
Avoid This Drink to Reduce The Risk of Stroke and Heart Attack
When fatigue sets in, many people look for a fast and easy energy boost. Coffee, sodas, and energy drinks are often the first choices. These beverages promise instant alertness and improved focus, making them especially appealing during busy workdays, study sessions, or long drives. One of the most well-known options is Red Bull, a drink famously advertised as one that “gives you wings.” However, behind the clever marketing lies growing concern about its impact on heart health.
Red Bull and Heart Health: A Concerning Connection
Scientific research has increasingly linked energy drinks like Red Bull to cardiovascular problems, including a higher risk of heart attack and stroke. Dr. Scott Willoughby, a senior researcher at the Cardiovascular Research Center at Royal Adelaide Hospital in Australia, has studied the effects of Red Bull on the body and reported alarming findings.
According to Dr. Willoughby, just one can of Red Bull can significantly change the thickness and behavior of the blood. In one study, participants showed blood consistency similar to that of individuals with existing heart disease only one hour after consumption.
This increase in blood viscosity can slow circulation and place extra strain on the heart. Over time, restricted blood flow may raise the risk of clot formation, high blood pressure, and other serious cardiovascular complications, especially in people who consume energy drinks regularly.
What’s Actually Inside Red Bull?
Red Bull’s stimulating effects come from a combination of powerful ingredients, including:
-
Caffeine – While small amounts can improve alertness, excessive caffeine can raise heart rate and blood pressure, increase anxiety, and disrupt sleep patterns.
-
Sugar – High levels of refined sugar cause rapid spikes in blood glucose followed by energy crashes, contributing to weight gain and metabolic problems.
-
Aspartame – This artificial sweetener has been associated with potential neurological, metabolic, and allergic effects, and remains controversial in long-term health discussions.
Notably, Red Bull’s original Austrian manufacturer advises consumers not to drink more than two cans per day. For a beverage marketed as a casual energy booster, this warning alone raises concerns about its potency and safety.
The Added Danger of Mixing Red Bull with Alcohol
One particularly risky habit is combining Red Bull with alcohol. Energy drinks can mask the sedative effects of alcohol, making people feel more alert than they actually are. This false sense of sobriety often leads to excessive drinking, impaired judgment, and a higher likelihood of accidents.
At the same time, this combination places significant stress on both the heart and nervous system. Increased heart rate, dehydration, and disrupted sleep are common outcomes, and in severe cases, the mixture has been linked to heart rhythm disturbances and emergency medical events.
Healthier Ways to Boost Your Energy
Instead of relying on highly caffeinated or chemically enhanced drinks, there are safer and more sustainable ways to maintain energy throughout the day:
-
Improve your diet – Focus on whole, nutrient-rich foods such as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains.
-
Increase omega-3 intake – Found in fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, omega-3s support heart and brain health.
-
Reduce sugar consumption – Avoid dramatic energy highs and crashes by limiting sugary snacks and drinks.
-
Manage stress – Practices like meditation, deep breathing, or taking regular breaks can significantly improve energy levels.
-
Prioritize sleep – Aim for 7–9 hours of quality sleep each night to allow your body to recover fully.
-
Stay active – Regular physical activity boosts circulation, improves mood, and enhances long-term energy.
Final Thoughts
While grabbing an energy drink may seem like a convenient solution during an afternoon slump or late-night study session, the potential long-term risks to your heart should not be ignored. Artificial stimulation often comes at a cost. By choosing healthier habits and supporting your body naturally, you can achieve steady, lasting energy—without putting your heart at risk.
News in the same category

Deep Vein Thrombosis: A Silent Killer That You Need to Know
Pineapple: Proven Health Benefits, Calories, Juice Benefits
The Best Foods to Cleanse and Prevent Clogged Arteries
13 Warning Signs of High Blood Sugar and 9 Ways to Take Control of Your Health
Progress Fighting Pancreatic Cancer — One of the Deadliest Malignancies

Drinking about 3 cups of green tea per day is associated with fewer white matter lesions in the brain—changes linked to aging and dementia risk

Magnesium Supplementation and Rapid Improvement in Major Depression

Targeting Fat Metabolism in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Stem Cells: The Therapeutic Potential of Avocadyne

