
The Most Likely Symptoms of a Gallbladder Problem (Don’t Ignore Them)
Most gallbladder-related conditions cause intense pain in the upper right area of the abdomen that can last anywhere from a few hours to several days. While gallstones are the most common cause of gallbladder disease, they are not the only reason the gallbladder may malfunction. Inflammation, infections, blockages, or abnormal growths in the gallbladder can also lead to symptoms such as shoulder pain, chest discomfort, nausea, vomiting, and noticeable changes in bowel movements.
Experiencing a gallbladder attack is often extremely uncomfortable and distressing. The pain can become severe and interfere with daily activities. In many cases, these attacks signal the need for dietary and lifestyle changes to reduce symptoms and lower the risk of complications such as gallbladder removal (cholecystectomy). Fortunately, many people can manage gallbladder problems effectively through healthier habits and early intervention.
This article explains the most common signs and symptoms of gallbladder disease, outlines possible causes, and discusses practical steps you can take to relieve symptoms and protect your digestive health.
What Is the Gallbladder and Where Is It Located?
The gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped organ measuring approximately 6–10 centimeters in length. It is located beneath the liver on the right side of the upper abdomen, just under the rib cage.
According to Encyclopaedia Britannica, the gallbladder stores around 50 milliliters of bile, a digestive fluid produced by the liver. Bile contains bile salts, cholesterol, and pigments such as bilirubin. Bilirubin is responsible for the yellow color of urine and the brown color of stool, which explains why gallbladder disorders often cause noticeable changes in urine and stool appearance.
The gallbladder’s primary function is to release bile into the small intestine during digestion, especially after eating fatty foods. This bile helps break down fats so they can be absorbed efficiently. The gallbladder is part of the biliary system, which plays a crucial role in digestion and waste removal.
Common Symptoms of Gallbladder Problems
Recognizing gallbladder symptoms early can help determine whether discomfort is caused by gallstones, infection, inflammation, or another underlying condition.
Intense Pain
Pain is the most recognizable symptom of gallbladder disease. It often begins gradually, intensifies within the first hour, and may last for hours or even days.
-
Upper right abdominal pain: This pain is typically felt under the ribs and is described as a deep, constant ache. It is commonly associated with gallstones, cholecystitis, or bile duct inflammation.
-
Right shoulder pain: Gallbladder pain often radiates to the right shoulder or the area between the shoulder blades.
-
Back pain: Many individuals experience pain spreading from the abdomen to the middle or upper back.
-
Chest pain: Gallbladder inflammation can sometimes mimic heart-related pain, causing squeezing or pressure-like discomfort in the chest.
Any combination of severe upper abdominal pain and chest discomfort should never be ignored.
Nausea and Vomiting
Nausea and vomiting frequently accompany gallbladder pain. These symptoms occur because bile flow is disrupted, interfering with digestion. The discomfort usually does not improve after passing gas or having a bowel movement, which helps distinguish gallbladder pain from other digestive issues.
Diarrhea
