
Top 8 warning signs of ovarian cancer women absolutely need to know
Every year, many women with ovarian cancer are initially misdiagnosed with conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), stress-related disorders, acid reflux, or urinary tract infections due to overlapping symptoms. Because ovarian cancer symptoms are often subtle and vague in the early stages, diagnosis is frequently delayed. If you are experiencing symptoms that concern you, the most important thing to remember is to stay calm and informed.
Having one or even several symptoms associated with ovarian cancer does not automatically mean you have the disease. According to the American Cancer Society, a woman’s lifetime risk of developing invasive ovarian cancer is approximately 1 in 73. While the risk is relatively low, awareness and early medical evaluation are key to improving outcomes.
Below are the eight most common warning signs of ovarian cancer that women should be aware of and never ignore if they persist.
1. Persistent Fatigue

Feeling exhausted occasionally is normal, but constant or unexplained fatigue is not. Ongoing low energy levels may signal that something is wrong internally. When fatigue interferes with daily activities and does not improve with rest, it should be evaluated by a healthcare provider.
2. Pelvic Pain or Discomfort
Pelvic pain or pressure—sometimes extending into the abdomen—can be a warning sign. Persistent pain should never be dismissed or masked with painkillers. Discomfort in the pelvic area, especially when it worsens over time, deserves prompt medical attention.
3. Constipation and Other Bowel Changes

Digestive issues are one of the most commonly overlooked symptoms of ovarian cancer. Persistent constipation, diarrhea, bloating, excessive gas, nausea, or vomiting may indicate pressure from an ovarian mass. If bowel changes continue for weeks without improvement, seeing a doctor is essential.
4. Lower Back Pain
Lower back pain that radiates toward the pelvis or is accompanied by a feeling of pelvic heaviness should not be ignored. While back pain is common, pain that is persistent, unexplained, or worsening requires medical evaluation to rule out underlying causes.
5. Loss of Appetite or Feeling Full Quickly
Feeling full after eating small amounts or experiencing a sudden decrease in appetite can be an early sign of ovarian cancer. Unintentional weight loss without changes in diet or activity is also concerning and should be investigated by a healthcare professional.
6. Frequent or Urgent Urination

A constant or urgent need to urinate—especially if it disrupts sleep or daily routines—may be caused by a urinary tract infection or pelvic floor weakness. However, if symptoms persist despite treatment, it is important to inform your doctor, as ovarian tumors can press against the bladder.
7. Pain During Sexual Intercourse
Pain during sex is often related to insufficient vaginal lubrication, but in women with ovarian cancer, pain is frequently felt deep in the pelvis, usually on one side. Ongoing discomfort during intercourse should always be discussed with a healthcare provider.
8. Abdominal Bloating or Swelling
Abdominal bloating is one of the most common and telling symptoms of ovarian cancer. Unlike temporary bloating, cancer-related bloating is persistent and progressively worsens. The abdomen may gradually increase in size and feel firm, making this a symptom that requires urgent medical evaluation.
Risk Factors Associated With Ovarian Cancer
The exact cause of ovarian cancer remains unknown, but several factors are associated with increased risk. Understanding these can help women make informed decisions about their health.
Reproductive History and Menstruation
Women who have never given birth are at higher risk. Early onset of menstruation (before age 12) or late menopause also increases risk. Research suggests that a higher number of lifetime menstrual cycles may be linked to a greater chance of developing ovarian cancer.
Age
Age is a significant risk factor. Women over 50 are at increased risk, and nearly half of ovarian cancer diagnoses occur in women over 60. While ovarian cancer can occur in younger women, it is far less common before the age of 40.
Genetic Mutations
Inherited mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes significantly raise ovarian cancer risk. These genes normally help suppress tumor growth. Women with a BRCA1 mutation have an estimated 40% lifetime risk, while those with a BRCA2 mutation face a 10–20% lifetime risk. Genetic counseling and testing may be beneficial for women with a strong family history.
Family History
A family history of ovarian, breast, or colorectal cancer increases a woman’s likelihood of developing ovarian cancer. This risk is especially elevated if close relatives were diagnosed at a younger age.
Certain Medications
Long-term use of hormone replacement therapy after menopause or prolonged, high-dose use of fertility medications may increase ovarian cancer risk. Women considering or using these treatments should discuss potential risks with their healthcare providers.
Additional Risk Factors
Other factors linked to increased risk include:
-
Obesity
-
Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS)
-
Smoking
-
Long-term use of an intrauterine device (IUD)
Diagnosis, Screening, and Early Action
Currently, there are no reliable screening tests for ovarian cancer in women without symptoms. If ovarian cancer is suspected, doctors may perform a pelvic exam, transvaginal ultrasound, and blood tests to look for cancer-related proteins.
Medical researchers continue to work toward better early detection methods. Until more effective screening tools are available, the best defense is self-awareness. Pay close attention to your body, trust your instincts, and seek medical advice if something feels wrong.
By staying informed and proactive, you can take an active role in your healthcare and become your own strongest advocate—especially when it comes to detecting serious conditions early.
News in the same category


