
Scientists develop nanorobots that rebuild teeth without the need for dentists
Dental sensitivity is one of the most common oral health complaints worldwide, affecting millions of people who experience sharp pain when consuming cold, hot, sweet, or acidic foods. While several treatments exist, most only offer temporary relief, and researchers continue to search for a long-lasting solution. Now, a groundbreaking idea could change the way dental sensitivity is treated: magnetic nanorobots designed to provide durable relief.
Scientists from the Indian Institute of Science (IISc), in collaboration with advanced technology startup Theranautilus, have unveiled a medical innovation that could redefine dental care. They have developed Calbots, magnetic nanorobots capable of addressing the root cause of dental sensitivity rather than merely masking its symptoms. The findings were published in the prestigious journal Advanced Science.
Nanorobots for Dental Sensitivity: A Breakthrough That Could Arrive Soon
Calbots are engineered to penetrate deeply into dentinal tubules—microscopic channels within the teeth that can transmit external stimuli directly to nerve endings. When enamel wears away and these tubules become exposed, sensitivity occurs. Unlike conventional treatments, which act only on the tooth’s surface, Calbots work from within.
These nanorobots can form long-lasting seals inside teeth affected by enamel erosion. As a result, a single application may be enough to provide prolonged relief from sensitivity, significantly reducing the need for repeated treatments.
What makes Calbots especially innovative is their use of a completely new type of bioceramic cement. “We didn’t want to create a slightly better version of what already exists,” explains Shanmukh Peddi, lead author of the study, postdoctoral researcher at the Centre for Nano Science and Engineering, and cofounder of Theranautilus. “Our goal was to solve a real problem in a way that no one had attempted before.”
Traditional treatments for dental sensitivity—such as desensitizing toothpastes—typically provide only superficial and short-term relief. This is why they must be applied consistently over long periods. Calbots, on the other hand, aim to deliver a deeper, more permanent solution.
How Calbots Work
Each Calbot is a 400-nanometer magnetic particle loaded with a patented bioceramic formula based on calcium silicate. Guided by an external magnetic field, the nanorobots travel into exposed dentinal tubules, reaching depths of approximately 300 to 500 micrometers.
Once inside, the nanorobots self-assemble and form stable, cement-like plugs that effectively block the tubules. This process recreates a durable seal that closely mimics the tooth’s natural protective environment, preventing stimuli from reaching the nerves.
The initial tests were conducted on extracted human teeth obtained for clinical reasons. Researchers artificially exposed the dentin to simulate sensitivity and then applied Calbots under a magnetic field for 20 minutes. During this time, the nanorobots successfully sealed the dentinal tubules.
High-resolution imaging confirmed the formation of deep and stable plugs. Following these results, animal trials were carried out in collaboration with scientists from the Centre for Neuroscience at IISc.
In these experiments, mice were given a choice between lukewarm and cold water. Healthy mice showed no preference, while mice with induced dental sensitivity avoided cold water entirely. Remarkably, mice treated with Calbots regained their ability to drink cold water, indicating a significant reduction in sensitivity.
A Promising Step Toward Regenerative Dentistry
Although further research and clinical trials are still required before Calbots become available to the public, this development represents a major milestone in regenerative dentistry. By targeting the underlying cause of dental sensitivity and offering long-lasting protection, nanorobot-based treatments could transform how dentists manage this widespread condition in the future.
If successful in human trials, Calbots may not only improve quality of life for patients but also reduce dependence on repetitive, short-term dental treatments—ushering in a new era of precision and durability in oral healthcare.
News in the same category