Gallbladder dysfunction can cause frequent or chronic diarrhea, particularly after eating fatty or spicy foods. Since bile helps digest fats, reduced bile release can lead to poor fat absorption, triggering loose stools. Soothing remedies such as ginger tea or herbal digestive teas may help reduce symptoms.
Acid Reflux or Bile Reflux
A poorly functioning gallbladder can contribute to reflux symptoms. Bile reflux occurs when bile flows backward into the stomach, causing burning pain, nausea, and vomiting. Acid reflux, on the other hand, results from excess stomach acid entering the esophagus. Both conditions are commonly reported among people with gallstones.
Bloating and Abdominal Fullness
Blockages or inflammation in the gallbladder may cause bloating and pressure in the upper abdomen. This discomfort often occurs alongside sharp right-sided pain and may last throughout a gallbladder attack. Reducing fatty foods and managing stress can help minimize bloating episodes.
Additional Warning Signs of Gallbladder Disease
Some symptoms indicate more serious gallbladder dysfunction and require medical attention.
Changes in Stool and Urine Color
Blocked bile flow may result in dark urine and pale, gray, or clay-colored stools. These changes occur because bile pigments are not reaching the intestines properly.
Jaundice
Yellowing of the skin or the whites of the eyes can occur when bilirubin builds up in the bloodstream. This may signal a bile duct blockage or a more serious liver or gallbladder condition.
Symptoms of Gallbladder Infection
Infections often develop when bile ducts are blocked. Symptoms include severe abdominal pain, fever, chills, sweating, and weakness. Without treatment, infections can spread to the liver or pancreas and become life-threatening.
Common Gallbladder Conditions
Several medical conditions can cause gallbladder symptoms:
-
Cholecystitis: Inflammation of the gallbladder, often caused by gallstones
-
Gallstones: Hardened deposits of bile that can block bile ducts
-
Gallbladder polyps: Small growths that may cause intermittent pain
-
Choledocholithiasis: Gallstones lodged in the common bile duct
-
Gallbladder abscess: A severe infection filled with pus
-
Cholangitis: Inflammation of the bile ducts
-
Porcelain gallbladder: Calcium buildup that hardens the gallbladder wall
-
Gallstone ileus: Intestinal blockage caused by gallstones
-
Ruptured gallbladder: A medical emergency often caused by trauma or severe inflammation
-
Gallbladder cancer: Rare, but possible in chronic cases
How to Manage Gallbladder Problems
Many gallbladder symptoms can be reduced through diet and lifestyle changes.
Gallbladder-Friendly Diet
A healthy gallbladder diet avoids fried foods, fatty meats, processed foods, pastries, and high-cholesterol meals. Instead, focus on:
-
Whole grains
-
Lean protein (fish, poultry)
-
Fruits and vegetables
-
Low-fat dairy products
Moderate coffee consumption and limited alcohol intake may also help reduce gallstone risk.
Natural Remedies and Supplements
-
Apple cider vinegar and apple juice: May help soften gallstones and reduce pain
-
Peppermint: Peppermint tea or oil can soothe digestive and biliary discomfort
-
Vitamin C: Supports bile production and may help prevent gallstone formation
Gallbladder cleanses are popular but lack scientific evidence and may cause side effects such as nausea and diarrhea.
When to See a Doctor
You should seek medical care immediately if you experience:
-
Sudden, severe upper right abdominal pain
-
Pain spreading to the back or shoulder
-
Fever and chills
-
Persistent nausea and vomiting
-
Pale stools or dark urine
-
Yellowing of the skin or eyes
Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent serious complications and improve long-term outcomes.
News in the same category

