
Warning: 4 things to avoid when napping to prevent illness

The Debate Over the Afternoon Nap: How to Make It Beneficial
The habit of taking an afternoon nap remains a subject of much debate. Some people say, "If I don't take a nap, I'll feel tired and sluggish in the afternoon," while others complain, "After my nap, I feel uncomfortable, with numb limbs, dizziness, and constant yawning." In fact, these are signs of improper and unscientific napping.
To make your afternoon nap truly beneficial for your health, you should avoid the following four taboos:
-
Avoid Napping for Too Long
The ideal duration for an afternoon nap is 30-60 minutes. If you sleep for too long, your central nervous system becomes overly suppressed, blood vessels in the brain constrict, reducing blood flow to the brain and slowing down metabolism. As a result, you will feel more tired and drowsy after waking up.Napping for too long can also interfere with your nighttime sleep and disrupt your natural biological cycle. Therefore, each nap should not exceed 30 minutes to maintain a stable biological rhythm.
-
Avoid Napping Immediately After Lunch
It is best to take a short nap about 30 minutes after lunch. After eating, bowel movements increase, and blood circulation focuses on the digestive system. If you nap immediately, your heart will supply less blood to other organs, especially the brain, which will make you feel more tired upon waking. -
Avoid Napping While Sitting
Many people have the habit of napping while sitting, but this posture causes the heart rate to slow down and blood vessels to dilate, which reduces blood flow to the brain. The consequence is cerebral hypoxia, leading to dizziness, tinnitus, weakness in the limbs, blurred vision, and pale skin after waking up.Older adults and those with weak heart function should be especially careful and avoid napping while sitting to protect their health.
-
Avoid Standing Up Immediately After Waking Up
Standing up suddenly after an afternoon nap can cause blood to not flow adequately to the brain, leading to dizziness or even fainting. This is particularly dangerous for the elderly.The recommended practice is to follow the "half-minute" steps: lie on the bed for another half-minute after waking up, sit on the edge of the bed with your feet dangling for half a minute, and then stand up and move.
Tips for a Healthy Afternoon Nap
To nap effectively and safely, if you don't have a bed, you can use a couch with a neck pillow. Avoid sleeping on your stomach and never nap while sitting.
For those wearing contact lenses, it is advised to remove them before napping to avoid eye discomfort. Rest for about 30 minutes after eating before taking a nap. Upon waking up, washing your face and drinking a cup of hot tea will help restore energy and improve alertness.
Who Should Avoid Napping?
The ideal nap duration varies from person to person. As people age, the function of various body systems declines, making it harder for some to sleep at night and easier for them to wake up early. However, some elderly individuals experience symptoms such as dizziness, headaches, palpitations, or fatigue after napping instead of feeling refreshed.
The following groups are advised not to take naps:
-
Elderly individuals whose weight exceeds the standard by about 20%.
-
People with severe circulatory system disorders.
-
Those who frequently suffer from dizziness due to cerebral vascular narrowing.
The reason for this is that during sleep, the heart rate slows down, blood flow to the brain decreases, and temporary brain ischemia can occur, leading to dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system and the onset of other health issues.
News in the same category


Are Vaccines Doing More Than Just Preventing Infection?

Sudden Confusion or Trouble Speaking: When It’s More Than Just Fatigue

Stop fighting with your eyeliner. 10 winter proof tricks seniors swear by
Deep Vein Thrombosis: A Silent Killer That You Need to Know
Pineapple: Proven Health Benefits, Calories, Juice Benefits
The Best Foods to Cleanse and Prevent Clogged Arteries
13 Warning Signs of High Blood Sugar and 9 Ways to Take Control of Your Health
Progress Fighting Pancreatic Cancer — One of the Deadliest Malignancies

Avoid This Drink to Reduce The Risk of Stroke and Heart Attack

Drinking about 3 cups of green tea per day is associated with fewer white matter lesions in the brain—changes linked to aging and dementia risk

Magnesium Supplementation and Rapid Improvement in Major Depression

Targeting Fat Metabolism in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Stem Cells: The Therapeutic Potential of Avocadyne

High-Dose Thiamine and Fatigue Relief in Hashimoto’s Disease: Insights from a Case Series

Psilocybin and the Biology of Aging: Emerging Experimental Evidence
Aspirin as an Immune-Modulating Agent in the Suppression of Cancer Metastasis

Gum disease bacteria found in alzheimer’s brains

Fecal Microbiota Transplantation and Its Potential Role in Severe Autism Spectrum Disorder

Raw Carrots and Their Impact on Cholesterol and Colon Function

Breakthrough in Pancreatic Cancer Immunotherapy
News Post

This root vegetable, dubbed the king of liver detoxification, is incredibly delicious and highly nutritious whether cooked, baked, or used in smoothies

Tips for cleaning greasy plastic and glass containers without scrubbing

One cook, one family cancer? 5 kitchen habits that poison your health, the first one almost everyone is guilty of

How to Travel Thousands of Miles Without Motion Sickness

The Amazing Benefits of Guava Leaf Water That Few People Know

Don't place a broom in these 4 locations, or you'll sweep away your good fortune.