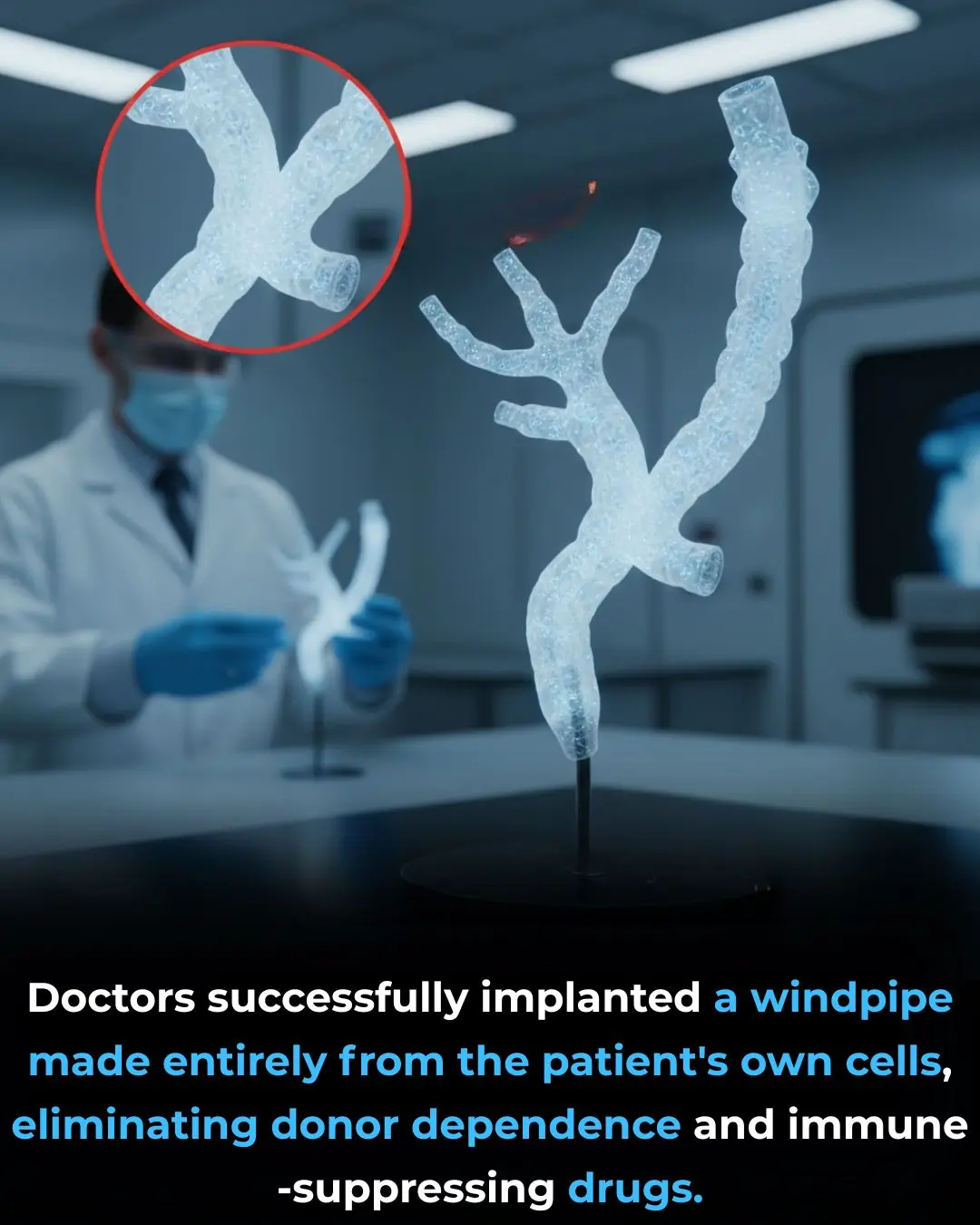
Bioprinted Windpipe: A Milestone in Regenerative Medicine

