
Bronchiectasis: Symptoms Most People Overlook
Bronchiectasis is a chronic lung condition that often goes undiagnosed for years. Its symptoms are frequently mistaken for recurring infections, asthma, or “just a bad cough.” Over time, untreated bronchiectasis can lead to serious lung damage.
Recognizing overlooked symptoms early can help prevent complications and improve quality of life.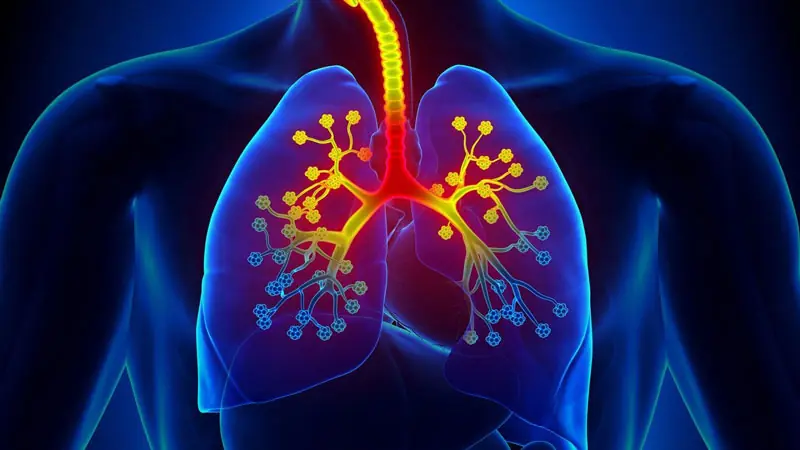
What Is Bronchiectasis?
Bronchiectasis occurs when the bronchial tubes become permanently widened and damaged. This damage prevents normal clearance of mucus, allowing bacteria to grow and infections to recur.
Once the airways are damaged, the condition becomes chronic—but with proper management, symptoms can be controlled.
Why Bronchiectasis Is Often Missed
-
Symptoms develop gradually
-
Chronic cough is often ignored
-
Many patients are treated repeatedly for infections without further testing
-
It overlaps with asthma and COPD symptoms
As a result, diagnosis is often delayed for years.
Commonly Overlooked Symptoms
1. Daily Productive Cough
A chronic cough producing mucus every day is a hallmark sign. Many people assume this is normal or related to smoking or allergies.
2. Thick or Discolored Mucus
Mucus may appear yellow, green, or brown and often has a foul smell, indicating infection.
3. Frequent Chest Infections
Repeated lung infections requiring antibiotics are a major warning sign.
4. Shortness of Breath
Breathing difficulty may worsen during activity or infections and is often misattributed to aging.
5. Fatigue and Weakness
Chronic inflammation and infection drain energy levels, leading to persistent tiredness.
6. Wheezing
Airflow obstruction can cause wheezing, especially during flare-ups.
7. Chest Pain
Some patients experience discomfort due to inflammation or repeated coughing.
8. Coughing Up Blood
Even small amounts of blood in mucus should never be ignored.
Causes of Bronchiectasis
-
Severe childhood infections
-
Recurrent pneumonia
-
Tuberculosis
-
Immune system disorders
-
Genetic conditions such as cystic fibrosis
-
Airway obstruction
-
Autoimmune diseases
In some cases, the cause remains unknown.
How Bronchiectasis Is Diagnosed
Diagnosis typically involves:
-
High-resolution CT scan of the chest
-
Lung function tests
-
Sputum cultures
-
Blood tests for immune disorders
CT imaging is the gold standard for confirmation.
Treatment and Management
1. Airway Clearance Techniques
-
Chest physiotherapy
-
Breathing exercises
-
Postural drainage
2. Medications
-
Antibiotics for infections
-
Bronchodilators
-
Mucus-thinning agents
-
Anti-inflammatory medications
3. Vaccinations
Preventing infections is critical.
4. Pulmonary Rehabilitation
Exercise and education programs improve lung function and endurance.
5. Surgery
Localized disease may be treated surgically if symptoms are severe.
Complications If Left Untreated
-
Progressive lung damage
-
Respiratory failure
-
Frequent hospitalizations
-
Reduced quality of life
Early diagnosis helps prevent these outcomes.
Living With Bronchiectasis
With proper care, many people live active, productive lives. Daily airway clearance and infection prevention are key.
When to See a Doctor
Seek evaluation if you have:
-
Chronic productive cough
-
Recurrent chest infections
-
Unexplained fatigue
-
Shortness of breath that worsens over time
Final Thoughts
Bronchiectasis is often overlooked but should never be ignored. Recognizing early symptoms and receiving proper treatment can slow disease progression and protect long-term lung health. Persistent cough and recurrent infections deserve thorough evaluation—not dismissal.
News in the same category

Strange Body Symptoms Explained: What Your Body May Be Telling You

Understanding Magnesium: Types, Symptoms, and Scientific Support

Herbal Balms You Should Keep at Home: Traditional Uses and Scientific Perspectives
How to flush sugar out of your body fast
Respiratory Failure: Causes and Emergency Signs

The Hidden Power of Nutrition: 14 Overlooked Nutrients That Transform Health
Lung Infections: Common Types and How to Treat Them

Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD): Misunderstood Signs

Dizziness and Balance Problems: What They May Indicate
Nerve Damage: Common Causes and Recovery Tips

The 4 hidden causes of persistent phlegm in your throat (& how to fix it naturally)
4 popular supplements that rapidly drain potassium from your body

Turmeric and vitamin D are allies against high blood pressure in diabetes
This is How Headaches Reveal What is Wrong With Your Health

#1 best way to reverse & slow dementia
How to shrink thyroid nodules naturally with 2 key minerals
The Number One Deficiency Behind Aging Spots
If You Get These Bruises On Your Body
News Post

Vitamin E Cream for Face – Vitamin E Oil benefits for Skin

DIY Turmeric Gel for Dark Spots, Pimples and Blemishes
Collagen booster night cream!!

Homemade hair oil that can totally change your hair

6 Coffee Eye Masks to Get Rid of Dark Circles | Under Eye Wrinkles | Eye bags & Puffy Eyes

10 Simple Yet Genius Life Hacks That Women Can Need at Least Once in Their Life

Natural Remedies for Managing Oily Scalp: Effective Tips for Balanced Hair

3 Overnight Skin Lightening Treatments That Actually Work – Natural and Effective

Tomato Benefits for Skin – Rub Tomato Slice on Face

Get Rid of Large Pores with Flaxseed Ice Cubes: A Natural Skincare Hack

Lips De-Pigmentation Treatment At Home

How to grow bean sprouts using plastic bottles quickly and easily; you'll have them ready to eat in 3 days.

The secret to 'magical' frying: No oil splattering, crispy, golden-brown food with just 3 simple tips.

5 tips to keep your bathroom smelling fresh all week without the hassle of cleaning.

10 amazing baking soda tips to solve many household problems.

When making spring roll filling, remember this one crucial step to prevent the spring rolls from becoming watery, the leaves from tearing, and to ensure they remain crispy even after cooling

Simply adding water isn't enough when cooking sticky rice: Follow this method for soft, chewy rice and half the cooking time.

Foods to Eat When You’re Sick: Nutritional Support for Faster Recovery

Strange Body Symptoms Explained: What Your Body May Be Telling You