China Unveils Its First Small Nuclear Reactor to Power 500,000 Homes and Cut Carbon Emissions

Physicists Discover Two New Types of Quantum Time Crystals
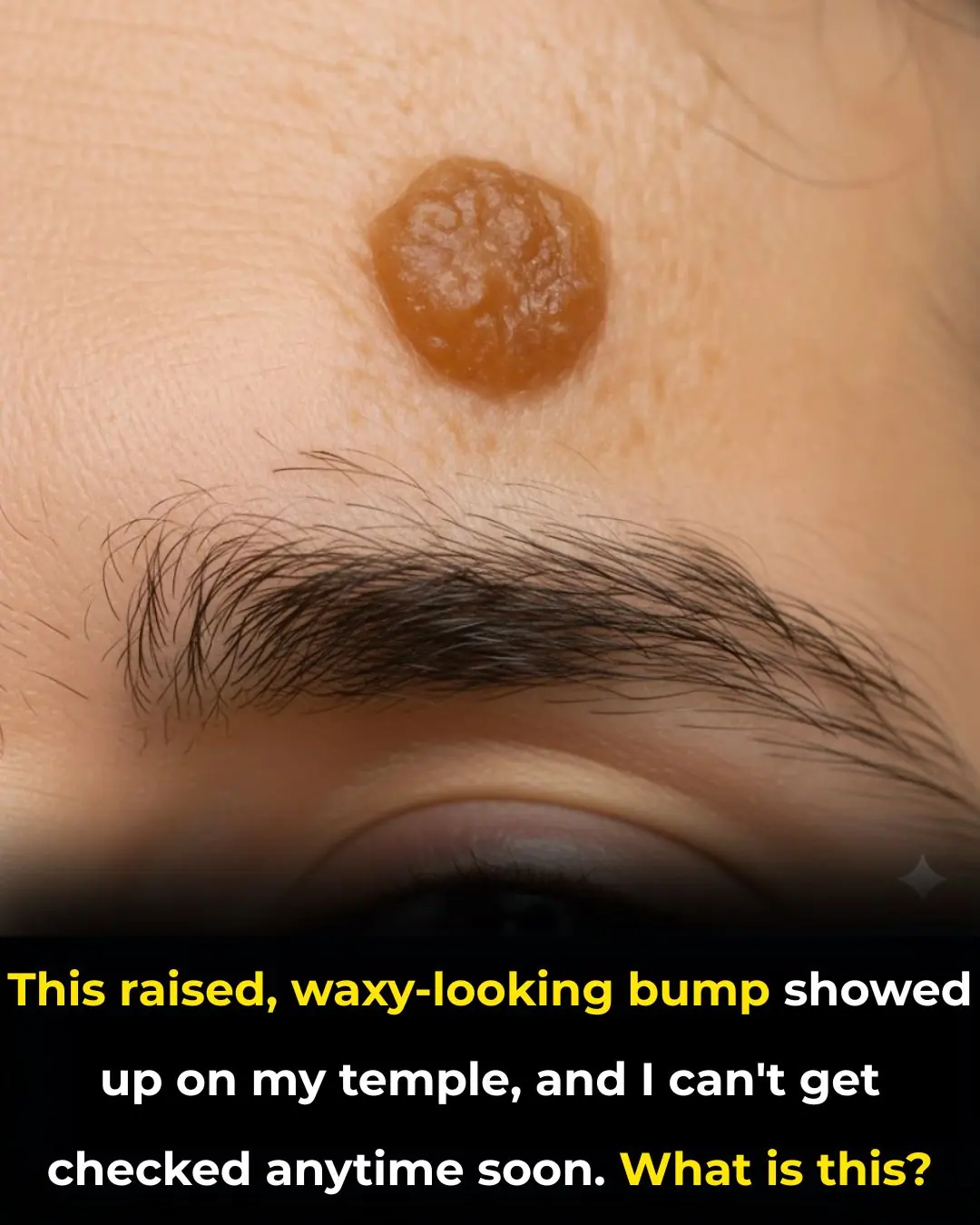
This raised, waxy-looking bump showed up on my temple, and I can’t get checked anytime soon. What is this?
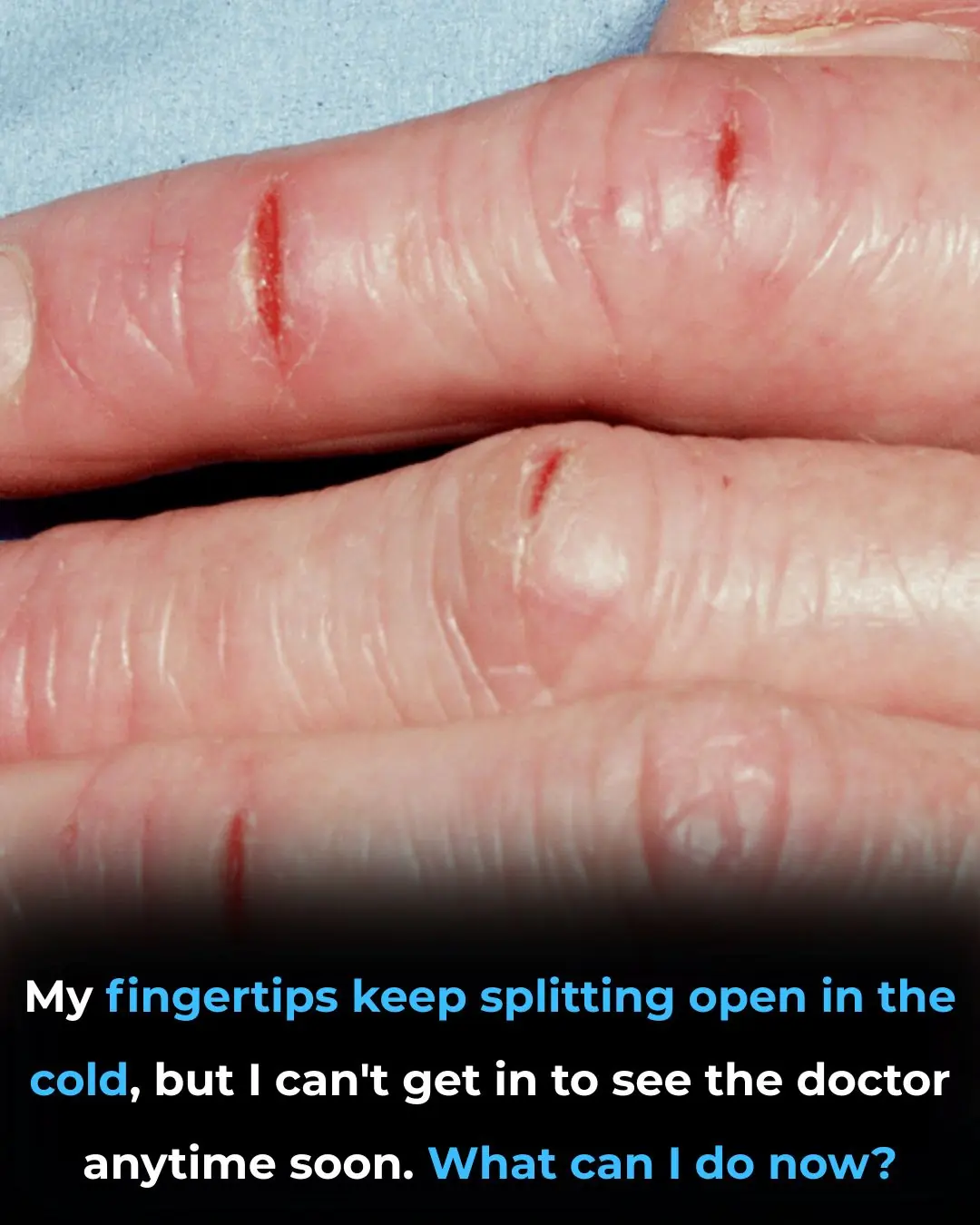
My fingertips keep splitting open in the cold, but I can’t get in to see the doctor anytime soon. What can I do now?

A 30-Year-Old Man Admitted to Hospital and Discovered to Have Acute Kidney Failure: It Was All Due to One Mistake in His Workout

Pour a handful of salt into the toilet bowl

Are Vaccines Doing More Than Just Preventing Infection?
Trick To Stop Mosquito Bite From Itching

Sudden Confusion or Trouble Speaking: When It’s More Than Just Fatigue

A Family of Four Diagnosed With Liver Cancer: Experts Identified the Cause the Moment They Entered the Kitchen

My nana says this works like a charm

Stop fighting with your eyeliner. 10 winter proof tricks seniors swear by