Bagworms Inside Your Home
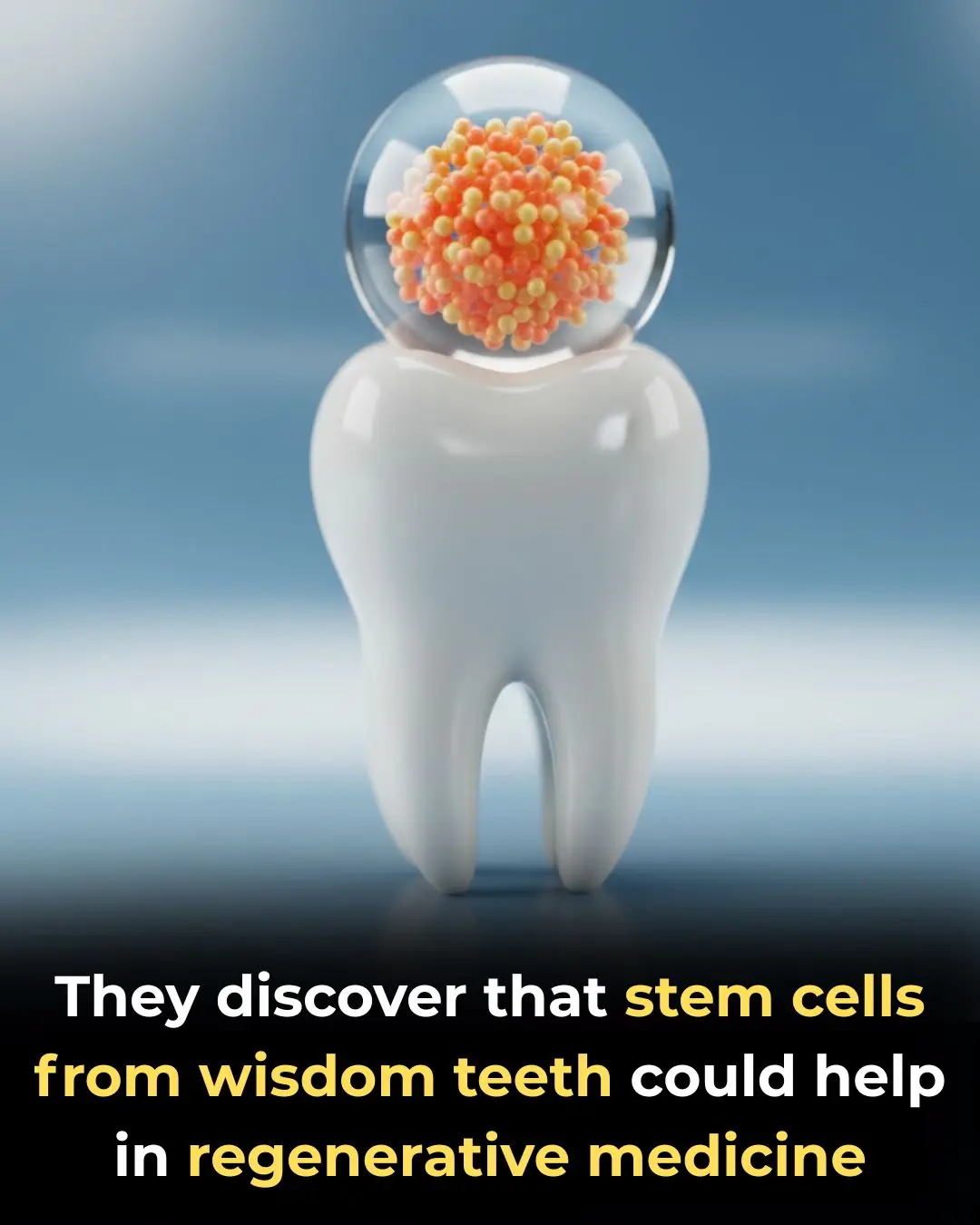
Scientists discover that stem cells from wisdom teeth could help in regenerative medicine

What the Research Shows

Rethinking Flu Transmission: New Evidence Challenges Long-Held Assumptions

Nanobot Technology: A New Frontier in Cardiovascular Disease Treatment

Redefining Diabetes Treatment

If your partner says goodbye with a kiss on the forehead, be very careful: this is what it really means
Here’s what the letter ‘M’ and the crescent moon on the palm of your hand truly signify

How Helicobacter pylori Revolutionized the Understanding of Stomach Ulcers

New Research Raises Brain Health Concerns About a Common Sweetener

🌟 Breakthrough in Cancer Treatment: Targeted Light Therapy

HHS to Reexamine Cell Phone and 5G Radiation Risks Following Direction From RFK Jr

