
Bioprinted Windpipe: A Milestone in Regenerative Medicine
How It Was Done
-
Biodegradable scaffold: A custom-designed structure was created to mimic the shape and function of a natural trachea.
-
Stem cell seeding: The scaffold was seeded with the patient’s own stem cells under controlled laboratory conditions.
-
Implantation: Once implanted, the scaffold supported natural tissue growth, allowing cells to regenerate and integrate seamlessly.
-
Outcome: The patient’s airway function was fully restored without the complications of immune rejection.
Why It Matters
Traditional organ transplants rely on donor tissue and require lifelong immunosuppressive therapy, which carries risks such as infections and cancer. By using the patient’s own cells, this approach:
-
Eliminates rejection risk.
-
Removes the need for immunosuppressive drugs.
-
Opens the door to personalized organ replacement.
Broader Implications
This achievement highlights the growing potential of bioprinting and tissue engineering:
-
Trauma recovery: Patients with severe airway injuries could regain normal breathing.
-
Cancer treatment: Those requiring tracheal removal could benefit from custom replacements.
-
Future applications: Researchers believe similar techniques could be applied to more complex organs such as kidneys, livers, or even hearts.
Challenges Ahead
-
Experimental stage: The procedure is still in early clinical trials.
-
Scalability: Producing complex organs consistently remains a major hurdle.
-
Long-term durability: Researchers must confirm that bioprinted tissues remain functional for decades.
Bottom Line
A bioprinted windpipe made from a patient’s stem cells has been successfully implanted, marking a transformative step in regenerative medicine. While broader clinical applications are still under research, this innovation signals a future where organ rejection and donor shortages may no longer limit transplantation.
Sources:
-
The Lancet – Clinical reports on stem cell–based trachea transplants
-
Nature Biotechnology – Advances in bioprinting and regenerative scaffolds
-
MIT Technology Review – Bioprinting organs: the future of transplantation
-
Peer-reviewed regenerative medicine studies on stem cell scaffolds
News in the same category


Grip Strength and Brain Health: More Than Muscle

Bagworms Inside Your Home
Scientists discover that stem cells from wisdom teeth could help in regenerative medicine

What the Research Shows

Rethinking Flu Transmission: New Evidence Challenges Long-Held Assumptions

Nanobot Technology: A New Frontier in Cardiovascular Disease Treatment

Redefining Diabetes Treatment

If your partner says goodbye with a kiss on the forehead, be very careful: this is what it really means
Here’s what the letter ‘M’ and the crescent moon on the palm of your hand truly signify

How Helicobacter pylori Revolutionized the Understanding of Stomach Ulcers

New Research Raises Brain Health Concerns About a Common Sweetener

🌟 Breakthrough in Cancer Treatment: Targeted Light Therapy

HHS to Reexamine Cell Phone and 5G Radiation Risks Following Direction From RFK Jr

Injectable Gel for Nerve Regeneration: A Breakthrough in Healing
Processed Meats and Cancer Risk: What You Need to Know
Microplastics in Human Testicles: A Wake-Up Call for Reproductive Health

