Type 2 Diabetes: Early Symptoms and Effective Ways to Control It
Type 2 diabetes is becoming one of the fastest-growing chronic diseases worldwide — and it’s no longer limited to older adults. Younger individuals, even teenagers, are now developing diabetes due to changes in diet, lifestyle, and stress levels. Detecting symptoms early and knowing how to manage blood sugar can prevent severe complications later in life.
This article covers early warning signs, major causes, and proven ways to control Type 2 diabetes effectively.
1. What Is Type 2 Diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or does not produce enough of it. Insulin helps move sugar from the bloodstream into cells for energy. When insulin isn’t working properly, sugar builds up in the blood — causing long-term damage to the heart, kidneys, nerves, and eyes.
2. Early Symptoms You Should Never Ignore
Excessive Thirst
High blood sugar pulls fluid from tissues, making you feel thirsty constantly.
Frequent Urination
Your kidneys work harder to remove excess sugar, causing frequent urination — especially at night.
Constant Fatigue
Sugar can't enter cells efficiently, leaving you tired even after resting.
Increased Hunger
When cells lack energy, your body signals hunger even if you’ve just eaten.
Blurry Vision
High glucose levels affect the tiny blood vessels in your eyes.
Slow-Healing Wounds or Infections
Cuts, bruises, and infections heal more slowly due to impaired circulation and immune function.
Tingling Hands and Feet
Nerve damage can occur early, causing numbness or tingling sensations.
3. What Causes Type 2 Diabetes?
Poor Diet
High consumption of:
-
Sweetened beverages
-
White rice, white bread
-
Fast food
-
Processed snacks
-
High-calorie desserts
leads to insulin resistance.
Sedentary Lifestyle
Desk jobs and low physical activity prevent your body from using glucose efficiently.
Obesity and Belly Fat
Excess belly fat increases inflammation and directly affects insulin sensitivity.
Genetics
A family history of diabetes greatly increases risk — especially in Asian populations.
Chronic Stress
Stress hormones raise blood sugar levels over time.
Lack of Sleep
Poor sleep disrupts hormones that control appetite and insulin.
4. Effective Ways to Control and Reverse Type 2 Diabetes
Eat a Balanced, Low-Glycemic Diet
Focus on:
-
Vegetables
-
Whole grains
-
Lean proteins
-
Healthy fats
-
Low-sugar fruits
Avoid high-glycemic foods that spike blood sugar.
Exercise Regularly
Aim for:
-
150 minutes of moderate exercise per week
-
Strength training 2–3 times weekly
Exercise increases insulin sensitivity and helps burn stored glucose.
Maintain a Healthy Weight
Losing even 5–10% of body weight can significantly improve blood sugar levels.
Stay Hydrated
Drinking water helps the kidneys flush out excess sugar naturally.
Manage Stress
Try:
-
Meditation
-
Deep breathing
-
Yoga
-
Walking
-
Digital detox
Reducing stress stabilizes blood sugar swings.
Get Enough Sleep
Aim for 7–8 hours per night to support hormonal balance.
Monitor Blood Sugar
Regular monitoring helps you understand patterns and adjust lifestyle habits accordingly.
Take Medications if Needed
Doctors may prescribe:
-
Metformin
-
Insulin (if required)
-
GLP-1 agonists
-
Other sugar-lowering medications
Medication plus lifestyle control works best for long-term health.
Conclusion
Type 2 diabetes develops quietly — sometimes with no obvious symptoms at all. Recognizing early signs and taking control of your lifestyle can prevent complications and even reverse the condition in many cases. Your daily habits are the most powerful tool you have to protect your long-term health.
News in the same category


