World’s First 3D-Printed Windpipe Successfully Implanted in South Korea
World’s First 3D-Printed Windpipe Successfully Implanted in South Korea
In a historic medical breakthrough, scientists and doctors in South Korea have successfully implanted a 3D-printed windpipe (trachea) into a woman who lost part of her airway after thyroid cancer surgery. This achievement marks the first time in the world that a bioprinted trachea has been transplanted into a human being. 3D Mag+1
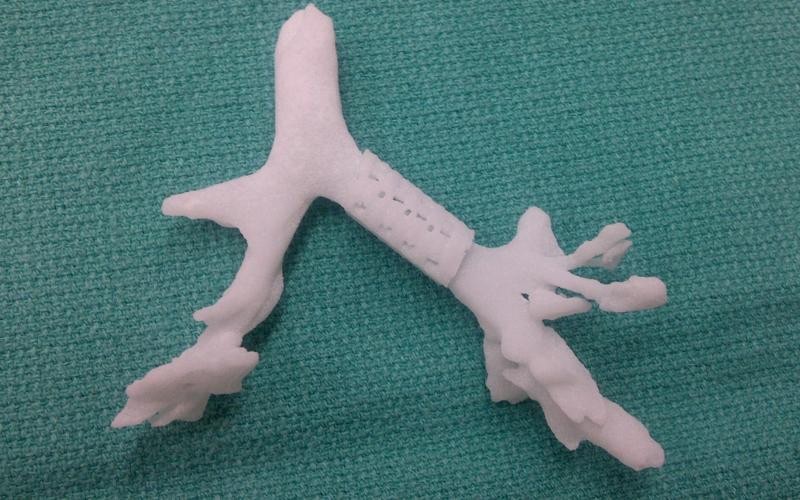
How the 3D-Printed Windpipe Was Made
The artificial windpipe was created using advanced 3D bioprinting technology. Unlike conventional implants made from metal or plastic, this trachea was printed with bio-inks containing living cells, including cartilage and mucosal cells. These cells were combined with a biodegradable polymer scaffold called polycaprolactone (PCL), which provided structural support while allowing new tissue to grow around it naturally. 3D Mag+1
To ensure a perfect fit, the medical team used detailed CT and MRI scans of the patient’s airway. The custom-designed trachea took less than two weeks to print and was implanted during a single half-day surgical procedure. 3D Printing
Remarkable Healing and Regeneration
Surgeons and doctors monitored the patient closely after the operation. Within just six months, they observed healthy blood vessel formation and tissue growth around the implanted windpipe — strong evidence that the body was accepting and integrating the new organ. Notably, the patient did not require immunosuppressant drugs because the implant was built using living cells that were compatible with her body. 3D Mag+1
This is a major milestone because traditional organ transplants often require long-term immune suppression to prevent rejection. The success of this implant shows the potential of regenerative medicine to bypass that limitation. 3D Mag
Who Led the Breakthrough
The pioneering project was led by a collaborative team from Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital, T&R Biofab, and other research partners. This group included surgeons, bioengineers, and medical specialists who have been developing 3D bioprinting technology for years. 3D Printing
Experts say this achievement is not merely a one-off success, but a milestone that could pave the way for printing and transplanting other complex organs. Future developments may include 3D-printed lungs, kidneys, hearts, and more, all grown from a patient’s own cells. LinkedIn
Why This Matters to Medicine
This breakthrough represents a new era in regenerative medicine and organ transplantation. For patients who suffer from congenital defects, injuries, and cancer-related tissue loss, traditional treatments are often limited or risky. Personalized 3D-printed organs could one day offer customized solutions with higher success rates and fewer complications. BBC Science Focus
While this is just the beginning, the success of the 3D-printed trachea implant highlights how bioprinting technologies are evolving rapidly and transforming what was once considered science fiction into real clinical practice. 3D Mag
News in the same category


How a 20-Minute Walk Can Positively Transform Your Brain and Body

12 Common Kitchen Mistakes You Should Avoid for Better Health and Safety

Understanding the Signs and Symptoms of Mineral Deficiencies

Revolutionary Graphene Filter Instantly Turns Seawater Into Drinkable Water—A Game-Changer for Global Water Shortages!

Revolutionary Brain Stimulation Technique Shows Potential to Reverse Alzheimer's Damage!

Breakthrough in Diabetes Treatment: Gene-Edited Cells May Cure Type 1 Diabetes Without Immunosuppressants!

Cutting Sugar for Just 9 Days Can Transform Your Liver Health – Here's How!

South Korea's Hilarious 'Space-Out Competition': The Ultimate Sport of Doing Absolutely Nothing!

Female Frogs 'Play Dead' to Escape Forced Mating – You Won't Believe How They Do It!

Objects People Were Confused About Their Purpose

Robot 'Kidnaps' Fellow Machines at Shanghai Exhibition, Sparking Debate on AI Autonomy and Labor Rights

Introducing the U-Hawk: The Autonomous Black Hawk Revolutionizing Heavy-Lift Aviation

China Unveils World's Largest Solar Farm, Powers Up with 3.5 GW in Xinjiang

Australia’s “Infinity Train” — A Self-Recharging Heavy-Haul Giant Powered by Gravity

The New York Hairstylist Who Spends His Day Off Helping the Invisible People of the City

The $400 Million Car Carrier That Sank Into the Atlantic: A Tale of Fire, Luxury Cars, and Environmental Risks

Sweden’s RFID/NFC Implant Trend: Unlocking Convenience or Opening the Door to Privacy Concerns?

Alice Walton’s Groundbreaking Medical School: A New Era for Medicine and Healthcare
News Post

How to Remove Yellow and Brown Stains From a Toilet Seat Before Replacing It

It Takes 1–2 Years for a Woman’s Body to Fully Recover After Pregnancy — Not Just 6 Weeks

The Natural Glow: Yeast and Yogurt Mask for Radiant Skin

How a 20-Minute Walk Can Positively Transform Your Brain and Body

12 Common Kitchen Mistakes You Should Avoid for Better Health and Safety

The 4 hidden causes of persistent phlegm in your throat (& how to fix it naturally)

Understanding the Signs and Symptoms of Mineral Deficiencies
4 popular supplements that rapidly drain potassium from your body

Turmeric and vitamin D are allies against high blood pressure in diabetes
This is How Headaches Reveal What is Wrong With Your Health

#1 best way to reverse & slow dementia
How to shrink thyroid nodules naturally with 2 key minerals

How to Unclog a Sink in an Emergency (When You Have Nothing on Hand)

Genius! My Nana’s Simple Trick for Cleaning Dusty Window Blinds With Almost No Effort

I Had No Clue About This Hidden Fridge Button — It Could Be Wasting You Serious Money

I Had No Idea These Kids’ Snacks Contain Petroleum-Based Chemicals

I Clean the Lint Trap—But I Found a Shocking Amount of Lint Inside the Dryer. Is This Dangerous?

Dark Purple Spots Keep Showing Up on Your Hands? Here’s What to Do While You Wait to See a Doctor