A Geologist Explains What Makes Greenland So Incredibly Special
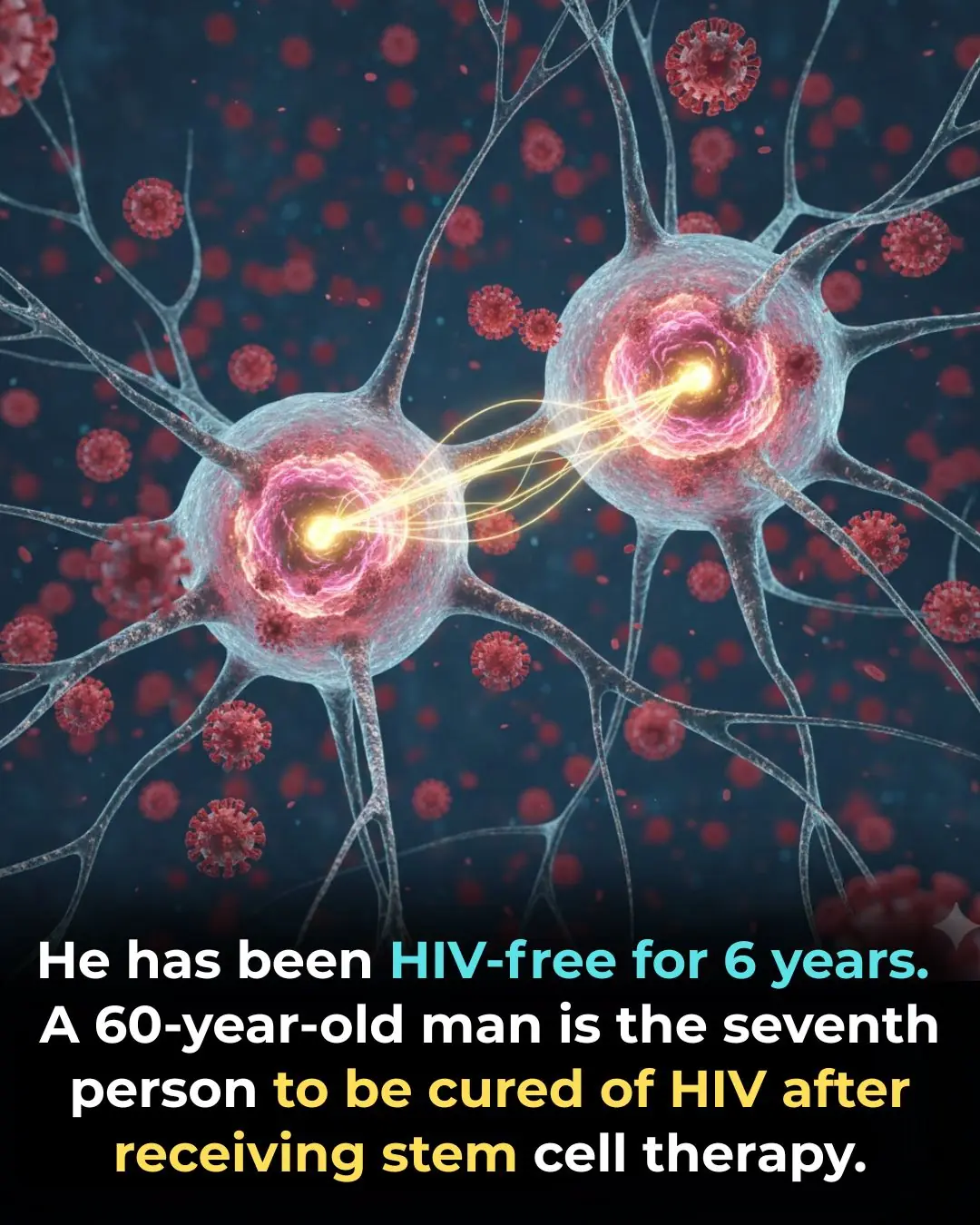
They Successfully Cured HIV in a 60-Year-Old German Man Using a