A major shredded cheese recall: here’s what shoppers need to check
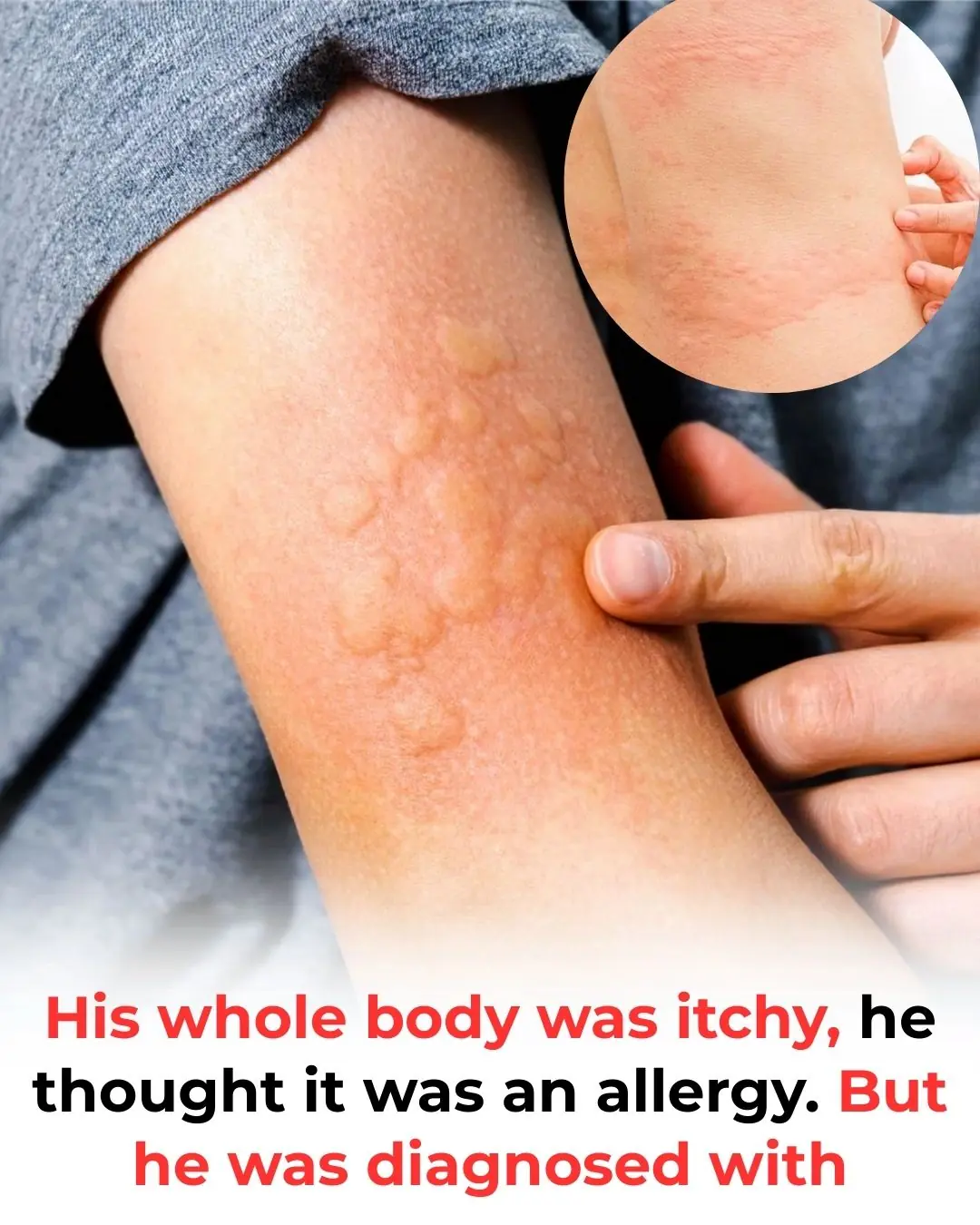
His whole body was itchy, he thought it was an allergy but then he was diagnosed