High-Dose Thiamine and Fatigue Relief in Hashimoto’s Disease: Insights from a Case Series
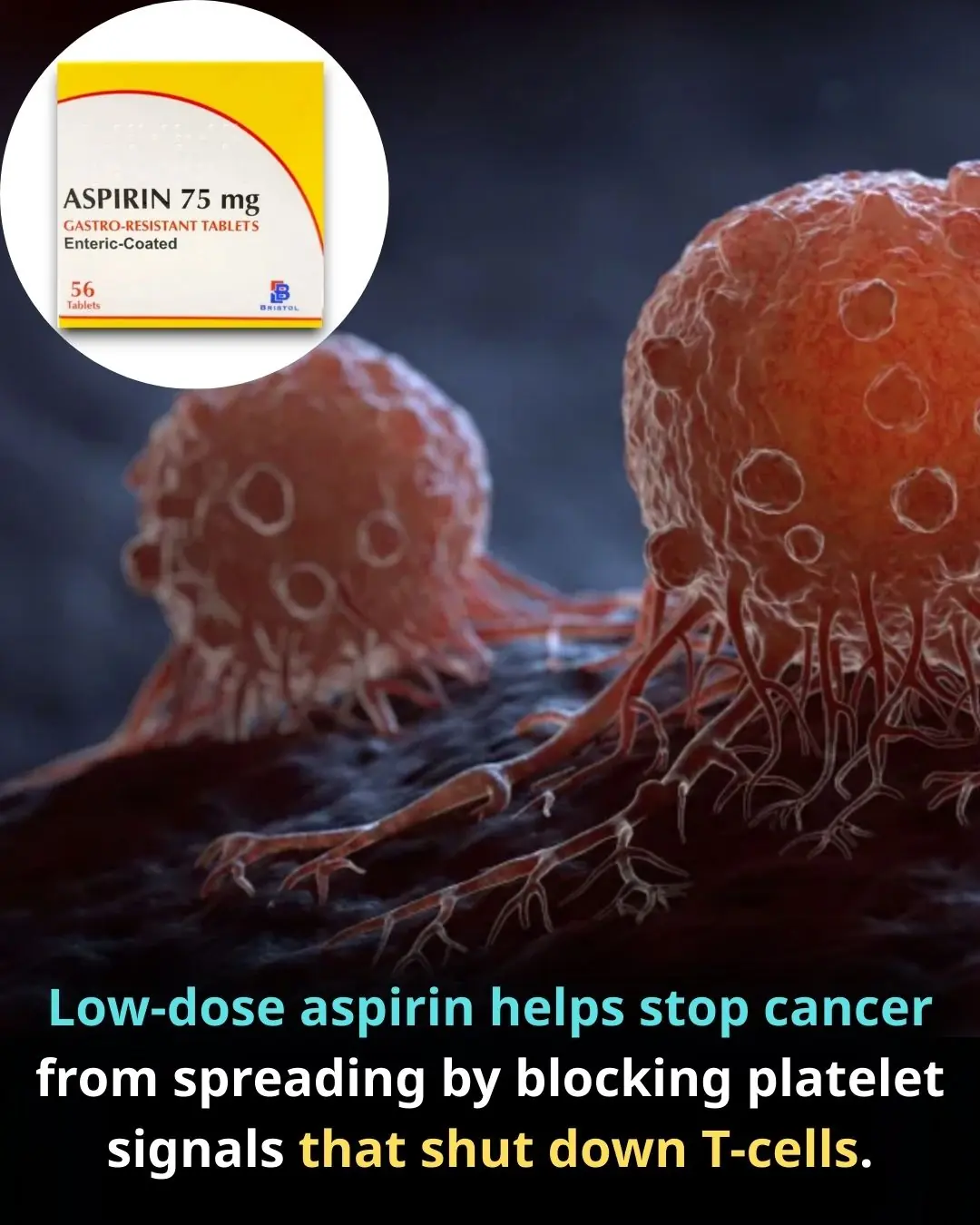
Aspirin as an Immune-Modulating Agent in the Suppression of Cancer Metastasis

Gum disease bacteria found in alzheimer’s brains

Fecal Microbiota Transplantation and Its Potential Role in Severe Autism Spectrum Disorder

Raw Carrots and Their Impact on Cholesterol and Colon Function

Breakthrough in Pancreatic Cancer Immunotherapy

Blue Blood in the Ocean: How Horseshoe Crabs Help Protect Human Health

You were raised by emotionally manipulative parents if you heard these 8 phrases as a child

The reason some seniors decline after moving to nursing homes
News Post

A Family of Four Diagnosed With Liver Cancer: Experts Identified the Cause the Moment They Entered the Kitchen