Sodium Bicarbonate and Immune Regulation: Evidence for an Anti-Inflammatory Mechanism
Oleocanthal from Extra-Virgin Olive Oil: A Multi-Targeted Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Cancer Compound

Fenbendazole and Unexpected Cancer Remission: Insights from a 2024 Case Report
Quercetin as an Exercise Mimetic: Enhancing Mitochondrial Biogenesis and Physical Performance
Dual “Don’t-Eat-Me” Signals: A New Paradigm in Cancer Immune Evasion

Cinnamon and Neuroprotection: Evidence for Anti-Alzheimer’s Mechanisms

High-Dose Thiamine and Cancer Cell Metabolism: Evidence from Experimental Cell-Line Studies
How to Improve Blood Circulation Naturally (Research Based)
Get Rid of Throat Mucus Faster With These Home Treatments (Evidence Based)
Why Hearing Running Water Makes You Suddenly Need to Pee

The strange phenomenon of sleep paralysis: When the body stops listening
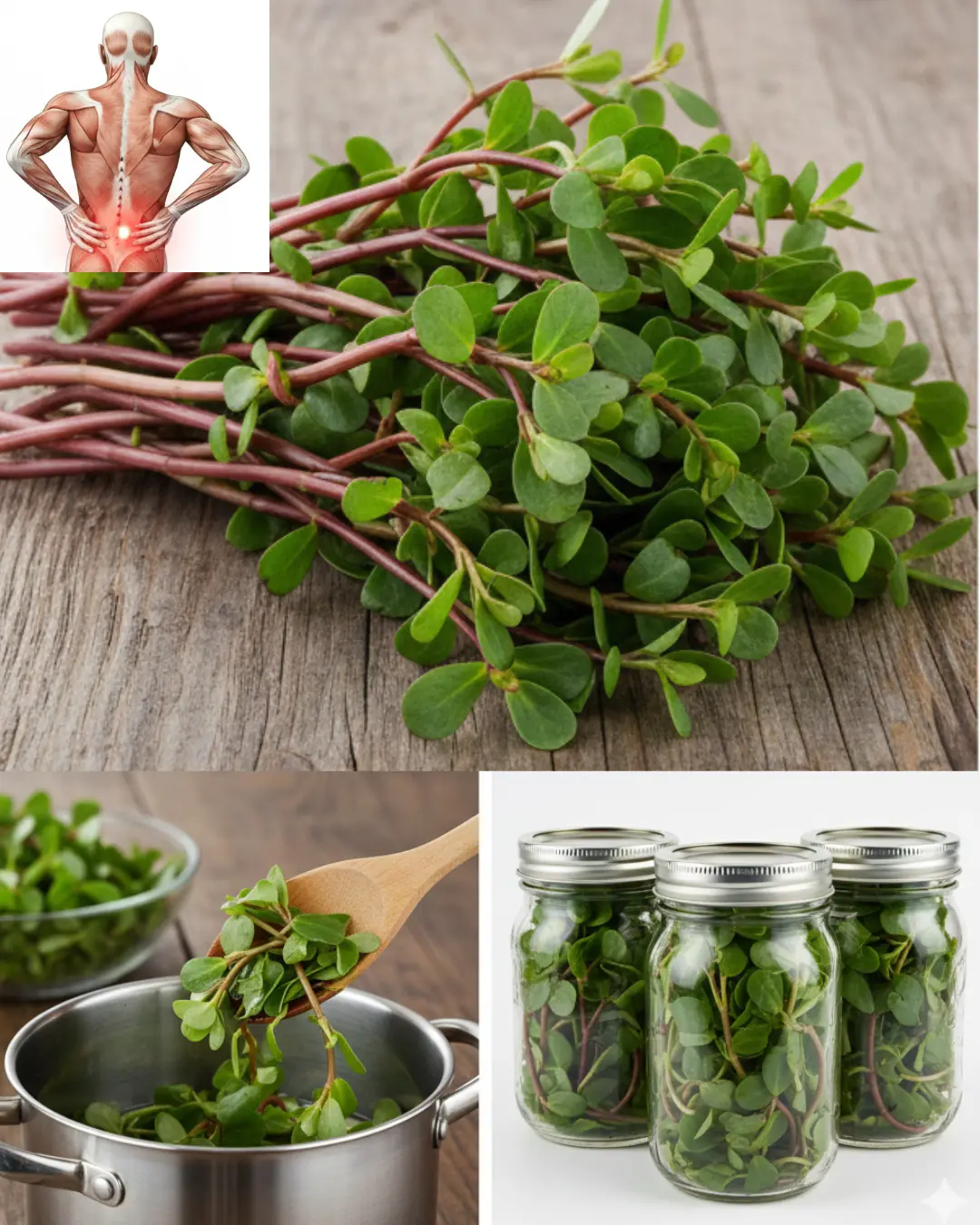