Stem Cell Transplant; He Has Been Disease-Free for 6 Years
News Post
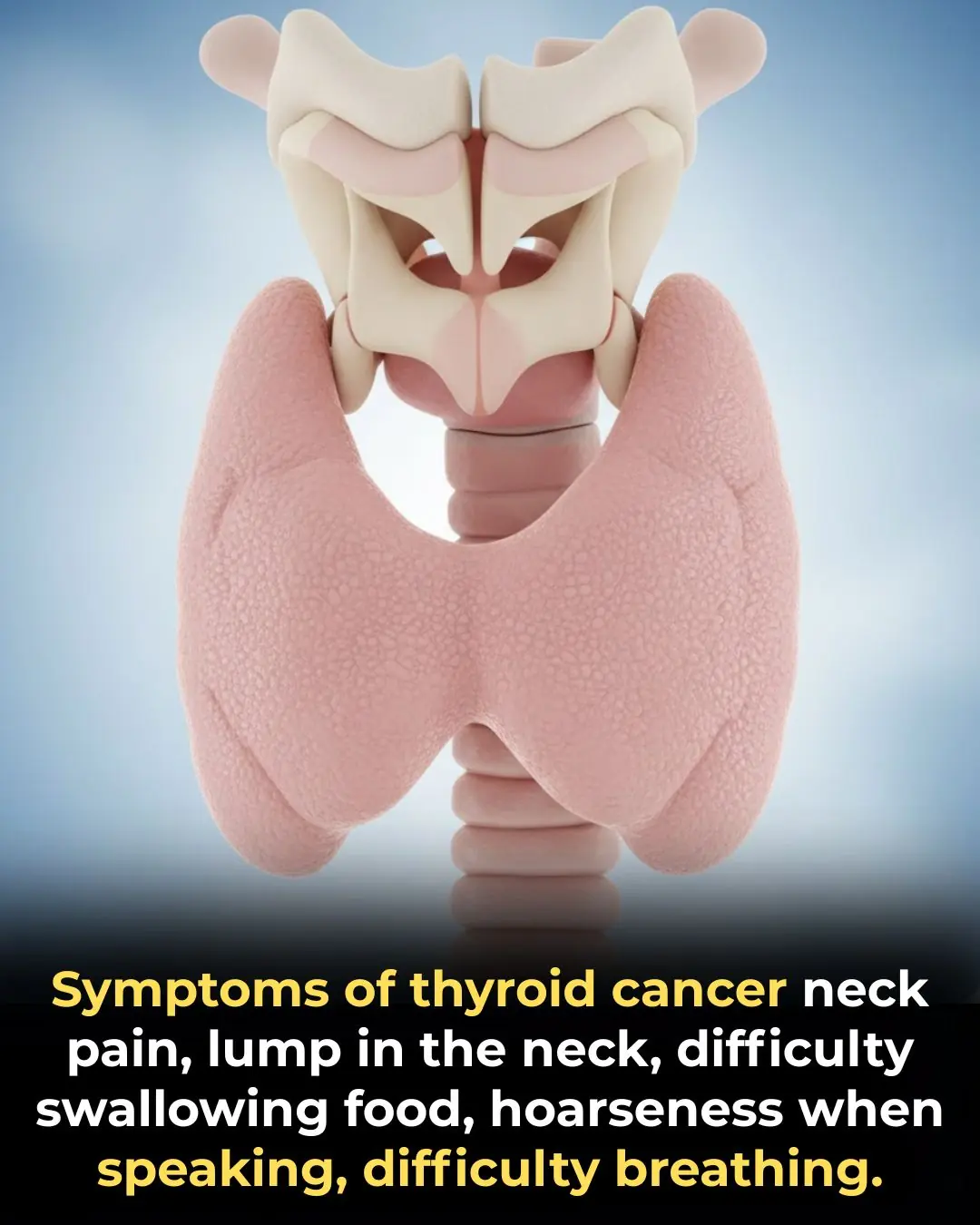
The 5 signs your body sends that warn you about thyroid cancer