My nana says this works like a charm

Stop fighting with your eyeliner. 10 winter proof tricks seniors swear by

Did not know this
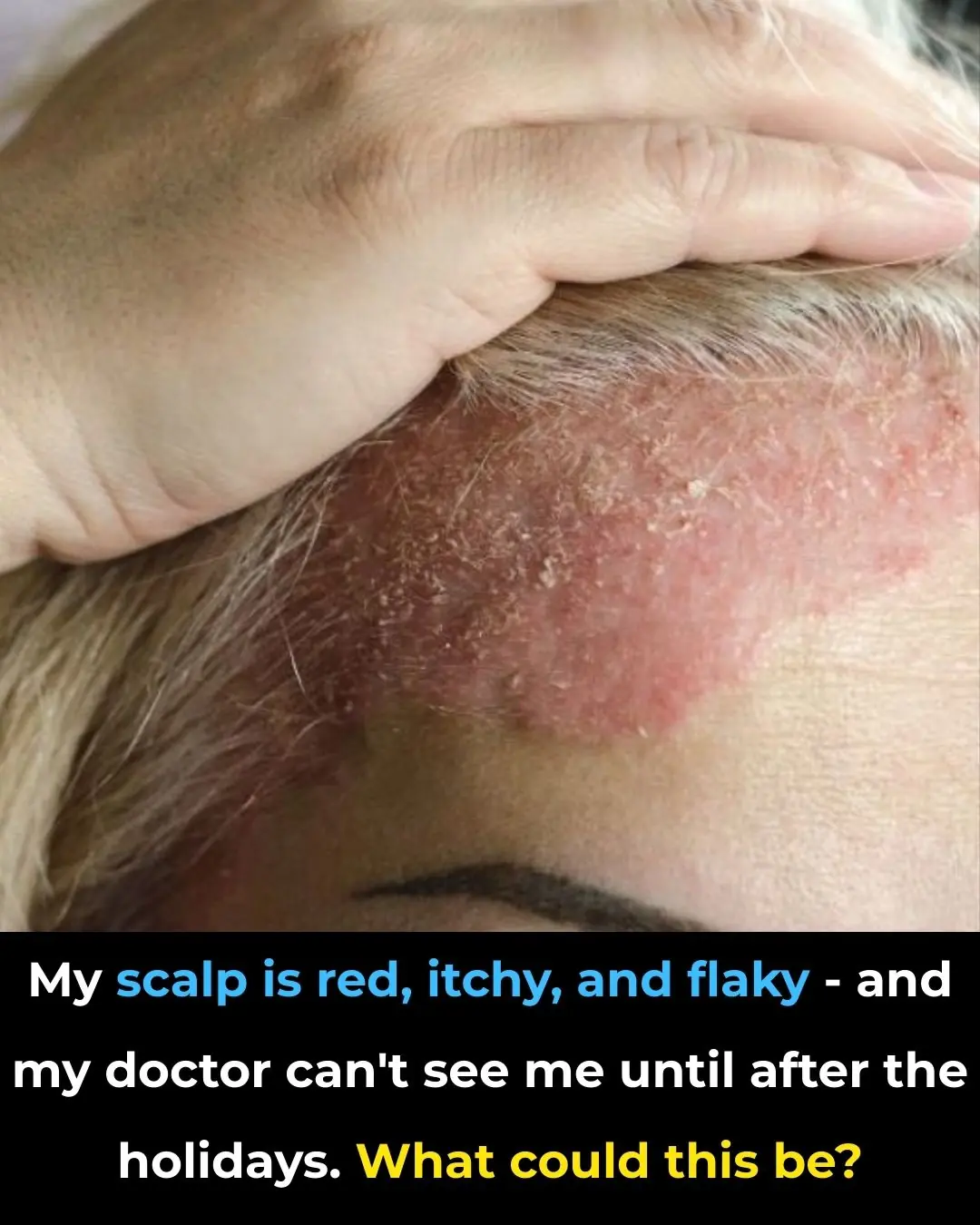
My scalp is red, itchy, and flaky — and my doctor can’t see me until after the holidays. What could this be?

Deep Vein Thrombosis: A Silent Killer That You Need to Know

Pineapple: Proven Health Benefits, Calories, Juice Benefits

The Best Foods to Cleanse and Prevent Clogged Arteries

13 Warning Signs of High Blood Sugar and 9 Ways to Take Control of Your Health

Progress Fighting Pancreatic Cancer — One of the Deadliest Malignancies

Should We Eat Eggs With BL00D Spots

Drinking about 3 cups of green tea per day is associated with fewer white matter lesions in the brain—changes linked to aging and dementia risk

Magnesium Supplementation and Rapid Improvement in Major Depression

Targeting Fat Metabolism in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Stem Cells: The Therapeutic Potential of Avocadyne

High-Dose Thiamine and Fatigue Relief in Hashimoto’s Disease: Insights from a Case Series

Psilocybin and the Biology of Aging: Emerging Experimental Evidence

Aspirin as an Immune-Modulating Agent in the Suppression of Cancer Metastasis

Gum disease bacteria found in alzheimer’s brains
