
Doctors prescribe LEVOTHYROXINE—but here’s what they don’t tell you
Levothyroxine is a synthetic form of the thyroid hormone thyroxine (T4), widely prescribed for people with hypothyroidism and other thyroid-related conditions. It mimics the action of hormones naturally produced by your thyroid gland, helping regulate vital body functions. In fact, it’s one of the most prescribed medications worldwide—millions of people take it daily to restore normal thyroid balance.
However, despite its widespread use, many patients remain unaware of how this medication truly works. Small mistakes in timing, dosage, or interactions with food and supplements can significantly reduce its effectiveness. This can turn a helpful treatment into a frustrating challenge.
In this article, we’ll explore what levothyroxine is, how it works, how to take it properly, and common questions people have about it—based on medical insights from Dr. Alberto Sanagustín and updated clinical recommendations.
What Is Levothyroxine and What Is It Used For?
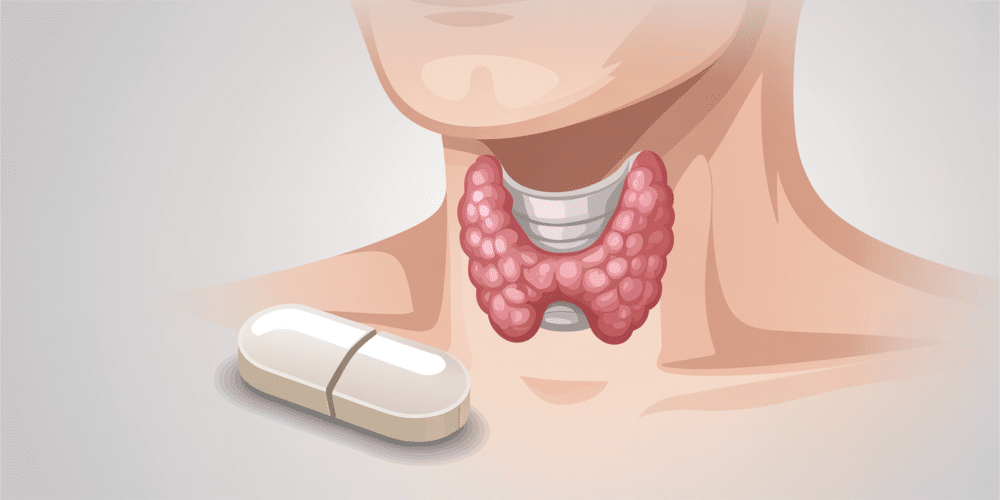
Levothyroxine is a synthetic version of thyroxine (T4), one of the two main hormones produced by the thyroid gland. Your thyroid plays a crucial role in regulating metabolism, energy production, and growth. When it underperforms—a condition known as hypothyroidism—you may experience symptoms like fatigue, weight gain, sensitivity to cold, constipation, hair loss, and dry skin.
Levothyroxine replaces the missing hormone, helping restore the body’s normal metabolic rhythm. By doing so, it improves energy levels, stabilizes mood, and supports healthy organ function.
It’s also used in other situations, such as after thyroid surgery, to suppress the growth of thyroid nodules or to prevent cancer recurrence. When taken correctly under medical supervision, it’s a safe and highly effective therapy.
How Does Levothyroxine Work in the Body?
Once taken orally, levothyroxine is absorbed in the intestine and converted into triiodothyronine (T3), the active form of thyroid hormone. T3 acts on nearly every cell in the body, influencing how fast or slow various systems function—heart rate, temperature control, digestion, and even mental alertness.
In hypothyroid patients, this replacement restores metabolic balance. However, because every person’s body absorbs and processes the drug differently, the dosage must be customized. Too much can cause symptoms of hyperthyroidism (anxiety, palpitations, insomnia), while too little can leave you feeling sluggish and tired. Regular blood tests are essential to fine-tune the correct dose.
Key Facts and Guidelines
-
Levothyroxine is a synthetic T4 hormone that replaces what your thyroid doesn’t produce.
-
It regulates metabolism, body temperature, heart rate, and more.
-
Take it on an empty stomach, at least 30–60 minutes before breakfast, with a full glass of water.
-
Avoid taking it with coffee, milk, calcium, or iron supplements, which reduce absorption.
-
Keep your timing consistent each day.
-
Dosage may change during pregnancy, weight fluctuations, or medication changes.
-
If you miss a dose, take it when remembered—never double up.
-
Do not switch brands without your doctor’s approval.
-
Store in a cool, dry place away from light and heat.
-
It can take 2–6 weeks to notice full improvement.
-
Treatment is often lifelong for chronic hypothyroidism.
-
Regular TSH and Free T4 blood tests are crucial for dose adjustments.
-
Be mindful of interactions with coffee, soy, high-fiber foods, and supplements.
-
Common side effects only occur with incorrect dosing.
Levothyroxine vs. Other Hypothyroidism Treatments
Levothyroxine remains the gold standard treatment for hypothyroidism. It provides a precise, stable, and predictable dose of T4, which your body can naturally convert to T3 as needed.
Older therapies—like desiccated thyroid extract from pigs—contain both T4 and T3 but in inconsistent ratios, making dosage control harder. Some people may benefit from combination T4/T3 therapy, but for most, levothyroxine alone ensures a smoother, more stable hormone level and fewer side effects.
How to Take Levothyroxine Correctly
Taking levothyroxine properly is crucial for it to work effectively.
Here’s how to do it right:
-
Take one tablet every morning, 30–60 minutes before eating or drinking anything except water.
-
Swallow it whole with a full glass of water—don’t crush or chew it.
-
Avoid taking it alongside coffee, tea, milk, calcium, or iron supplements, as they reduce absorption.
-
Stick to the same time every day to maintain steady hormone levels.
-
If mornings are difficult, you can take it at bedtime, as long as you haven’t eaten for at least 3–4 hours.
What Determines the Correct Dosage?