Surprising Health Benefits of Purslane (Portulaca oleracea)
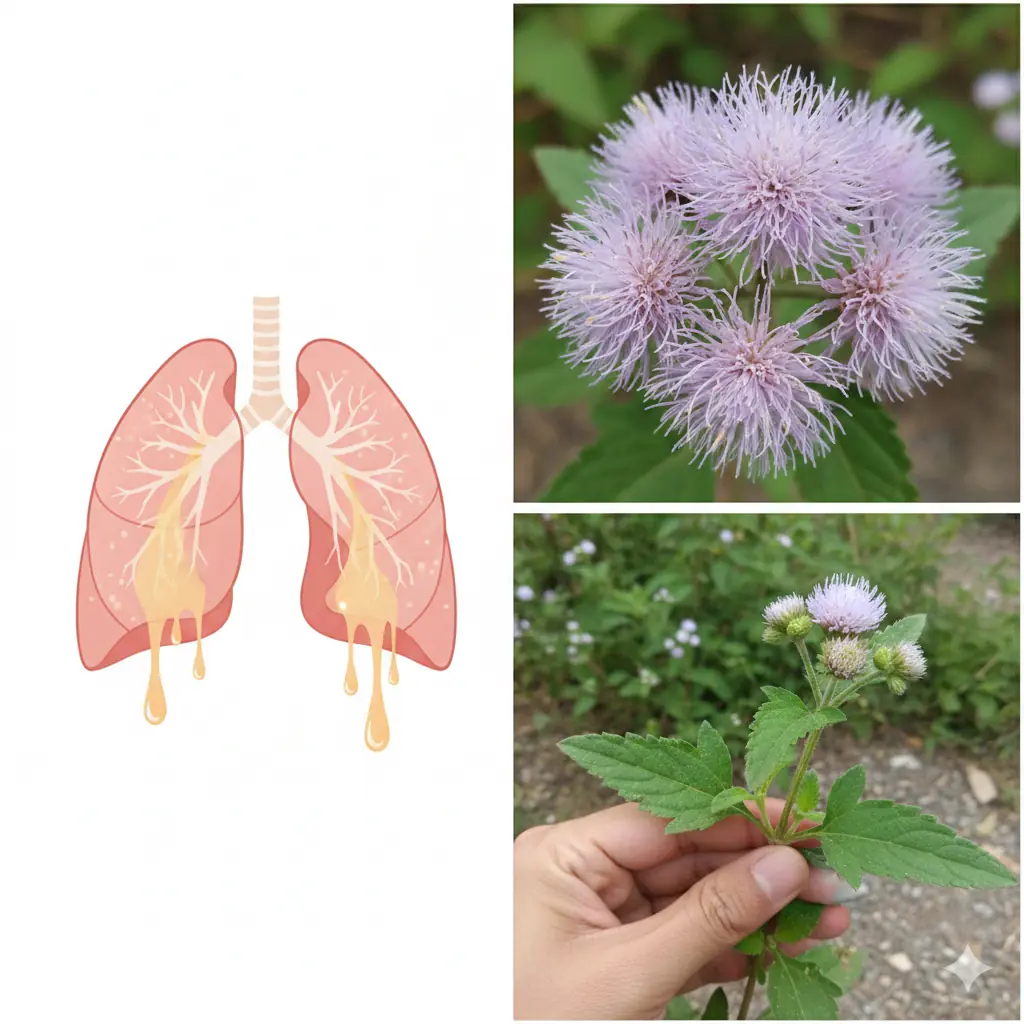

Ageratum Conyzoides: A Valuable Herb with Many Health Benefits

The man died of colorectal cancer, his family broke down in tears: "He ate healthily but liked to do three things."

Women Who Regularly Eat These 4 Foods Can Prevent Premature Graying, Keeping Hair Dark and Shiny Even at 60

The Root that Helps the Liver Detoxify and Effectively Reduce Inflammation
There’s this crusty little spot that keeps scabbing and reopening, and I can’t get in to see anyone yet. What could this be?
News Post

Nighttime Olfactory Enrichment and Cognitive Enhancement in Older Adults

Sodium Bicarbonate and Immune Regulation: Evidence for an Anti-Inflammatory Mechanism

Oleocanthal from Extra-Virgin Olive Oil: A Multi-Targeted Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Cancer Compound

Fenbendazole and Unexpected Cancer Remission: Insights from a 2024 Case Report

Quercetin as an Exercise Mimetic: Enhancing Mitochondrial Biogenesis and Physical Performance