Chronic Gastritis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
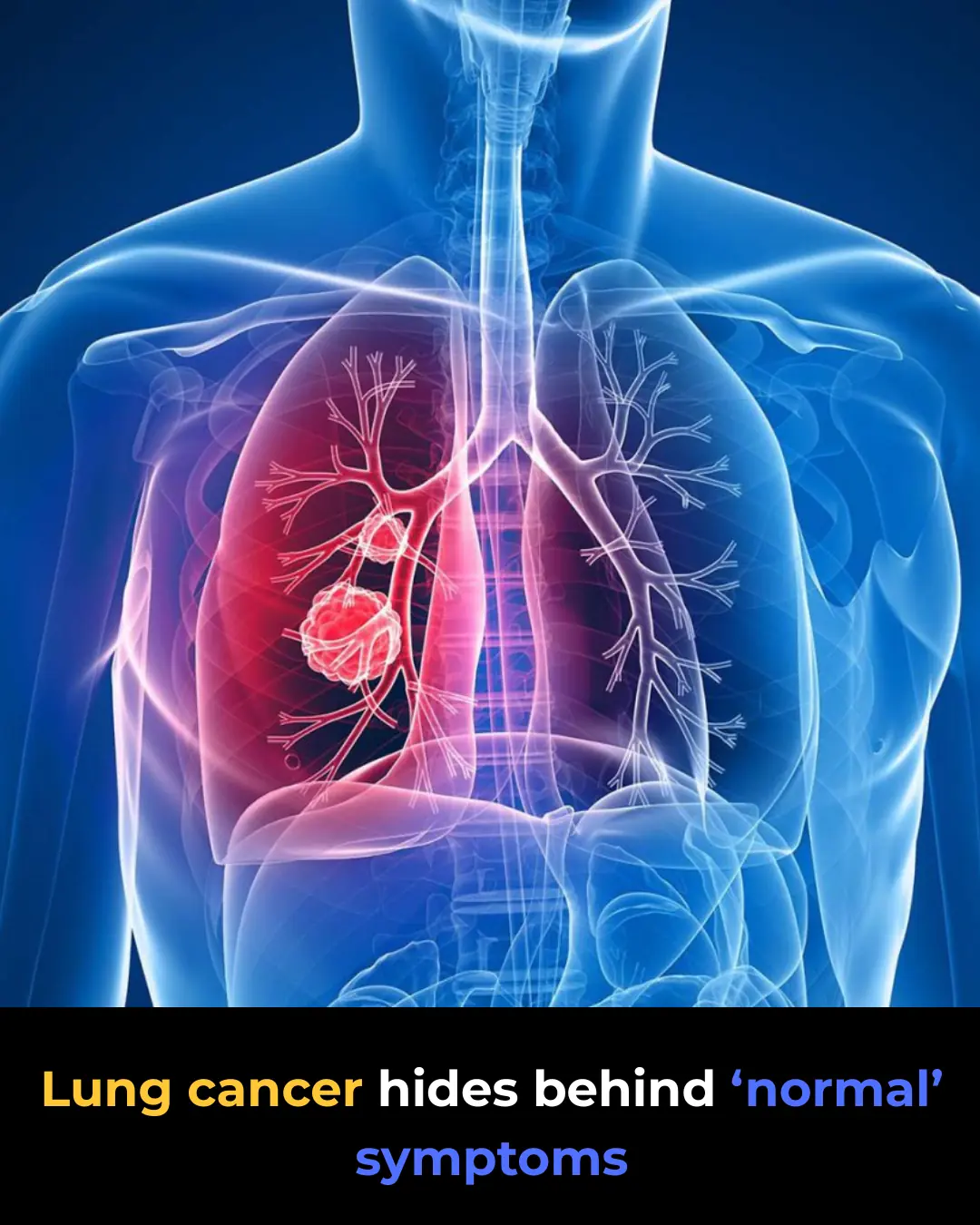
Lung Cancer: 8 Common Symptoms Often Misdiagnosed

