
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD): Misunderstood Signs
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) is one of the most misunderstood mental health conditions. Many people casually describe themselves as “a little OCD” because they like things neat or organized. In reality, OCD is far more complex, distressing, and disruptive than simple habits or preferences.
Millions of people live with OCD silently, often for years, because the signs are subtle, misunderstood, or mistaken for personality traits. Recognizing these signs early can make a life-changing difference.
What Is OCD?
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder is a chronic mental health condition characterized by two key components:
-
Obsessions: intrusive, unwanted thoughts, images, or urges that cause intense anxiety
-
Compulsions: repetitive behaviors or mental acts performed to reduce that anxiety
The cycle of obsessions and compulsions can consume hours each day and significantly interfere with work, relationships, and daily functioning.
Commonly Misunderstood Signs of OCD
1. Intrusive Thoughts (Not Desires)
One of the most misunderstood aspects of OCD is intrusive thoughts. These thoughts are unwanted and often disturbing.
Examples include:
-
Fear of harming loved ones
-
Unwanted sexual or violent images
-
Blasphemous or morally distressing thoughts
People with OCD do not want these thoughts and feel deep shame or fear because of them.
2. Mental Compulsions Are Often Invisible
Not all compulsions are physical behaviors like handwashing.
Mental compulsions may include:
-
Repeating words or prayers silently
-
Mentally reviewing past actions
-
Constant reassurance-seeking in one’s mind
Because these actions are internal, OCD often goes unnoticed.
3. Excessive Doubt and “What If” Thinking
People with OCD struggle with uncertainty.
Common doubts include:
-
“What if I didn’t lock the door properly?”
-
“What if I contaminated something?”
-
“What if I hurt someone without realizing it?”
This doubt fuels repetitive checking and reassurance behaviors.
4. Perfectionism Driven by Anxiety
OCD-related perfectionism is not about high standards—it’s about fear.
Tasks may be repeated endlessly because:
-
Things don’t feel “just right”
-
A mistake feels catastrophic
-
Incomplete tasks cause extreme distress
5. Avoidance Behaviors
Many people with OCD avoid situations that trigger obsessive thoughts.
Examples:
-
Avoiding knives due to harm-related fears
-
Avoiding public places due to contamination concerns
-
Avoiding relationships due to intrusive thoughts
Avoidance can shrink a person’s life over time.
6. Guilt and Shame
People with OCD often feel intense guilt for having thoughts they believe reflect who they are.
This leads to:
-
Hiding symptoms
-
Delayed diagnosis
-
Increased isolation
What Causes OCD?
There is no single cause, but contributing factors include:
-
Genetic vulnerability
-
Brain chemistry imbalances (especially serotonin)
-
Overactivity in certain brain circuits
-
Stressful or traumatic life events
OCD is not caused by personality weakness or poor parenting.
How OCD Is Diagnosed
Diagnosis is made through:
-
Clinical interviews
-
Symptom history
-
Standardized assessment tools
There is no blood test or scan that diagnoses OCD, but brain imaging supports its neurological basis.
Effective Treatment Options
1. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Specifically, Exposure and Response Prevention (ERP) is the gold standard.
ERP helps patients:
-
Face fears gradually
-
Resist compulsive behaviors
-
Tolerate uncertainty
2. Medication
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are commonly used and effective for many patients.
3. Combination Treatment
For moderate to severe OCD, therapy and medication together often produce the best outcomes.
When to Seek Help
If obsessive thoughts or compulsions:
-
Consume more than 1 hour per day
-
Cause significant distress
-
Interfere with work, school, or relationships
professional help is strongly recommended.
Final Thoughts
OCD is not about being neat, organized, or quirky. It is a serious, treatable mental health condition rooted in anxiety and brain function. With proper treatment and understanding, people with OCD can regain control and live fulfilling lives.
News in the same category

Strange Body Symptoms Explained: What Your Body May Be Telling You

Understanding Magnesium: Types, Symptoms, and Scientific Support

Herbal Balms You Should Keep at Home: Traditional Uses and Scientific Perspectives
How to flush sugar out of your body fast

Bronchiectasis: Symptoms Most People Overlook
Respiratory Failure: Causes and Emergency Signs

The Hidden Power of Nutrition: 14 Overlooked Nutrients That Transform Health
Lung Infections: Common Types and How to Treat Them

Dizziness and Balance Problems: What They May Indicate
Nerve Damage: Common Causes and Recovery Tips

The 4 hidden causes of persistent phlegm in your throat (& how to fix it naturally)
4 popular supplements that rapidly drain potassium from your body