Dual “Don’t-Eat-Me” Signals: A New Paradigm in Cancer Immune Evasion

Cinnamon and Neuroprotection: Evidence for Anti-Alzheimer’s Mechanisms

High-Dose Thiamine and Cancer Cell Metabolism: Evidence from Experimental Cell-Line Studies
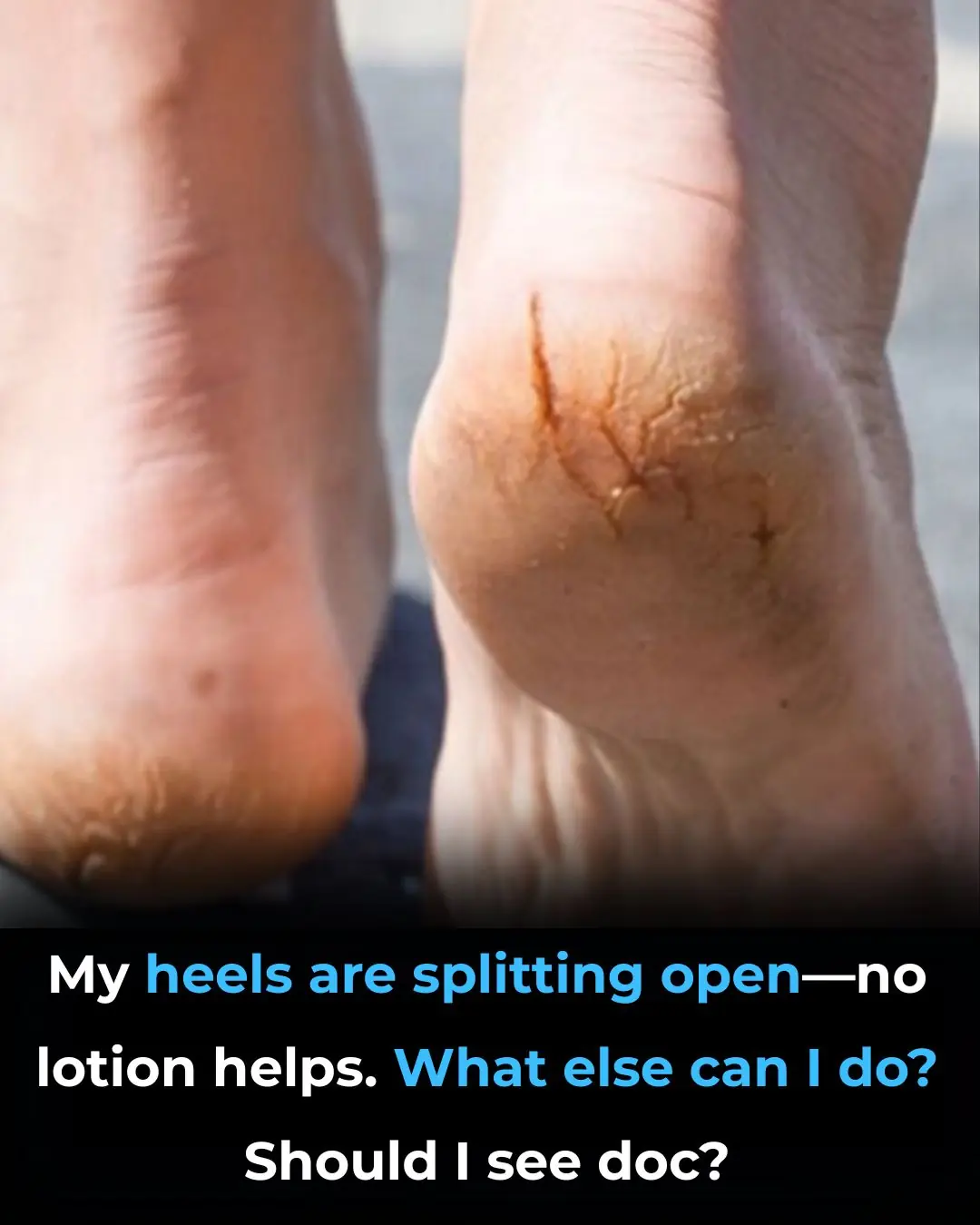
My heels are splitting open—no lotion helps. What else can I do? Should I see doc?
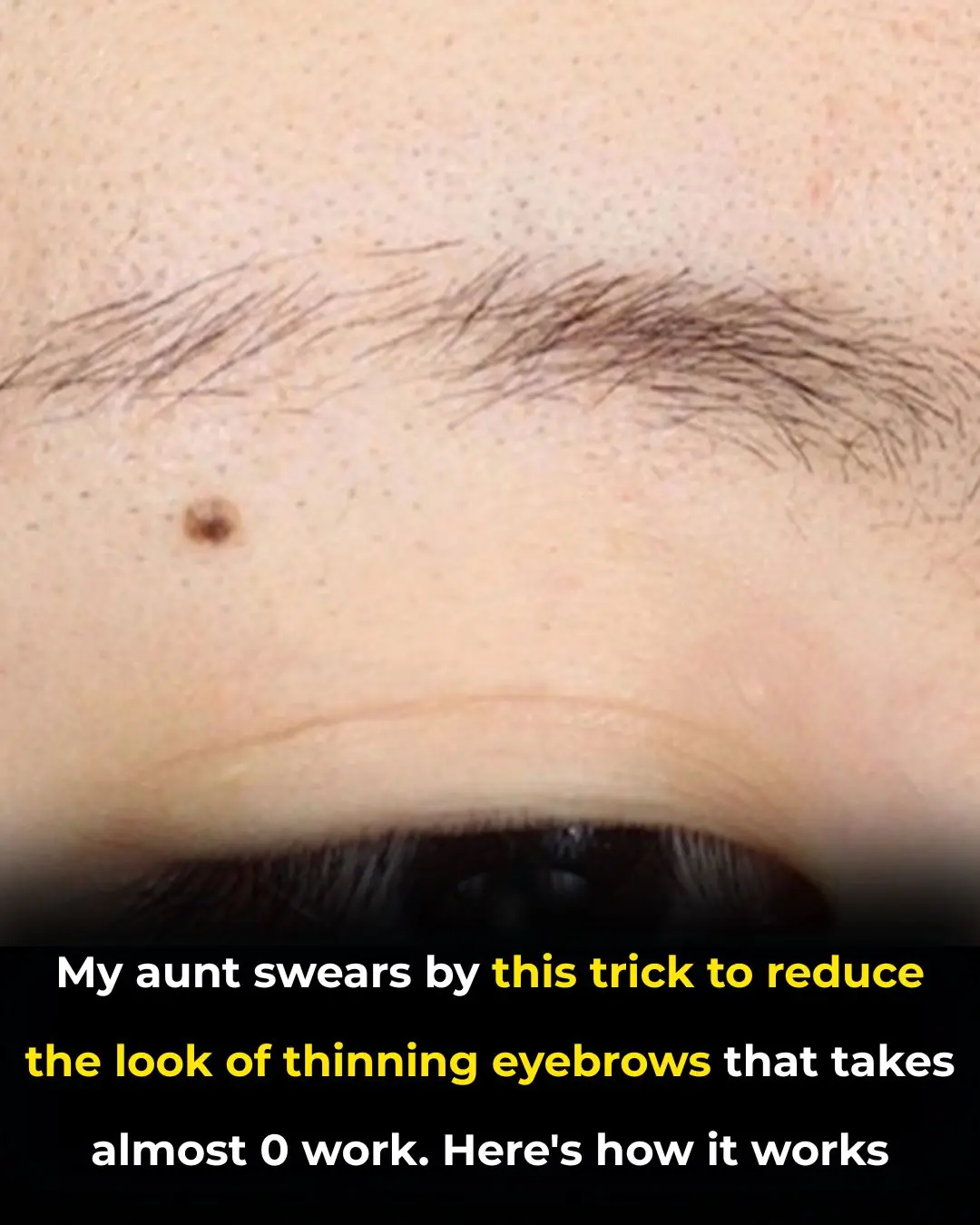