Scientists develop nanorobots that rebuild teeth without the need for dentists

Horrifying CT Scans Reveal Woman’s Body Infested With Parasites After Eating Raw Pork For A Decade

When soaking clams, don't use plain water; add this spice, and the clams will release all the sand in no time, saving you a lot of time.

To boil chicken perfectly, with golden, crispy skin that doesn't crack or turn red, everyone should know to use this water!

Here are some surprising and quick tips for cleaning rust from gas stoves, making them shine like new, without spending a lot of money.

Grip Strength and Brain Health: More Than Muscle
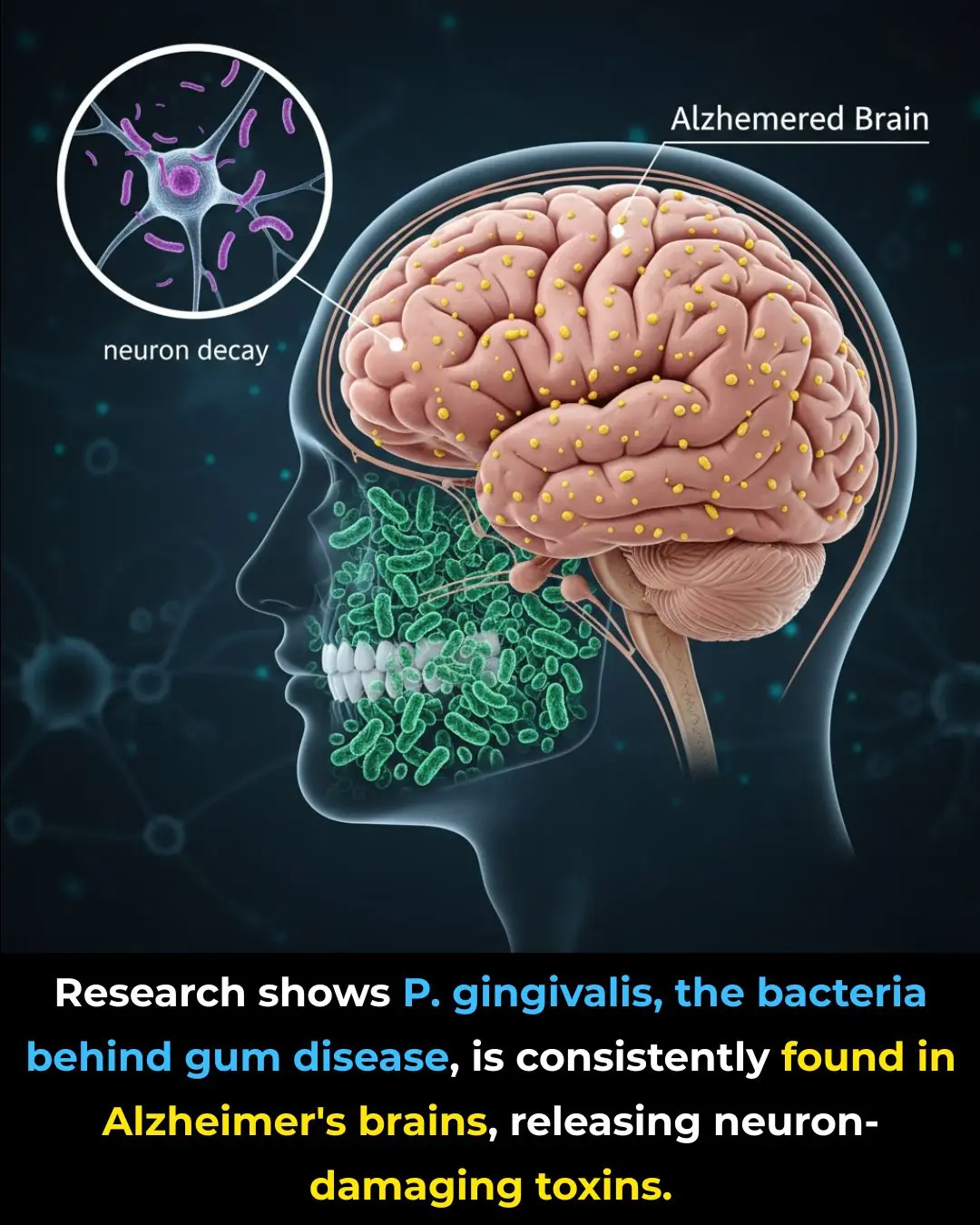