Doctor reveals 5 nutrient deficiencies linked to brain fog, dementia and Alzheimer’s

10 powerful plants to eliminate excess mucus and phlegm naturally

Why This Doctor Chooses Not to Prescribe Statins for High Cholesterol — and What He Recommends Instead

5 Foods You Must Avoid If You Have High Blood Pressure

21 Effective Home Remedies for Kidney Stones to Relieve Pain Fast

People with heart problems should avoid these 4 things to reduce stimulation to the heart

12 Bizarre Symptoms of Vitamin D Deficiency You Need to Know
8 warning signs of colon cancer you should never ignore
The daily drink that helps clear blocked arteries naturally

This old school home remedy will soothe your back, joints & knee pain in just 7 days!

Sleep Apnea: Symptoms, Risks, and Treatment Solutions
Viral Pneumonia vs. Bacterial Pneumonia: Key Differences

Allergic Rhinitis: What Triggers It and How to Manage It

COPD Exacerbation: Symptoms That Indicate a Flare-Up

Bile Reflux vs. Acid Reflux: Key Differences You Need to Know

Ulcerative Colitis vs. Crohn’s Disease: What Makes Them Different

How to lower blood sugar without giving up carbs
Don’t Ignore These Warning Signs of Vitamin B12 Deficiency!
News Post

Starlings Obscure the Sky Over Rome: A Dystopian Viral Photo

Sperm Donor with Rare Gene Mutation Leads to Urgent Screening Across 14 Countries

Cockroach Milk: A Potential Future Superfood with Remarkable Nutritional Value

This volcano just erupted for the 1st time in 10,000 years

Study Finds Yogurt May Help Reduce Chronic Inflammation and Lower Disease Risk

DIY Coffee Face Packs for Glowing Skin – Coffee Benefits for Skin

Homemade Vitamin C Serum | DIY Vitamin C Serum for Clear Skin

Study Highlights Health Risks of Prolonged Use of Wireless Earbuds: Radiation Concerns and Safety Tips

Sleepy Polar Bear Portrait Wins the Wildlife Photographer of the Year People’s Choice Award

How to Get Soft Pink Lips Naturally

Australia's Roads Shine Bright: Glow-in-the-Dark Markings Illuminate Streets Without Electricity