There’s no universal dosage—it depends on age, weight, overall health, and lab results. Doctors start with a low dose and adjust it based on TSH and Free T4 levels after 6–8 weeks.
You should never adjust your dose on your own, even if you still feel tired or sluggish. Hormonal balance takes time, and both underdosing and overdosing can cause serious issues.
What If You Miss a Dose?
If you forget to take a dose, take it as soon as you remember—unless it’s close to your next scheduled time. In that case, skip it. Never double up. Missing an occasional dose is not dangerous, but frequent lapses can cause your hormone levels to fluctuate, making symptoms return.
Can I Switch Levothyroxine Brands?
Different brands may contain the same active ingredient but have different inactive fillers that can affect absorption. Therefore, once you find a brand that works for you, stay consistent. If a pharmacy substitutes a different one, let your doctor know. You might need a blood test after switching to ensure stability.
Proper Storage
Store levothyroxine in its original container, away from heat, light, and humidity. Avoid bathrooms and kitchens. The optimal storage temperature is between 15–30°C (59–86°F). Keep it tightly sealed and out of children’s reach.
How Long Until It Works?
Some people feel better within a few days, but for most, it takes 2–6 weeks to experience full benefits. Improvement depends on your hormone levels, dosage, and how well your body absorbs the medication. Patience and consistency are key.
Duration of Treatment
For most patients, hypothyroidism is a lifelong condition, so treatment continues indefinitely. In rare cases—like temporary thyroid inflammation or postpartum thyroiditis—your doctor may decide to reduce or stop treatment later, but only after careful testing.
Common Side Effects and Long-Term Use
When taken at the correct dose, levothyroxine is well tolerated. Side effects typically occur only when the dosage is too high, causing symptoms like:
-
Nervousness or anxiety
-
Rapid heartbeat
-
Sweating or tremors
-
Insomnia
-
Weight loss
Long-term excessive dosing can lead to osteoporosis and heart rhythm problems, especially in older adults. This is why routine testing is so important.
Hair Loss and Levothyroxine
Some temporary hair shedding may occur during the first few months of treatment—this is normal as your body adjusts. Persistent hair loss, however, may signal an incorrect dose or another condition such as nutritional deficiency or autoimmune issues. Always discuss such symptoms with your doctor.
Pregnancy, Fertility, and Breastfeeding
Levothyroxine is safe and essential during pregnancy. Untreated hypothyroidism can affect both the baby’s brain development and the mother’s health. Doses often need to be increased during pregnancy and carefully monitored.
It’s also safe while breastfeeding, as only minimal amounts pass into breast milk. Moreover, treating hypothyroidism can improve fertility in both men and women.
Lifestyle Tips to Improve Absorption
-
Take your pill at the same time daily.
-
Wait at least 30–60 minutes before breakfast, or 3 hours after dinner if taken at night.
-
Separate levothyroxine from iron, calcium, or antacids by at least 4 hours.
-
Limit coffee, soy, high-fiber foods, and cruciferous vegetables near dosing time.
-
Stay hydrated and maintain a consistent diet.
Alcohol and Levothyroxine
Moderate alcohol use doesn’t directly interfere with levothyroxine, but excessive drinking can harm the liver and thyroid function, potentially altering hormone metabolism. If you drink, do so in moderation and discuss with your doctor if you have liver or heart conditions.
Special Precautions
Tell your doctor if you have any of the following:
-
Heart disease or arrhythmia
-
Osteoporosis
-
Malabsorption issues (like celiac disease)
-
History of hyperthyroidism
Elderly patients or those with heart conditions often start with lower doses and gradual adjustments.
Can It Be Used for Weight Loss?
Absolutely not. Levothyroxine should never be used as a weight-loss drug in people with normal thyroid function. Doing so can cause dangerous side effects like heart palpitations, insomnia, anxiety, and muscle loss. It only helps regulate weight when hypothyroidism is the underlying cause.
The Bottom Line
Levothyroxine is a cornerstone of thyroid health management—safe, effective, and life-changing when taken properly. The key to success lies in consistency, correct timing, and regular medical monitoring. By following these principles and staying in communication with your healthcare provider, you can maintain stable thyroid hormone levels and enjoy better energy, focus, and overall well-being.
News in the same category