Injectable Gel for Nerve Regeneration: A Breakthrough in Healing
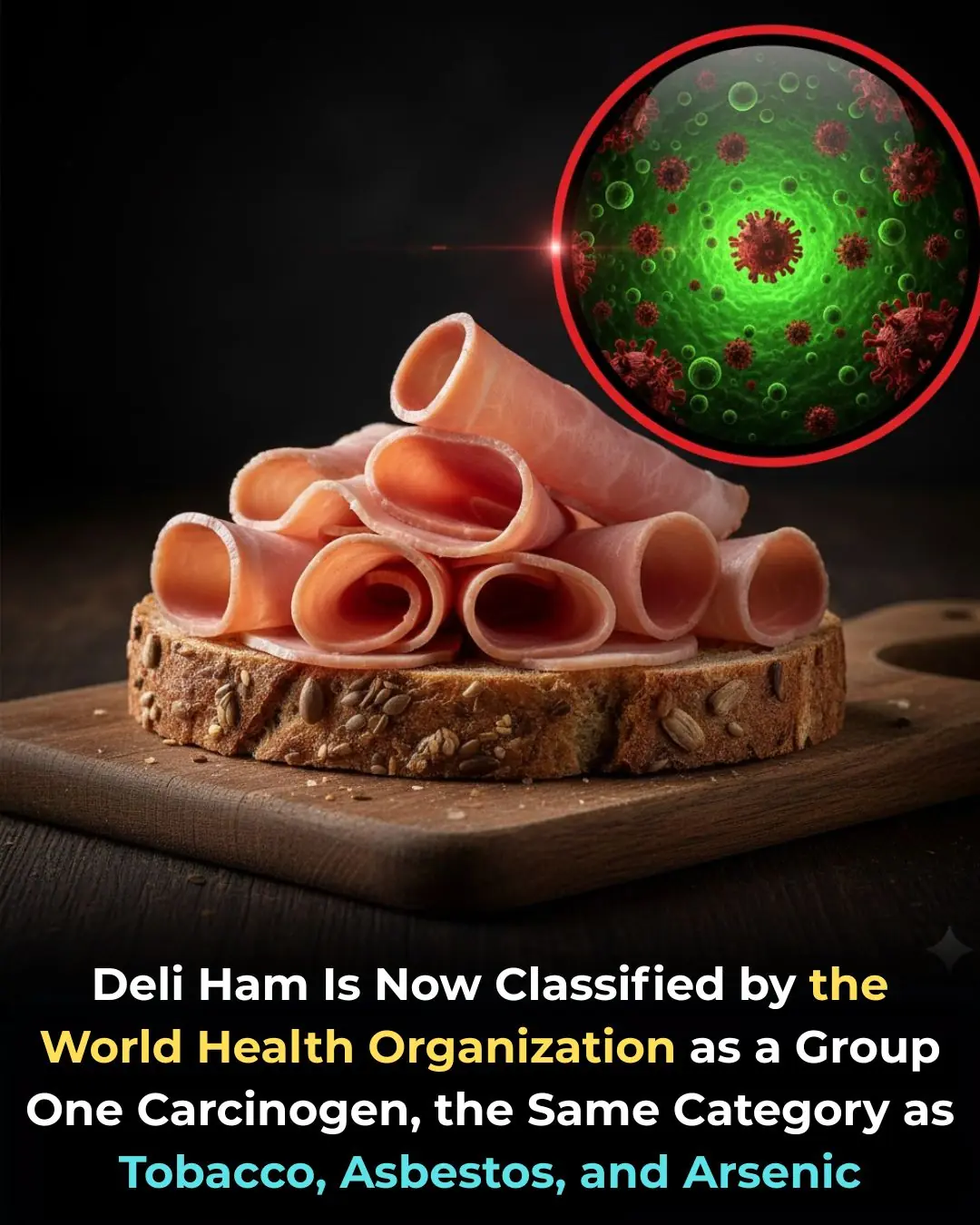
Processed Meats and Cancer Risk: What You Need to Know
Microplastics in Human Testicles: A Wake-Up Call for Reproductive Health

A Geologist Explains What Makes Greenland So Incredibly Special
They Successfully Cured HIV in a 60-Year-Old German Man Using a Stem Cell Transplant; He Has Been Disease-Free for 6 Years
News Post
The 5 signs your body sends that warn you about thyroid cancer

Horrifying CT Scans Reveal Woman’s Body Infested With Parasites After Eating Raw Pork For A Decade

When soaking clams, don't use plain water; add this spice, and the clams will release all the sand in no time, saving you a lot of time.

To boil chicken perfectly, with golden, crispy skin that doesn't crack or turn red, everyone should know to use this water!

Here are some surprising and quick tips for cleaning rust from gas stoves, making them shine like new, without spending a lot of money.