Prisoner Claims Life Sentence Ended After Brief Death, Court Rejects Appeal
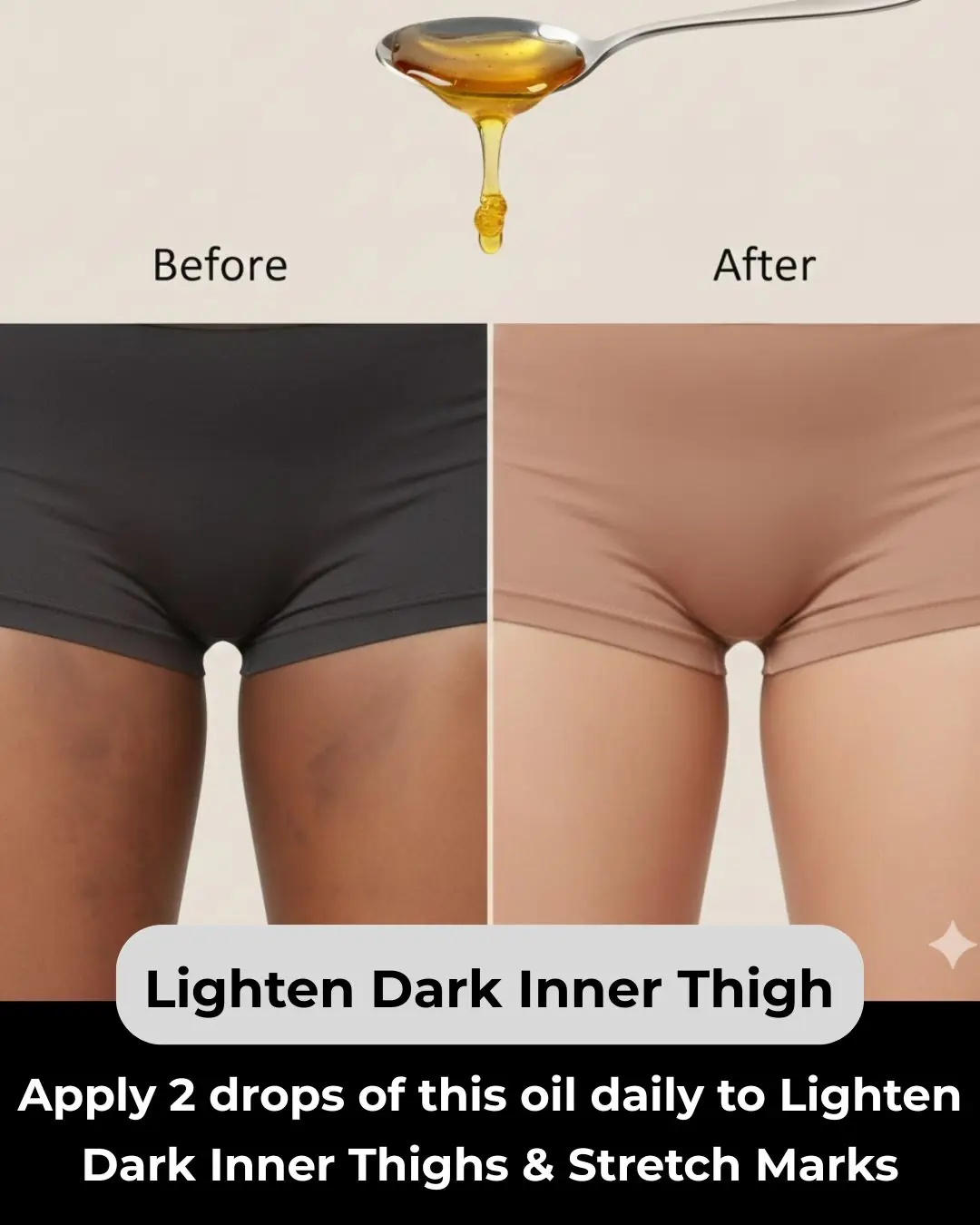
6 Home Remedies to Get Rid of Dark Inner Thighs: Lighten Dark Inner Thighs