My aunt swears by this trick to reduce the look of thinning eyebrows that takes almost 0 work. Here's how it works
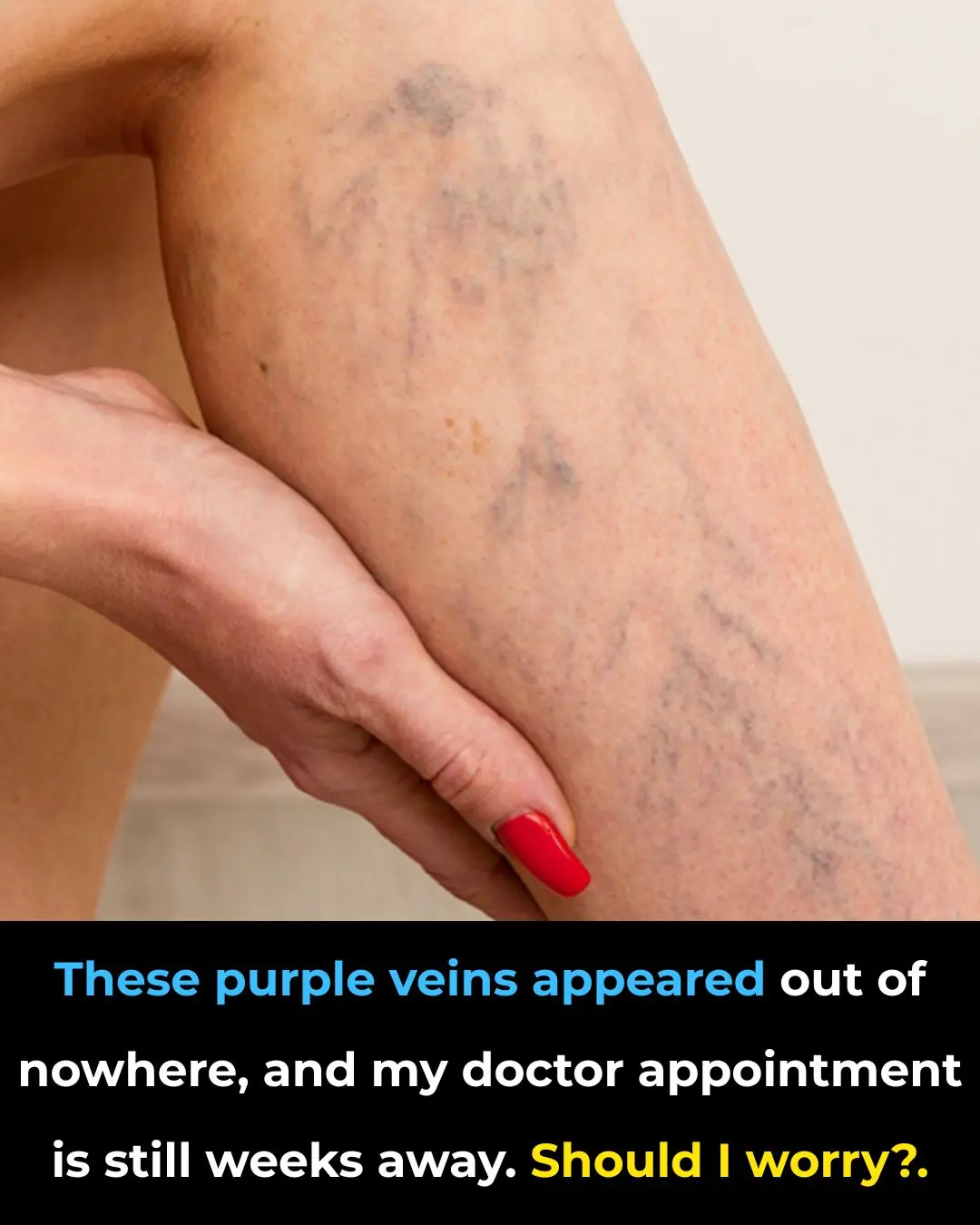
These purple veins appeared out of nowhere, and my doctor appointment is still weeks away. Should I worry?

Brown flat spots keep showing up on the back of my hands. Doctor appt is forever away. What should I do?

How to Improve Blood Circulation Naturally (Research Based)

The Most Effective Ways to Naturally Get Rid of Clogged Ears

Get Rid of Throat Mucus Faster With These Home Treatments (Evidence Based)

If A Woman Says These 6 Things Regularly, She’s Way Smarter Than You Even Realize

11 Clever Phrases Smart People Use to End Pointless Arguments

Mopping the floor with this ingredient will make it sparkling clean, like new, and dust-free for a whole week.