Turmeric and vitamin D are allies against high blood pressure in diabetes
This is How Headaches Reveal What is Wrong With Your Health

#1 best way to reverse & slow dementia
How to shrink thyroid nodules naturally with 2 key minerals
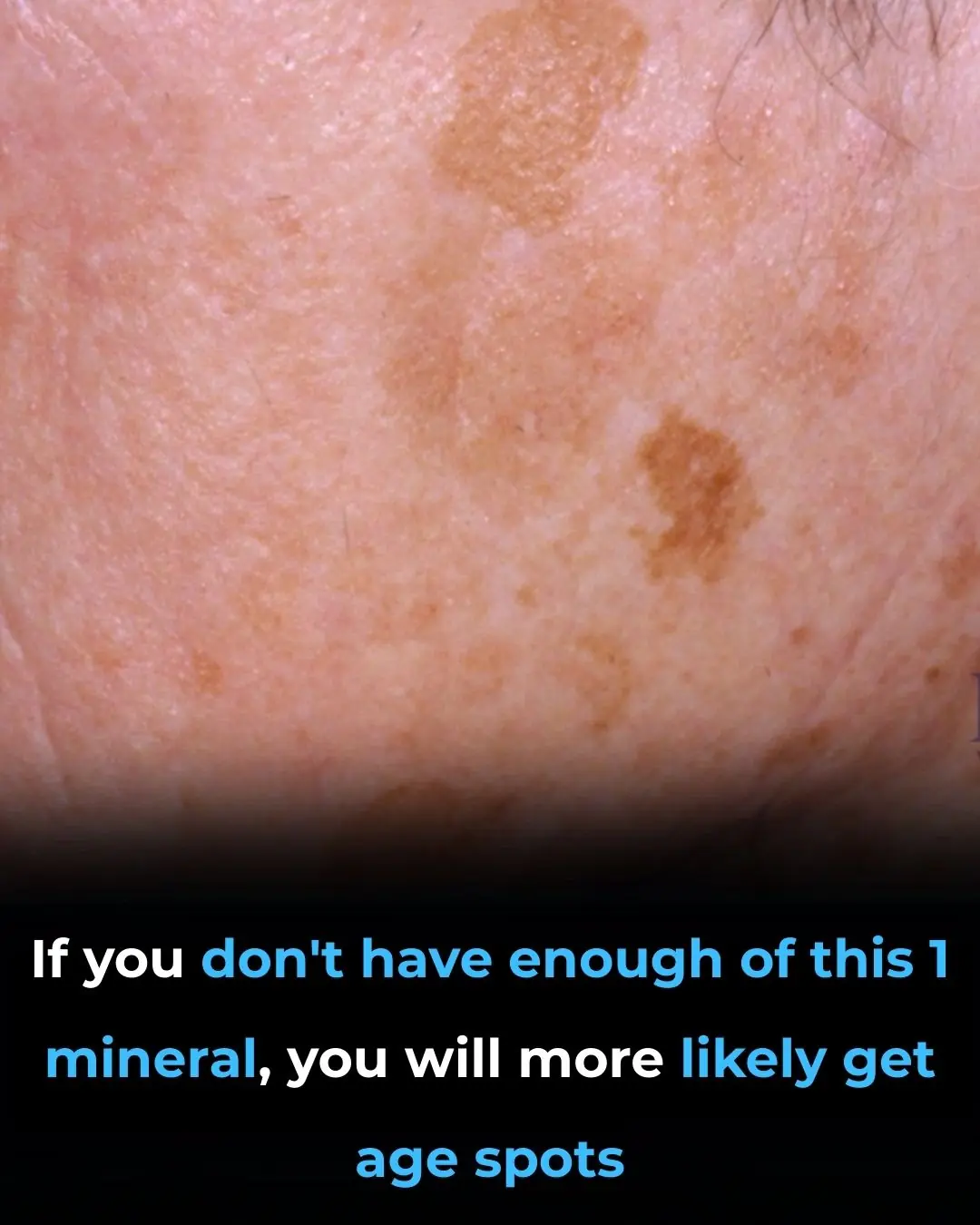
The Number One Deficiency Behind Aging Spots
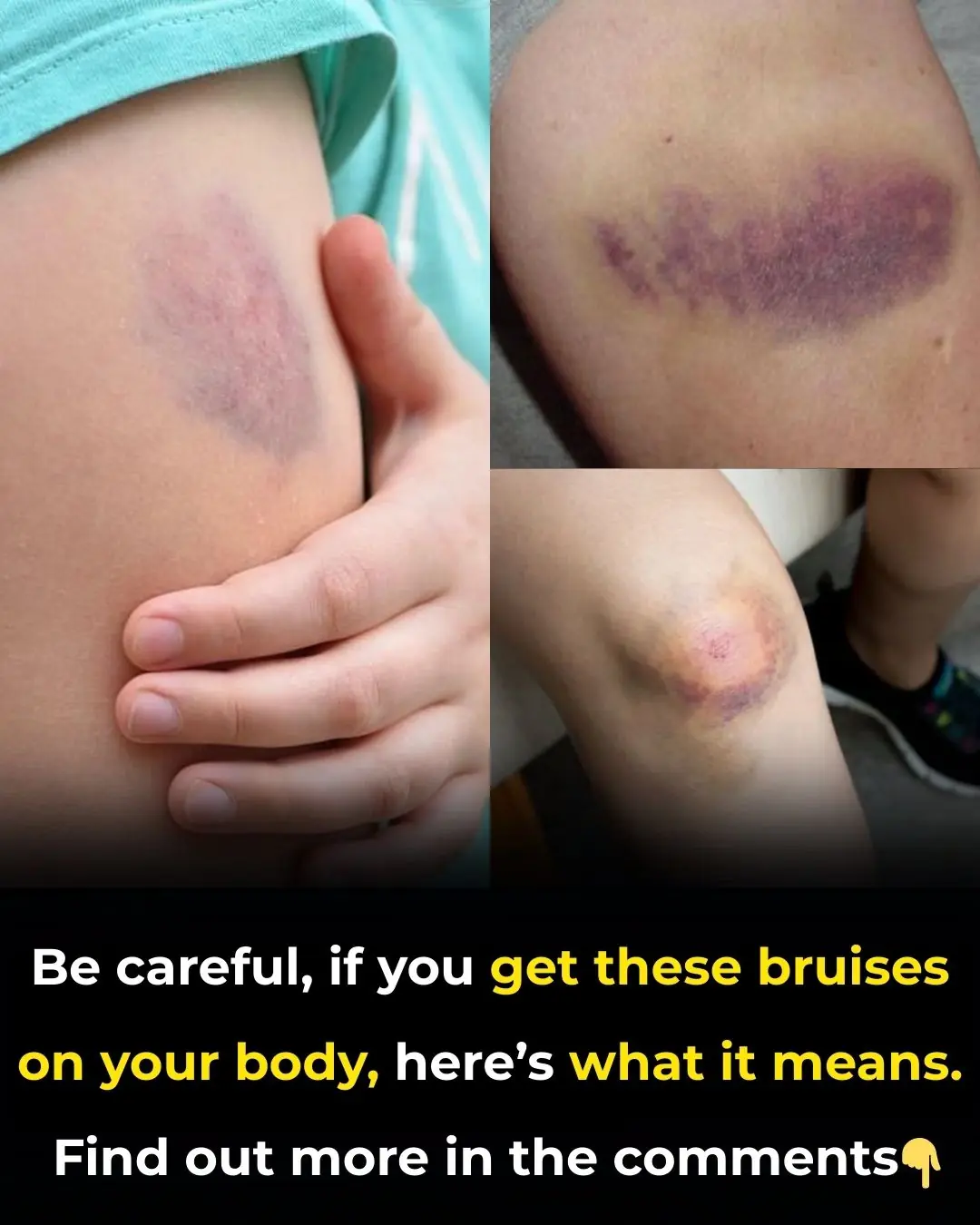
If You Get These Bruises On Your Body
News Post