More Americans Refusing Vitamin K Shots for Newborns: Study

5 Banana Face Masks for All Skin Concerns

15 Best Skin Gels for Glowing Skin & Wrinkles

How to lower blood sugar without giving up carbs

Rice Water Uses for Skin: Benefits and How to Use It for Radiant Skin
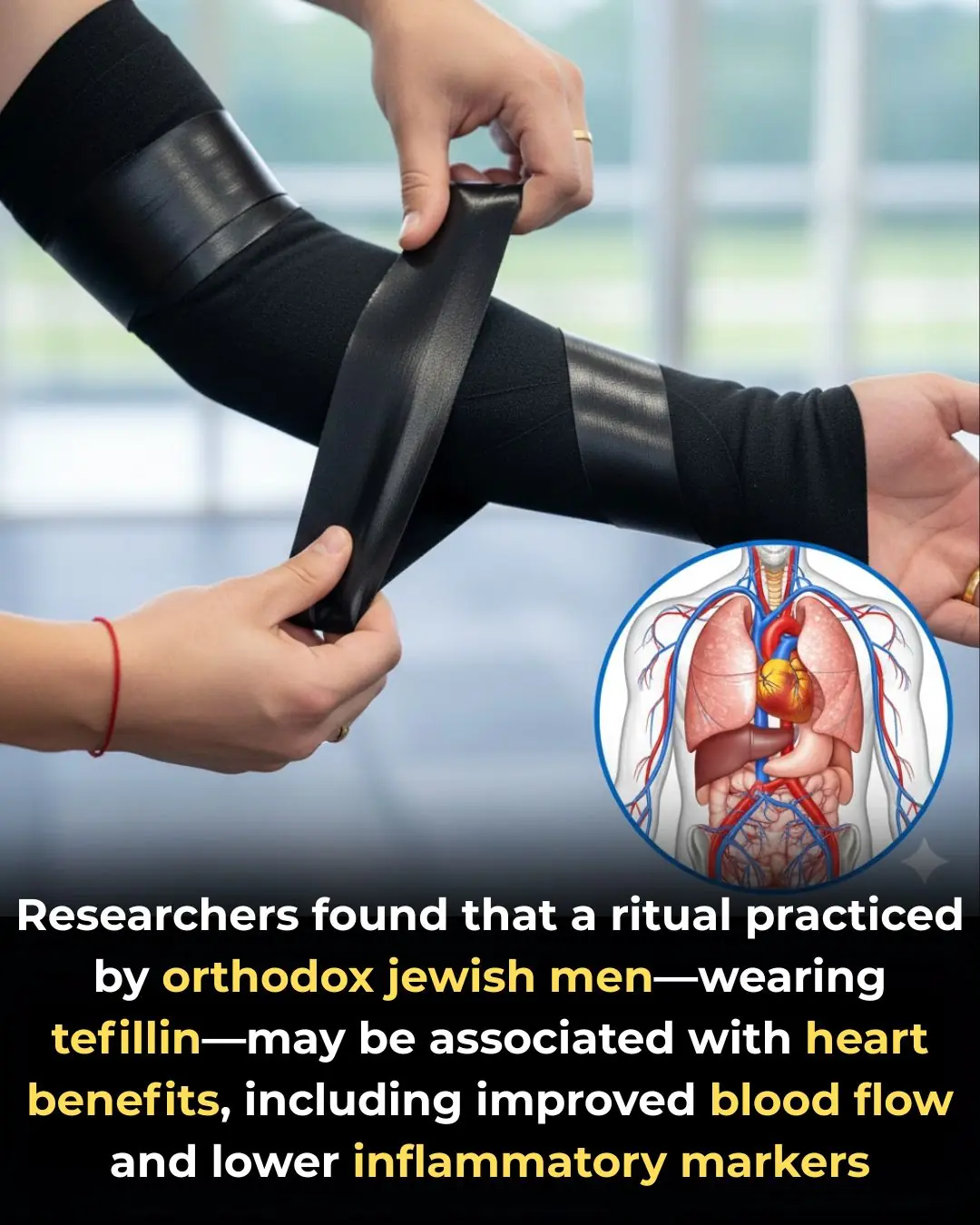
Study Suggests Wearing Tefillin During Daily Prayer May Offer Unexpected Heart Health Benefits