Oral Health and Dementia: The Hidden Connection
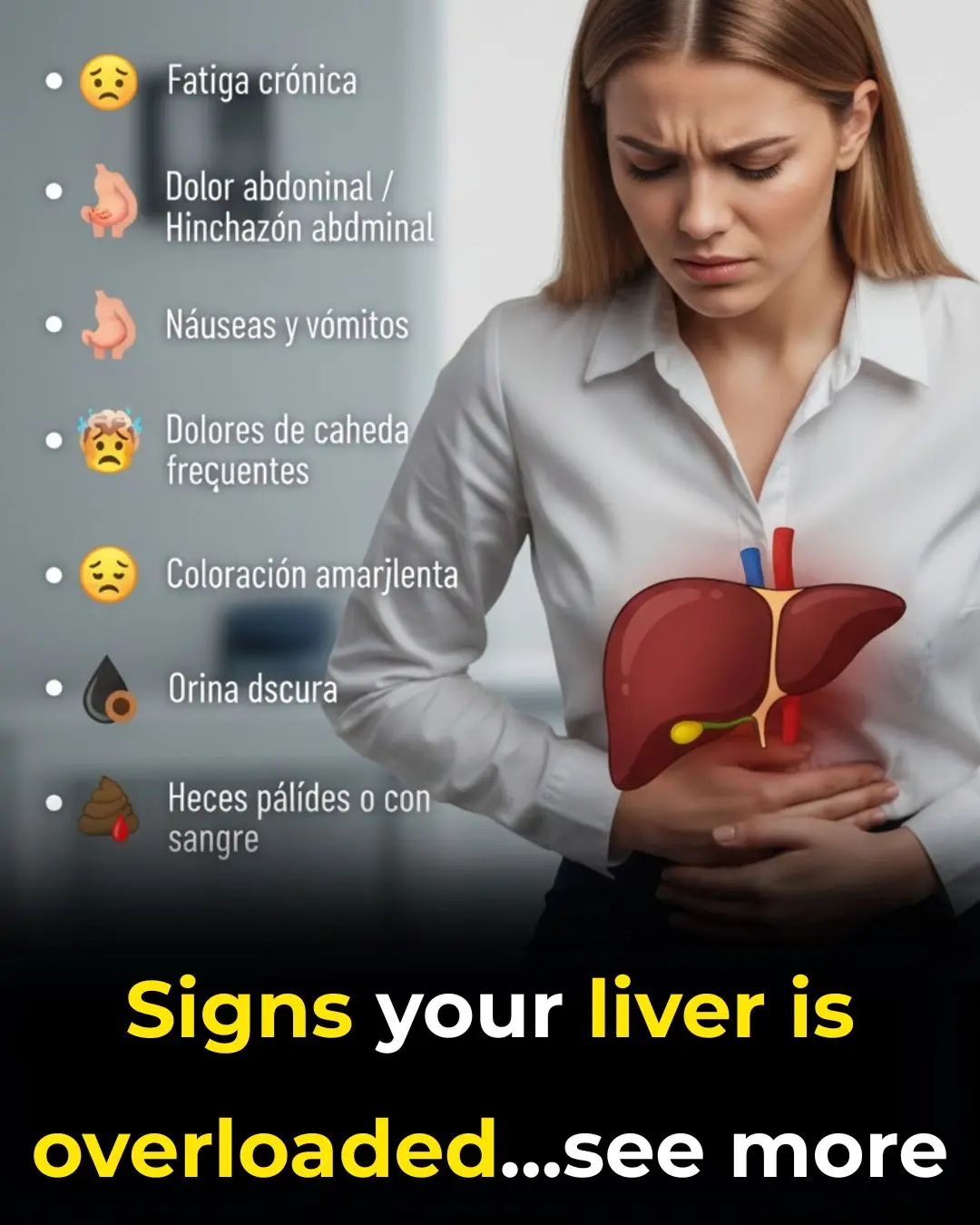
Fatty Liver: Symptoms, Types, Causes, and Treatment

Anesthesia doesn't put you to sleep: how it really disconnects the brain from reality

Doctor Reveals Eating Dragon Fruit Causes…

Doctors Reveal That Eating Bell Peppers Frequently Causes..

The Unknown Symptom of Alzheimer's That Manifests at Night

Doctors reveal that eating onion causes...

Andropause, Male Menopause: 7 Facts and Symptoms You Didn’t Know About It

Doctors reveal that eating green onions causes …See more

What Really Happens to Your Body When You Sit Too Much

Doctors reveal that eating canned peaches causes ...
