know Early

15 Plants That Can Grow Easily in Water — A Beautiful, Soil-Free Way to Green Your Home

Most people get this wrong and toss out the can. Here’s the right way to read ‘Best By’ or ‘Best Before’ dates

I Had No Idea! The Remarkable Story of the Stone Breaker Plant

Stop throwing out old hoses — 10 brilliant hacks to use them around the house

This Method Is So Brilliant — I Wish I’d Thought of It Sooner!

Silent Kidney Disease: Symptoms, Causes, and Prevention Tips

When boiling duck, don't add ginger and cold water: Add this and the meat will lose all its stench, and you won't get tired of eating it.

How to make steamed chicken with lemongrass, golden brown chicken, soft and delicious, irresistible