Winter Vomiting Disease On Uptick In Midwest
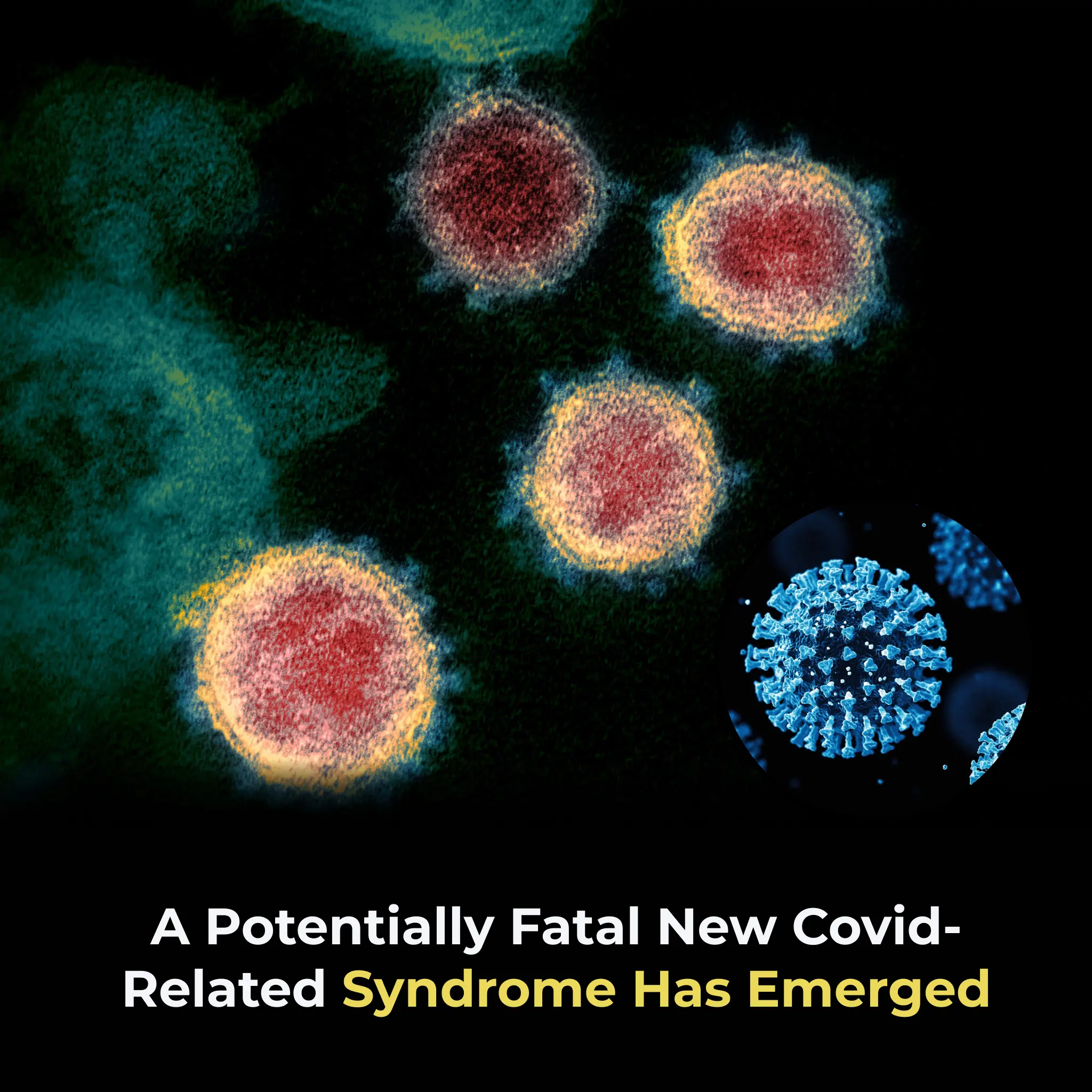
A Potentially Fatal New Covid-related Syndrome Has Emerged
The FIRST Sign of VITAMIN B12 DEFICIENCY Is…