Vitamin E Cream for Face – Vitamin E Oil benefits for Skin

DIY Turmeric Gel for Dark Spots, Pimples and Blemishes
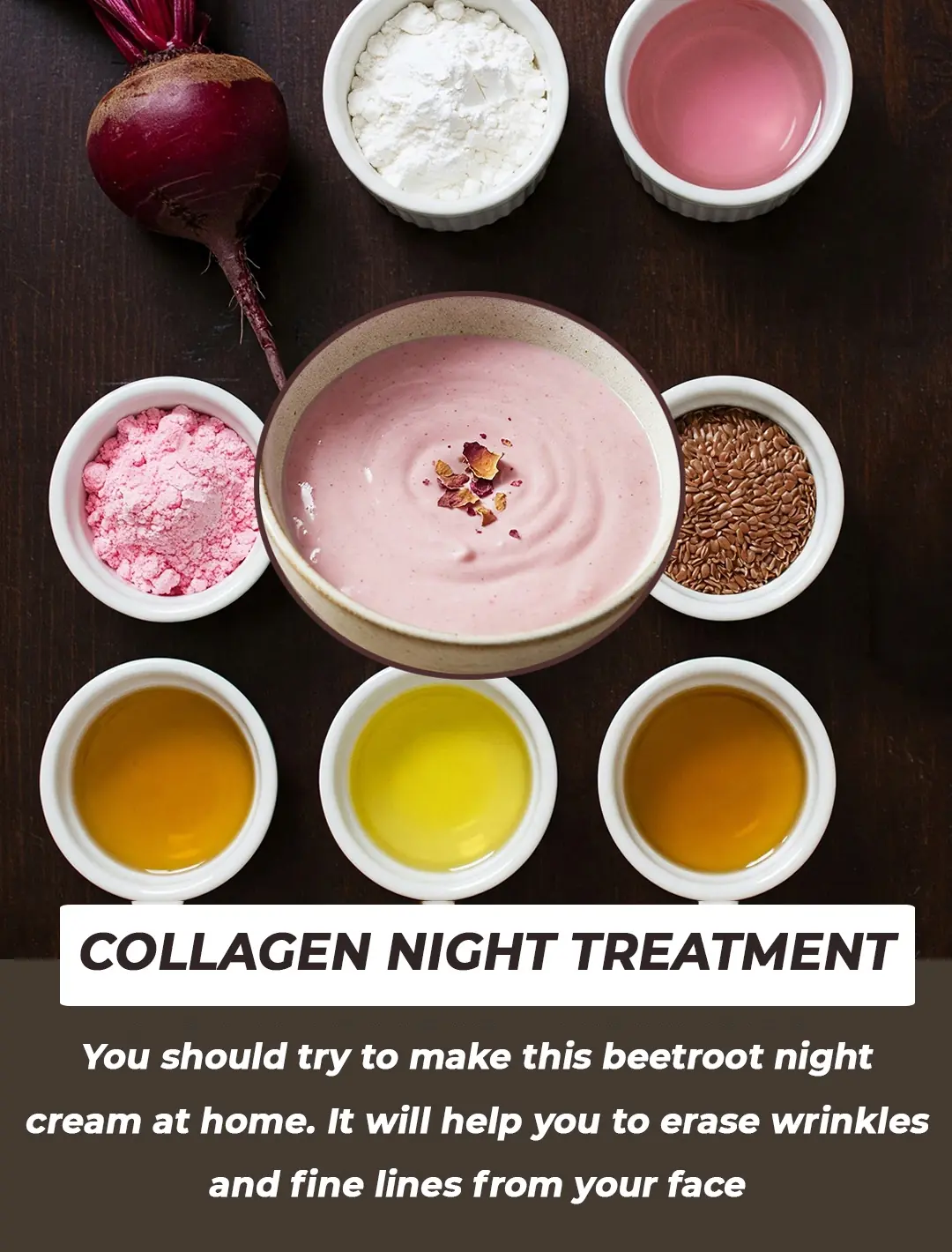
Collagen booster night cream!!

Homemade hair oil that can totally change your hair

6 Coffee Eye Masks to Get Rid of Dark Circles | Under Eye Wrinkles | Eye bags & Puffy Eyes

10 Simple Yet Genius Life Hacks That Women Can Need at Least Once in Their Life

Natural Remedies for Managing Oily Scalp: Effective Tips for Balanced Hair

3 Overnight Skin Lightening Treatments That Actually Work – Natural and Effective

Tomato Benefits for Skin – Rub Tomato Slice on Face

Get Rid of Large Pores with Flaxseed Ice Cubes: A Natural Skincare Hack

Lips De-Pigmentation Treatment At Home

How to grow bean sprouts using plastic bottles quickly and easily; you'll have them ready to eat in 3 days.

The secret to 'magical' frying: No oil splattering, crispy, golden-brown food with just 3 simple tips.

5 tips to keep your bathroom smelling fresh all week without the hassle of cleaning.

10 amazing baking soda tips to solve many household problems.

When making spring roll filling, remember this one crucial step to prevent the spring rolls from becoming watery, the leaves from tearing, and to ensure they remain crispy even after cooling

Simply adding water isn't enough when cooking sticky rice: Follow this method for soft, chewy rice and half the cooking time.

Foods to Eat When You’re Sick: Nutritional Support for Faster Recovery

Strange Body Symptoms Explained: What Your Body May Be Telling You