Doctors warn: these everyday antacids could be putting your heart in danger
Doctors Reveal What Really Happens When You Use Castor Oil
The Natural Secret Doctors Never Tell You That Melts Away Uric Acid Fast

9 Convincing Reasons to Consume More Dates

Two handfuls of peanuts daily boost memory in 4 months

Prunes and bone health: surprising benefits beyond constipation relief
12 Weird Diabetes Skin Problems You Need To Know
High Cholesterol: Causes, Risks, and Natural Ways to Lower It
Acid Reflux (GERD): When Should You See a Doctor?

Hypothyroidism: The Silent Condition With Easily Overlooked Symptoms
3 pain areas on your body that might be early cancer warning signs
A New Era of Near Vision Clarity Through VIZZ Eye Drops

Vaping harms your heart more than you realize

Ever Wake Up But Can’t Move
Gout Disease: The Untold Truth and 5 Common Treatment Mistakes
Arthritis Explained: Types, Causes, and Natural Pain Relief Methods
High Blood Pressure: Why It’s Dangerous and How to Stabilize It Naturally

MEDICATIONS YOU SHOULD NEVER TAKE WITH COFFEE

10 Best Foods to Detox Your Kidneys and Protect Renal Health
News Post

A Nearby Earth-Sized World Raising New Hopes for Habitability

How Finnish Forest Kindergartens Let Kids Thrive in Any Weather
Taiwan Researchers Develop Promising Hair-Regrowth Serum With Dramatic Lab Result

Pick the Breakfast You’d Eat

What Happens to Your Body When You Eat Canned Tuna Every Day

Why Some Children Don’t Visit Their Parents Often

The Hidden Fish Puzzle That’s Stumping the Internet

So this is what it does, here is the answer

The Hidden Details in Women’s Underwear — And What They Really Mean

Experts reveal that eating bananas in the morning cause

Why Cutting Your Own Hair Is About More Than Just Saving Money

Why Are Tree Trunks Painted White

Penguins Reject Cheaper Fish as Japanese Aquarium Tries to Cut Costs

I Thought I Found Insect Eggs Under My Bed

This is the correct way to wash grapes; washing them wrong can make them even dirtier

Emirates Airlines: A Legacy of Unmatched Safety and Reliability in Aviation

Dragon Bravo Fire: Arizona's Megafire Threatens the Grand Canyon and Beyond

The zodiac signs with a supernatural sixth sense… See now

Mussel Beds: New Zealand's Natural Solution for Ocean Health and Sustainability