Your Body Is Lacking Magnesium If…

Two handfuls of peanuts daily boost memory in 4 months
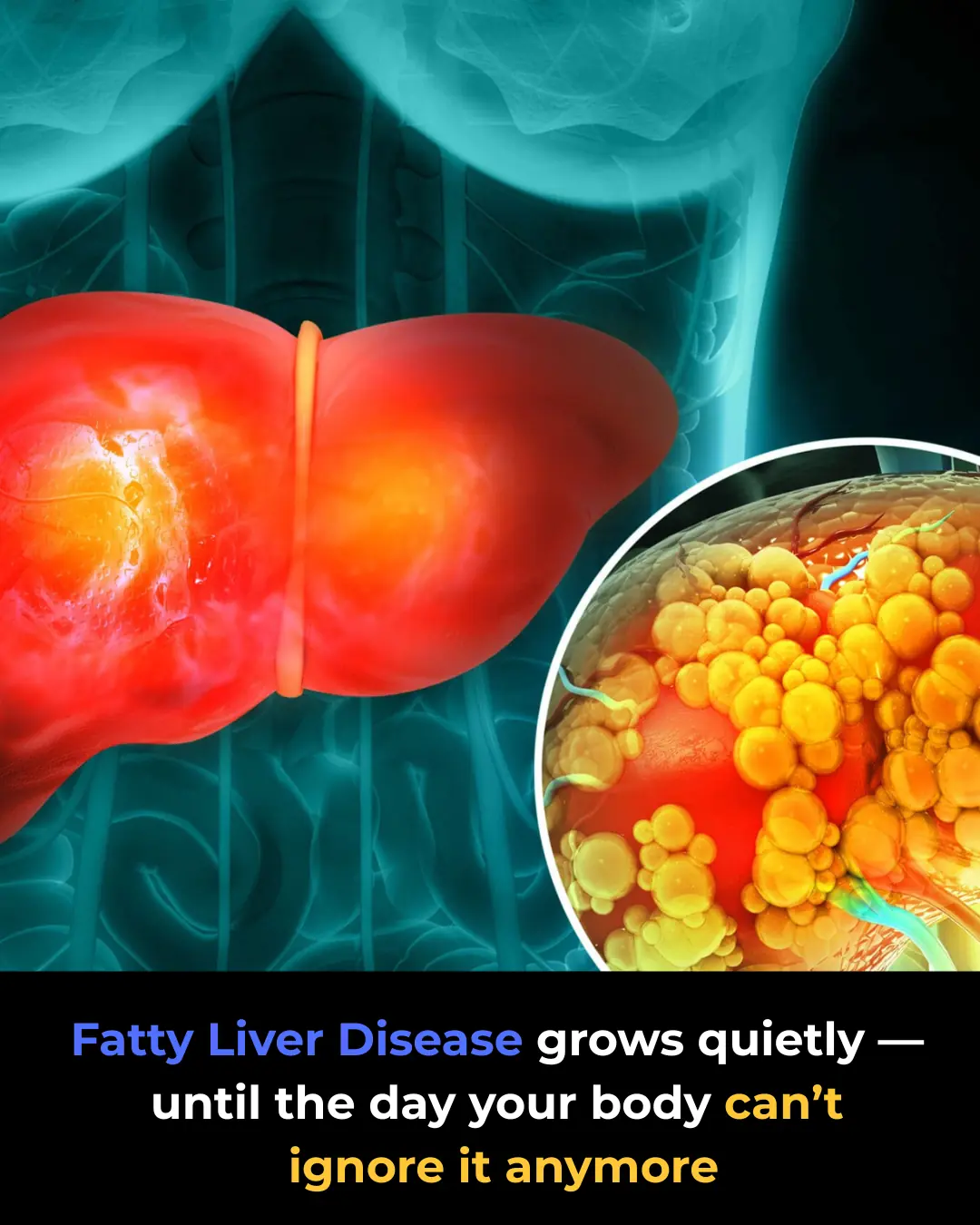
Fatty Liver Disease: What Doctors Want You to Know Early
Silent Kidney Disease: Symptoms, Causes, and Prevention Tips
10 Warning Signs of Heart Disease Most People Ignore

Doctors reveal that eating beets causes...

People with heart problems should avoid these 4 things to reduce stimulation to the heart
12 Bizarre Symptoms of Vitamin D Deficiency You Need to Know
Natural Remedies and Prevention Strategies for Bunions: What Really Works
Natural Scar Remedies: How Scars Form and the Most Effective Evidence-Based Treatments to Help Them Fade
Eight Digestive Red Flags You Should Never Ignore: Causes, Risks, and When to Seek Medical Care
News Post

Millions of glucose monitors recalled across 17 countries — here’s what users should check

A major shredded cheese recall: here’s what shoppers need to check

His whole body was itchy, he thought it was an allergy but then he was diagnosed

Chronic Gastritis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options

Lung Cancer: 8 Common Symptoms Often Misdiagnosed

Winter Vomiting Disease On Uptick In Midwest

A Potentially Fatal New Covid-related Syndrome Has Emerged
Stroke in Young Adults: Why It’s Becoming More Common

The FIRST Sign of VITAMIN B12 DEFICIENCY Is…

Your Body Is Lacking Magnesium If…

Two handfuls of peanuts daily boost memory in 4 months

Fatty Liver Disease: What Doctors Want You to Know Early

15 Plants That Can Grow Easily in Water — A Beautiful, Soil-Free Way to Green Your Home

Most people get this wrong and toss out the can. Here’s the right way to read ‘Best By’ or ‘Best Before’ dates

I Had No Idea! The Remarkable Story of the Stone Breaker Plant

Stop throwing out old hoses — 10 brilliant hacks to use them around the house

This Method Is So Brilliant — I Wish I’d Thought of It Sooner!

Silent Kidney Disease: Symptoms, Causes, and Prevention Tips