Grip Strength and Brain Health: More Than Muscle
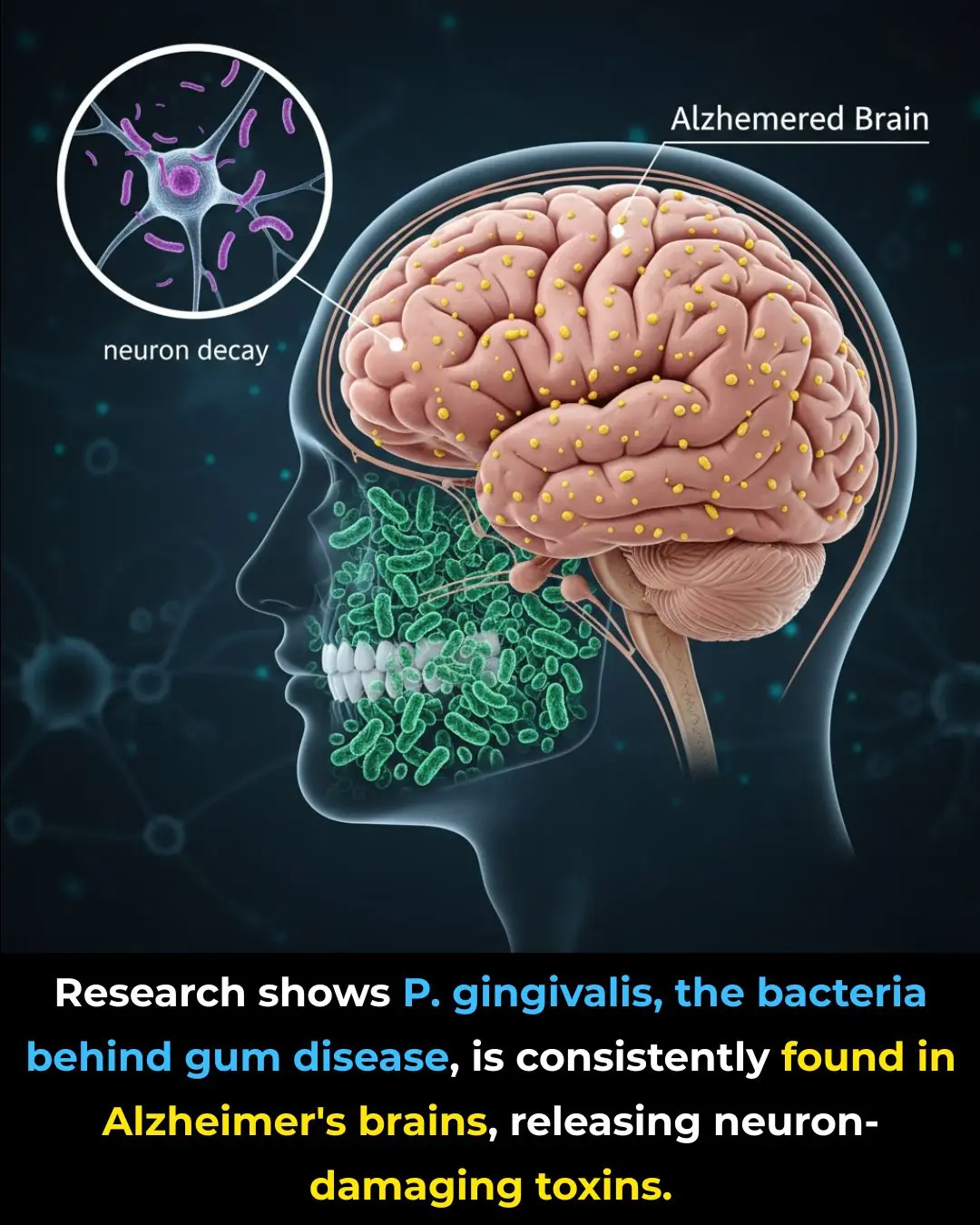
Oral Health and Dementia: The Hidden Connection

Bioprinted Windpipe: A Milestone in Regenerative Medicine
Fatty Liver: Symptoms, Types, Causes, and Treatment

Anesthesia doesn't put you to sleep: how it really disconnects the brain from reality

Doctor Reveals Eating Dragon Fruit Causes…

Doctors Reveal That Eating Bell Peppers Frequently Causes..

The Unknown Symptom of Alzheimer's That Manifests at Night

Doctors reveal that eating onion causes...

Andropause, Male Menopause: 7 Facts and Symptoms You Didn’t Know About It

Doctors reveal that eating green onions causes …See more

What Really Happens to Your Body When You Sit Too Much

Doctors reveal that eating canned peaches causes ...
